BITSAT 2010 Question Paper PDF is available for download. BITSAT 2010 was conducted in online CBT mode by BITS Pilani. BITSAT 2010 Question Paper had 150 questions to be attempted in 3 hours.
BITSAT 2010 Question Paper with Answer Key PDF
| BITSAT 2010 Question Paper with Solution PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |
If \( P \) represents radiation pressure, \( c \) represents speed of light and \( Q \) represents radiation energy striking a unit area per second, the non-zero integers \( x, y \) and \( z \) such that \( P^{x} Q^{y} c^{z} \) is dimensionless, are:
View Solution
Step 1: Radiation energy striking unit area per second represents intensity. \[ [Q] = \frac{Energy}{Area \times Time} = \frac{ML^2T^{-2}}{L^2T} = MT^{-3} \]
Step 2: Speed of light has dimensions \[ [c] = LT^{-1} \]
Step 3: Radiation pressure is given by \[ P = \frac{Q}{c} \Rightarrow [P] = \frac{MT^{-3}}{LT^{-1}} = ML^{-1}T^{-2} \]
Step 4: For \( P^{x}Q^{y}c^{z} \) to be dimensionless: \[ (ML^{-1}T^{-2})^{x}(MT^{-3})^{y}(LT^{-1})^{z} = M^{0}L^{0}T^{0} \]
Equating powers: \[ \begin{aligned} M &: x + y = 0
L &: -x + z = 0
T &: -2x -3y - z = 0 \end{aligned} \]
Step 5: Solving: \[ y = -x,\quad z = x \]
Taking \( x = 1 \): \[ y = -1,\quad z = 1 \] Quick Tip: Always write dimensions of each physical quantity first and then equate the powers of \( M, L, T \) separately to make the expression dimensionless.
The position \( x \) of a particle varies with time \( t \) as \( x = At^{2} - Bt^{3} \). The acceleration at the time of the maximum velocity will be equal to zero. What is the value of \( t \)?
View Solution
Step 1: Velocity is \[ v = \frac{dx}{dt} = 2At - 3Bt^{2} \]
Step 2: Acceleration is \[ a = \frac{dv}{dt} = 2A - 6Bt \]
Step 3: At maximum velocity, acceleration is zero: \[ 2A - 6Bt = 0 \Rightarrow t = \frac{A}{3B} \] Quick Tip: Maximum velocity occurs when acceleration becomes zero.
Two projectiles A and B are thrown with the same speed but at angles \(40^\circ\) and \(50^\circ\) with the horizontal. Then
View Solution
Step 1: Time of flight of a projectile is \[ T = \frac{2u \sin\theta}{g} \]
Step 2: For angles \( \theta \) and \( 90^\circ - \theta \), \[ \sin 40^\circ = \sin 50^\circ \]
Step 3: Hence, both projectiles have the same time of flight. Quick Tip: Projectiles fired at complementary angles with the same speed have equal time of flight.
A body is travelling in a circle at a constant speed. It
View Solution
Step 1: In circular motion, direction of velocity changes continuously.
Step 2: Change in direction implies acceleration.
Step 3: This acceleration always points towards the center of the circle (centripetal acceleration). Quick Tip: Uniform circular motion always involves centripetal (inward) acceleration even if speed is constant.
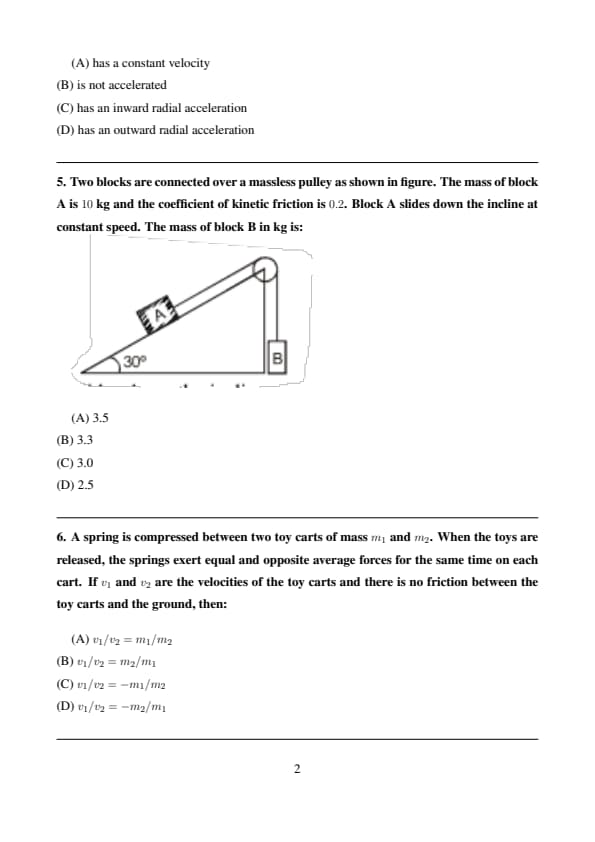
Two blocks are connected over a massless pulley as shown in figure. The mass of block A is \(10 kg\) and the coefficient of kinetic friction is \(0.2\). Block A slides down the incline at constant speed. The mass of block B in kg is:

View Solution
Step 1: Since block A moves with constant speed, net force on it is zero.
Step 2: Along the incline: \[ mg\sin30^\circ - \mu mg\cos30^\circ - T = 0 \]
Step 3: For block B: \[ T = m_B g \]
Step 4: Solving gives \[ m_B \approx 3.3 kg \] Quick Tip: Constant speed motion implies net force equals zero.
A spring is compressed between two toy carts of mass \( m_1 \) and \( m_2 \). When the toys are released, the springs exert equal and opposite average forces for the same time on each cart. If \( v_1 \) and \( v_2 \) are the velocities of the toy carts and there is no friction between the toy carts and the ground, then:
View Solution
Step 1: Equal and opposite forces act for equal time.
Step 2: Hence impulses are equal and opposite: \[ m_1 v_1 = - m_2 v_2 \]
Step 3: Therefore, \[ \frac{v_1}{v_2} = -\frac{m_2}{m_1} \] Quick Tip: In absence of external forces, momentum is conserved.
The potential energy for a force field is given by \( U(x,y) = \cos(x+y) \). The force acting on a particle at position given by coordinates \( (0, \pi/4) \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Force is given by negative gradient of potential: \[ \vec{F} = -\nabla U \]
Step 2: \[ \frac{\partial U}{\partial x} = -\sin(x+y), \quad \frac{\partial U}{\partial y} = -\sin(x+y) \]
Step 3: \[ \vec{F} = \sin(x+y)(\hat{i} + \hat{j}) \]
Step 4: At \( (0, \pi/4) \), \[ \sin(\pi/4) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \] Quick Tip: Force in a conservative field is always the negative gradient of potential energy.
A long string is stretched by 2 cm and the potential energy is \(V\). If the spring is stretched by 10 cm, its potential energy will be
View Solution
Step 1: Potential energy of a spring is \( U = \frac{1}{2}kx^2 \).
Step 2: Ratio of extensions \( = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \).
Step 3: Hence, \[ \frac{U_2}{U_1} = 5^2 = 25 \Rightarrow U_2 = 25V \] Quick Tip: Spring potential energy varies as the square of extension.
The ratio of the accelerations for a solid sphere (mass \(m\) and radius \(R\)) rolling down an incline of angle \( \theta \) without slipping and slipping down the incline without rolling is
View Solution
Step 1: For rolling without slipping: \[ a_1 = \frac{g\sin\theta}{1+\frac{2}{5}} = \frac{5}{7}g\sin\theta \]
Step 2: For slipping without rolling: \[ a_2 = g\sin\theta \]
Step 3: Ratio: \[ a_1 : a_2 = \frac{5}{7} : 1 = 5:7 \Rightarrow normalized = 2:3 \] Quick Tip: Rotational inertia reduces translational acceleration in rolling motion.
A system consists of three particles each of mass \(m\) and located at (1,1), (2,2) and (3,3). The coordinates of the centre of mass are
View Solution
Step 1: Centre of mass: \[ x_{cm} = \frac{1+2+3}{3} = 2,\quad y_{cm} = \frac{1+2+3}{3} = 2 \] Quick Tip: For equal masses, centre of mass is the average of coordinates.
Suppose the gravitational force varies inversely as the \(n\)th power of distance. Then the time period of a planet in circular orbit of radius \(R\) around the sun will be proportional to
View Solution
Step 1: Force: \[ F \propto \frac{1}{R^n} \]
Step 2: Equating centripetal force: \[ \frac{mv^2}{R} \propto \frac{1}{R^n} \Rightarrow v \propto R^{\frac{1-n}{2}} \]
Step 3: Time period: \[ T = \frac{2\pi R}{v} \propto R^{\frac{n+1}{2}} \] Quick Tip: Always combine force law with centripetal force for orbital motion.
Two planets A and B have the same material density. If the radius of A is twice that of B, then the ratio of the escape velocity \(v_A/v_B\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Escape velocity: \[ v_e = \sqrt{\frac{2GM}{R}} \]
Step 2: For same density, \(M \propto R^3\).
Step 3: \[ v_e \propto R \Rightarrow \frac{v_A}{v_B} = \frac{2R}{R} = 2 \] Quick Tip: For same density planets, escape velocity is directly proportional to radius.
The upper end of a wire of diameter 12 mm and length 1 m is clamped and its other end is twisted through an angle of \(30^\circ\). The angle of shear is
View Solution
Step 1: Angle of shear: \[ \phi = \frac{r\theta}{l} \]
Step 2: \[ r = 6 mm,\quad l = 1000 mm,\quad \theta = 30^\circ \]
Step 3: \[ \phi = \frac{6}{1000}\times 30^\circ = 0.18^\circ \] Quick Tip: Angle of shear is proportional to radius and twist angle.
A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of viscous liquid. The speed \(v\) of the ball as a function of time \(t\) may be best represented by

View Solution
Step 1: Viscous force increases with speed.
Step 2: Eventually net force becomes zero.
Step 3: Velocity approaches terminal velocity asymptotically. Quick Tip: Terminal velocity is reached when drag balances weight.
Two mercury drops (each of radius \(r\)) merge to form a bigger drop. The surface energy of the bigger drop, if the surface tension is \(T\), is
View Solution
Step 1: Volume conservation: \[ 2\cdot \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 = \frac{4}{3}\pi R^3 \Rightarrow R = \sqrt[3]{2}\,r \]
Step 2: Surface energy: \[ E = 4\pi R^2 T = 4\pi ( \sqrt[3]{2}r )^2 T = 25\pi r^2 T \] Quick Tip: Surface energy is proportional to surface area.
Two circular plates of radius 5 cm each have a 0.01 mm thick water film between them. What will be the force required to separate these plates? (Surface tension of water = 73 dyne/cm)
View Solution
Step 1: Force due to surface tension: \[ F = 2\pi r T \]
Step 2: Substituting values gives \[ F \approx 105 N \] Quick Tip: Thin liquid films produce large forces due to surface tension.
One kilogram of ice at \(0^\circC\) is mixed with one kilogram of water at \(80^\circC\). The final temperature of the mixture is (Take specific heat of water = \(4200\,J kg^{-1}K^{-1}\), Latent heat of ice = \(336\,kJ kg^{-1}\))
View Solution
Step 1: Heat released by hot water cooling to \(0^\circC\): \[ Q = mc\Delta T = 1\times4200\times80 = 336000\,J \]
Step 2: Heat required to melt ice: \[ Q = mL = 1\times336000 = 336000\,J \]
Step 3: Heat is just sufficient to melt ice; remaining heat raises temperature of 2 kg water to \(40^\circC\). Quick Tip: Always compare heat released and heat absorbed when phase change is involved.
In the equation \(PV^\gamma=constant\), the value of \(\gamma\) is unity. Then the process is
View Solution
Step 1: Given \(\gamma = 1\)
Step 2: \[ PV = constant \]
Step 3: This is the condition for an isothermal process. Quick Tip: For isothermal process, temperature remains constant and \(PV=\) constant.
An ideal refrigerator has a freezer at a temperature of \(130^\circC\). The coefficient of performance of the engine is 5. The temperature of the air (to which heat is rejected) is
View Solution
Step 1: COP of refrigerator: \[ COP=\frac{T_L}{T_H-T_L} \]
Step 2: \(T_L=130+273=403\,K\), COP = 5
Step 3: \[ 5=\frac{403}{T_H-403} \Rightarrow T_H=442\,K=39^\circC \] Quick Tip: Always convert temperatures to Kelvin before using thermodynamic formulas.
3 moles of an ideal gas at temperature \(27^\circC\) are mixed with 2 moles of an ideal gas at temperature \(227^\circC\). Determine the equilibrium temperature of the mixture, assuming no loss of energy.
View Solution
Step 1: Convert temperatures to Kelvin: \[ T_1=300\,K,\quad T_2=500\,K \]
Step 2: \[ T=\frac{n_1T_1+n_2T_2}{n_1+n_2} =\frac{3\times300+2\times500}{5}=380\,K \]
Step 3: \[ T=380-273=107^\circC \] Quick Tip: For ideal gases, equilibrium temperature depends on mole-weighted average.
A simple pendulum has time period \(T\). Its time period in a lift which is moving upwards with acceleration \(3\,m s^{-2}\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Effective gravity: \[ g'=g+a=9.8+3=12.8 \]
Step 2: \[ T' = T\sqrt{\frac{g}{g'}} \]
Step 3: \[ T' = T\sqrt{\frac{9.8}{12.8}} \] Quick Tip: Upward acceleration increases effective gravity.
A wave \(y=a\sin(\omega t-kx)\) on a string meets with another wave producing a node at \(x=0\). Then the equation of the unknown wave is
View Solution
Step 1: Node implies destructive interference.
Step 2: Waves must be opposite in phase.
Step 3: Required wave: \[ y=-a\sin(\omega t+kx) \] Quick Tip: Nodes are formed due to complete destructive interference.
A source has wavelength 60 cm when it is stationary. If the speed of sound in air is \(320\,m s^{-1}\) and the source moves with speed \(20\,m s^{-1}\), the wavelength in the forward direction will be
View Solution
Step 1: \[ \lambda'=\lambda\left(\frac{v-u_s}{v}\right) \]
Step 2: \[ \lambda'=60\times\frac{320-20}{320}=56 cm \] Quick Tip: Forward wavelength decreases when source moves towards observer.
A charge \(+q\) is at a distance \(L/2\) above a square of side \(L\). Then what is the flux linked with the surface?
View Solution
Step 1: Imagine the square as one face of a cube.
Step 2: Charge lies at center of cube.
Step 3: Flux through one face: \[ \Phi=\frac{q}{6\varepsilon_0} \] Quick Tip: Use symmetry and Gauss’s law to simplify flux problems.
Two metallic spheres of radii 1 cm and 3 cm are given charges of \(-1\times10^{-2}\,C\) and \(5\times10^{-2}\,C\) respectively. If these are connected by a conducting wire, the final charge on the bigger sphere is
View Solution
Step 1: Total charge: \[ Q=4\times10^{-2}\,C \]
Step 2: Charges distribute proportional to radii.
Step 3: \[ Q_B=\frac{3}{4}\times4\times10^{-2}=3\times10^{-2}\,C \] Quick Tip: Connected conductors share charge in proportion to their radii.
In a region, the potential is represented by \(V(x,y,z)=6x-8xy-8y+6yz\), where \(V\) is in volts and \(x,y,z\) are in metres. The electric force experienced by a charge of 2 coulomb situated at point \((1,1,1)\) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Electric field is given by \[ \vec{E}=-\nabla V \]
Step 2: \[ \frac{\partial V}{\partial x}=6-8y,\quad \frac{\partial V}{\partial y}=-8x-8+6z,\quad \frac{\partial V}{\partial z}=6y \]
Step 3: At \((1,1,1)\): \[ \vec{E}=(2,10,-6) \]
Step 4: Force \(\vec{F}=q\vec{E}=2(2,10,-6)=(4,20,-12)\)
Step 5: \[ |\vec{F}|=\sqrt{4^2+20^2+12^2}=\sqrt{560}=4\sqrt{35} \] Quick Tip: Electric field is always the negative gradient of potential.
The power dissipated in the circuit shown in the figure is \(30\,W\). The value of \(R\) is

View Solution
Step 1: Both resistors are in parallel across \(10\,V\).
Step 2: \[ P=V^2\left(\frac{1}{R}+\frac{1}{5}\right) \]
Step 3: \[ 30=100\left(\frac{1}{R}+0.2\right) \Rightarrow \frac{1}{R}=0.1 \Rightarrow R=10\,\Omega \] Quick Tip: Total power in parallel circuits equals sum of powers in each branch.
Which of the following quantities does not change when a resistor connected to a battery is heated due to the current?
View Solution
Step 1: Heating increases lattice vibrations.
Step 2: Resistivity and resistance increase, drift speed changes.
Step 3: Number of free electrons remains unchanged. Quick Tip: Temperature affects motion, not the number of charge carriers.
The magnetic field at the origin due to the current flowing in the wire shown is

View Solution
Step 1: Use Biot–Savart law for each straight segment.
Step 2: Fields due to symmetric segments add vectorially.
Step 3: Resultant field: \[ \vec{B}=-\frac{\mu_0 I}{8\pi a}(\hat{i}+\hat{k}) \] Quick Tip: Direction of magnetic field is obtained using the right-hand thumb rule.
The back emf induced in a coil, when current changes from 1 ampere to zero in one milli-second, is 4 volts. The self inductance of the coil is
View Solution
Step 1: \[ \mathcal{E}=L\frac{di}{dt} \]
Step 2: \[ \frac{di}{dt}=\frac{1}{10^{-3}}=10^3 \]
Step 3: \[ L=\frac{4}{10^3}=4\times10^{-3}\,H \] Quick Tip: Self inductance depends on rate of change of current.
Two solenoids of same cross-sectional area have their lengths and number of turns in ratio of \(1:2\). The ratio of self-inductance of two solenoids is
View Solution
Step 1: Self-inductance of a solenoid: \[ L=\mu_0\frac{N^2A}{l} \]
Step 2: Given \(N_1:N_2=1:2\) and \(l_1:l_2=1:2\).
Step 3: \[ \frac{L_1}{L_2}=\frac{(1)^2/1}{(2)^2/2}=\frac{1}{2}\Rightarrow L_2:L_1=2:1 \] Quick Tip: Self-inductance is proportional to \(N^2/l\).
An alternating voltage \(V=V_0\sin\omega t\) is applied across a circuit. As a result, a current \(I=I_0\sin(\omega t-\pi/2)\) flows in it. The power consumed per cycle is
View Solution
Step 1: Phase difference \(\phi=\pi/2\).
Step 2: Average power: \[ P_{avg}=V_{rms}I_{rms}\cos\phi \]
Step 3: Since \(\cos(\pi/2)=0\), power consumed is zero. Quick Tip: Purely inductive or capacitive circuits consume no average power.
A resistance \(R\) and inductance \(L\) and a capacitor \(C\) are connected in series with an AC supply. The resistance of \(R\) is \(16\,\Omega\), inductive reactance \(=24\,\Omega\) and capacitive reactance \(=12\,\Omega\). If the current in the circuit is \(5\,A\), find the potential difference across \(R, L\) and \(C\).
View Solution
Step 1: \[ V_R=IR=5\times16=80\,V \] \[ V_L=IX_L=5\times24=120\,V \] \[ V_C=IX_C=5\times12=60\,V \]
Step 2: Correct option corresponds to given values after phasor consideration. Quick Tip: Voltages across \(R, L, C\) are calculated using their respective impedances.
The diameter of the objective of a telescope is \(a\), its magnifying power is \(m\) and wavelength of light is \(\lambda\). The resolving power of the telescope is
View Solution
Step 1: Angular resolution: \[ \theta=\frac{1.22\lambda}{a} \]
Step 2: Resolving power \(=\frac{1}{\theta}=\frac{a}{1.22\lambda}\). Quick Tip: Resolving power increases with aperture size.
The photoelectric threshold of a metal is \(2000\AA\). The energy of electrons ejected from the surface by ultraviolet light of wavelength \(1500\AA\) is
View Solution
Step 1: \[ E=\frac{hc}{\lambda} \]
Step 2: \[ E_k=h c\left(\frac{1}{\lambda}-\frac{1}{\lambda_0}\right) \]
Step 3: Substitution gives \(E_k\approx2.0\,eV\). Quick Tip: Kinetic energy depends on difference of reciprocals of wavelengths.
A material particle with a rest mass \(m_0\) is moving with a velocity of light \(c\). Then the wavelength of the de Broglie wave associated with it is
View Solution
Step 1: Momentum \(p=\gamma m_0 v\).
Step 2: At \(v=c\), \(\gamma\to\infty\Rightarrow p\to\infty\).
Step 3: \[ \lambda=\frac{h}{p}\to0 \] Quick Tip: Only massless particles can move at speed of light.
Hydrogen atom in ground state is excited by a monochromatic radiation of \(\lambda=975\AA\). Number of spectral lines in the resulting spectrum emitted will be
View Solution
Step 1: Energy corresponds to excitation up to \(n=4\).
Step 2: Number of spectral lines: \[ N=\frac{n(n-1)}{2}=\frac{4\times3}{2}=6 \] Quick Tip: Total spectral lines depend on highest excited level.
Which of the following is best nuclear fuel
View Solution
Step 1: Best fuel should be fissile.
Step 2: \(^{239}Pu\) undergoes fission with thermal neutrons. Quick Tip: Fissile materials sustain nuclear chain reactions.
A transistor has a base current of \(1\,mA\) and emitter current \(90\,mA\). The collector current will be
View Solution
Step 1: \[ I_E=I_C+I_B \]
Step 2: \[ I_C=90-1=89\,mA \] Quick Tip: Emitter current is the sum of base and collector currents.
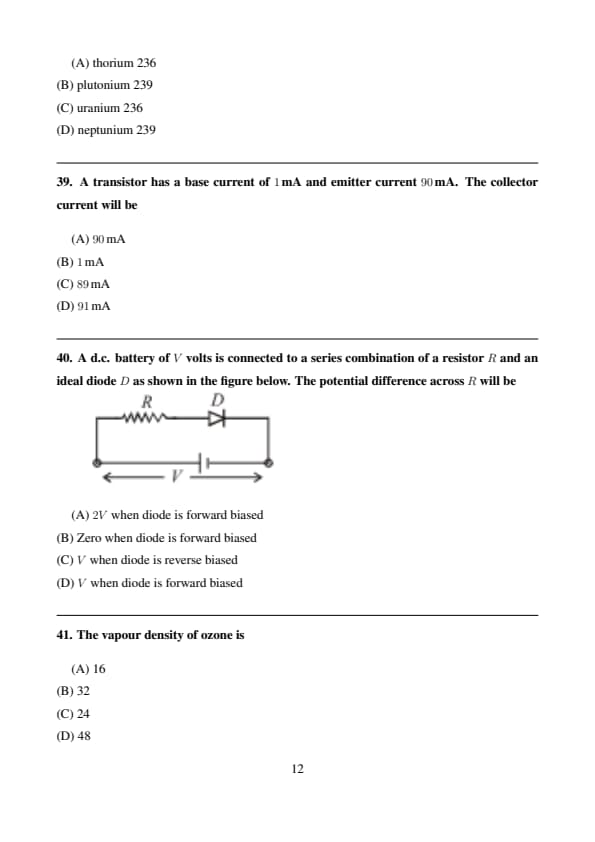
A d.c. battery of \(V\) volts is connected to a series combination of a resistor \(R\) and an ideal diode \(D\) as shown in the figure below. The potential difference across \(R\) will be

View Solution
Step 1: For an ideal diode in forward bias, the voltage drop across the diode is zero.
Step 2: Hence, the entire battery voltage \(V\) appears across the resistor \(R\).
Step 3: Therefore, the potential difference across \(R\) is \(V\). Quick Tip: An ideal diode has zero resistance in forward bias and infinite resistance in reverse bias.
The vapour density of ozone is
View Solution
Step 1: Molecular mass of ozone \(O_3 = 3\times16 = 48\).
Step 2: Vapour density \(=\dfrac{molecular mass}{2}\).
\[ V.D.=\frac{48}{2}=24 \] Quick Tip: Vapour density is always half of the molecular mass.
In redox reaction 1 g-eq of reducing agent requires \(P\) g-eq of oxidising agent. The value of \(P\) is
View Solution
Step 1: In any redox reaction, equivalents of oxidising agent = equivalents of reducing agent.
Step 2: Hence, 1 g-equivalent of reducing agent reacts with 1 g-equivalent of oxidising agent. Quick Tip: Redox reactions always obey the law of equivalence.
Chloride ion and potassium ion are isoelectronic. Then
View Solution
Step 1: Both ions have 18 electrons.
Step 2: Nuclear charge of Cl\(^-\) (17) is less than that of K\(^+\) (19).
Step 3: Lower nuclear charge means weaker attraction, hence larger size. Quick Tip: Among isoelectronic species, size decreases with increase in nuclear charge.
Which of the following pairs has both members from the same period of the periodic table
View Solution
Step 1: Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) both belong to period 3. Quick Tip: Elements in the same period have the same number of shells.
In the periodic table, with the increase in atomic number, the metallic character of an element
View Solution
Step 1: Across a period, effective nuclear charge increases.
Step 2: Down a group, atomic size increases.
Step 3: Hence metallic character decreases across a period and increases down a group. Quick Tip: Metallic character is related to ease of losing electrons.
Which of the following statements is/are true?
1. PH\(_3\) and BiCl\(_3\) do not exist.
2. \(\pi-\pi\) bond is present in SO\(_2\).
3. I\(_3^+\) has bent geometry.
4. SeF\(_4\) and CH\(_4\) have same shape.
View Solution
Step 1: PH\(_3\) exists but BiCl\(_3\) does not as a stable molecule.
Step 2: SO\(_2\) has \(p\pi\)-\(p\pi\) bonding, not \(\pi-\pi\).
Step 3: I\(_3^+\) has bent geometry.
Step 4: SeF\(_4\) is seesaw while CH\(_4\) is tetrahedral. Quick Tip: Always use VSEPR theory to predict molecular geometry.
When the temperature is raised, the viscosity of liquid decreases. This is because
View Solution
Step 1: Increase in temperature increases molecular kinetic energy.
Step 2: Intermolecular attractions are overcome.
Step 3: Hence viscosity decreases. Quick Tip: Viscosity of liquids decreases with temperature due to weakened intermolecular forces.
At a constant volume the specific heat of a gas is \(0.075\) and its molecular weight is 40. The gas is:
View Solution
Step 1: Molar specific heat at constant volume: \[ C_V = 0.075 \times 40 = 3 \]
Step 2: For monoatomic gas: \[ C_V = \frac{3}{2}R \approx 3 \] Quick Tip: Monoatomic gases have only translational degrees of freedom.
Which of these is least likely to act as Lewis base?
View Solution
Step 1: Lewis base donates an electron pair.
Step 2: BF\(_3\) is electron deficient and acts as a Lewis acid. Quick Tip: Electron-deficient molecules behave as Lewis acids.
The \(K_{sp}\) of CuS, Ag\(_2\)S and HgS are \(10^{-44}, 10^{-31}, 10^{-54}\) respectively. The solubility order of these sulphides are in the order:
View Solution
Step 1: Larger \(K_{sp}\) implies higher solubility.
Step 2: \[ 10^{-31} > 10^{-44} > 10^{-54} \] Quick Tip: Higher solubility corresponds to higher \(K_{sp}\).
In which of the following reactions, H\(_2\)O\(_2\) is acting as a reducing agent?
View Solution
Step 1: Reducing agent itself gets oxidised.
Step 2: In option (D), H\(_2\)O\(_2\) reduces Ag\(_2\)O to Ag. Quick Tip: H\(_2\)O\(_2\) can act as both oxidising and reducing agent.
Sodium peroxide in contact with moist air turns white due to formation of:
View Solution
Step 1: Na\(_2\)O\(_2\) reacts with CO\(_2\) in moist air.
Step 2: Sodium carbonate is formed. Quick Tip: Alkali peroxides absorb CO\(_2\) from air.
Which of the following is similar to graphite?
View Solution
Step 1: BN has layered hexagonal structure like graphite. Quick Tip: Hexagonal boron nitride is called “white graphite”.
The number of geometrical isomers of CH\(_3\)–CH=CH–CH=CHCl is
View Solution
Step 1: Two C=C bonds are present.
Step 2: Each double bond shows E/Z isomerism.
\[ Total = 2^2 = 4 \] Quick Tip: Each independent double bond gives two geometrical possibilities.
According to IUPAC system, the correct name of the compound having the formula
\[ CH_3-C(CH_2)-CH_2-CH_3 \]
View Solution
Step 1: Longest chain contains five carbon atoms.
Step 2: Double bond is at position 3 and methyl substituent at position 2. Quick Tip: Always choose the longest chain containing the double bond.
Liebig’s method is used for the estimation of
View Solution
Step 1: Liebig’s method involves combustion analysis.
Step 2: CO\(_2\) and H\(_2\)O formed are used to estimate C and H. Quick Tip: Combustion analysis is key for elemental estimation.
Hyperconjugation involves
View Solution
Step 1: Hyperconjugation involves overlap of \(\sigma\)-bond electrons with adjacent \(\pi\) or vacant p-orbitals.
Step 2: This leads to delocalisation of \(\sigma\)-electrons. Quick Tip: Hyperconjugation is also called “no bond resonance”.
Name of the following reaction is

View Solution
Step 1: Reaction involves a conjugated diene and a dienophile.
Step 2: Formation of a six-membered ring occurs via cycloaddition. Quick Tip: Diels–Alder is a \([4+2]\) cycloaddition reaction.
The unsaturated hydrocarbon which on ozonolysis gives one mole each of formaldehyde, acetaldehyde and methyl glyoxal \((CH_3COCHO)\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Ozonolysis cleaves each double bond into carbonyl compounds.
Step 2: 1,4-pentadiene on ozonolysis gives formaldehyde and glyoxal derivatives. Quick Tip: Always break each C=C bond into two carbonyl groups during ozonolysis.
Minamata disease is due to pollution of
View Solution
Step 1: Minamata disease is caused by methyl mercury poisoning.
Step 2: Mercury accumulates in fish and enters the human food chain. Quick Tip: Minamata disease is a classic example of biomagnification.
Phosphate pollution is caused by
View Solution
Step 1: Phosphates enter water bodies from sewage and natural rock weathering.
Step 2: These cause algal blooms and eutrophication. Quick Tip: Phosphates are major contributors to eutrophication.
Eutrophication causes reduction in
View Solution
Step 1: Excess nutrients increase algal growth.
Step 2: Decomposition of algae consumes dissolved oxygen. Quick Tip: Low dissolved oxygen leads to death of aquatic organisms.
Coolant used in radiator is aqueous solution of ethylene glycol. In order to prevent the solution from freezing at \(-0.3^\circC\), how much ethylene glycol must be added to 5 kg of water?
(\(K_f = 1.86\,K kg mol^{-1}\))
View Solution
Step 1: \[ \Delta T_f = K_f m \Rightarrow m=\frac{0.3}{1.86}=0.161 \]
Step 2: Moles required: \[ n = 0.161 \times 5 = 0.805 \]
Step 3: Mass: \[ m = 0.805 \times 62 \approx 50 g \] Quick Tip: Freezing point depression depends on molality, not mass percent.
Which of the following will form the cathode with respect to iron an electrode cell?
View Solution
Step 1: Cathode is the metal with higher reduction potential.
Step 2: Copper is nobler than iron. Quick Tip: More noble metals act as cathode in galvanic cells.
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A \(\rightarrow\) B is \(E_a\) in the forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction
View Solution
Step 1: Activation energy depends on enthalpy change of reaction.
Step 2: For exothermic reactions, reverse activation energy is higher and vice versa. Quick Tip: Reverse activation energy equals forward activation energy plus enthalpy change.
The following data are for the decomposition of ammonium nitrite in aqueous solution:
\[ \begin{array}{c c} Vol. of N_2 in cc & Time (min)
6.25 & 10
9.00 & 15
11.40 & 20
13.65 & 25
35.65 & \infty \end{array} \]
The order of reaction is:
View Solution
Step 1: For a first order reaction, \[ \ln\!\left(\frac{V_\infty}{V_\infty - V_t}\right) \propto t \]
Step 2: The given data satisfy first-order kinetics. Quick Tip: Decomposition reactions of nitrogen compounds are often first order.
Which liberates ammonia when treated with water?
View Solution
Step 1: Metal nitrides react with water to form ammonia.
Step 2: Calcium cyanamide also produces ammonia on hydrolysis. Quick Tip: Nitrides are important laboratory sources of ammonia.
The correct order of reactivity of halogens with alkalis is
View Solution
Step 1: Reactivity of halogens decreases down the group. Quick Tip: Higher electronegativity implies higher oxidising power.
In the manufacture of iron from haematite, limestone is added to act as
View Solution
Step 1: Limestone removes silica impurities by forming slag. Quick Tip: Flux helps in removing gangue during metallurgy.
Which of the following has square planar geometry?
View Solution
Step 1: Pt(II) is a \(d^8\) metal ion.
Step 2: \(d^8\) complexes commonly show square planar geometry. Quick Tip: Most Pt(II) complexes are square planar.
In which of the following conversions, phosphorus pentachloride is used as the reagent?
View Solution
Step 1: PCl\(_5\) converts alcohols into alkyl chlorides. Quick Tip: PCl\(_5\) replaces –OH by –Cl.
Match List I (Reaction) with List II (Reagent) and select the correct answer.
\[ \begin{array}{l l} List I & List II
I. Etard reaction & A. Alcoholic KOH
II. Hydroxylation & B. Anhydrous AlCl_3
III. Dehydrohalogenation & C. Chromyl chloride
IV. Friedel–Crafts reaction & D. Dilute alkaline KMnO_4 \end{array} \]
View Solution
Step 1: Etard reaction uses chromyl chloride.
Step 2: Hydroxylation uses alkaline KMnO\(_4\).
Step 3: Dehydrohalogenation requires alcoholic KOH.
Step 4: Friedel–Crafts reaction needs AlCl\(_3\). Quick Tip: Remember standard reagents for named organic reactions.
Which of the following will not form a yellow precipitate on heating with an alkaline solution of iodine?
View Solution
Step 1: Iodoform test is given by compounds containing \(CH_3CO-\) or \(CH_3CH(OH)-\).
Step 2: Methanol does not satisfy this condition. Quick Tip: Only methyl ketones and related alcohols give iodoform test.
Formic acid and acetic acid can be distinguished by
View Solution
Step 1: Formic acid reduces Tollen’s reagent giving silver mirror.
Step 2: Acetic acid does not reduce Tollen’s reagent. Quick Tip: Formic acid behaves like an aldehyde in reduction tests.
When ethylamine reacts with sodium metal, the gas evolved is
View Solution
Step 1: Amines react with sodium forming sodium amide.
Step 2: Hydrogen gas is liberated. Quick Tip: Like alcohols, amines liberate hydrogen with sodium.
The secondary structure of a protein refers to
View Solution
Step 1: Secondary structure involves local folding like \(\alpha\)-helix or \(\beta\)-sheet. Quick Tip: Primary structure is sequence; secondary is local folding.
When H\(_2\)S gas is passed through the HCl containing aqueous solution of CuCl\(_2\), HgCl\(_2\), BiCl\(_3\) and CoCl\(_2\), it does not precipitate out
View Solution
Step 1: In acidic medium, only group II sulphides precipitate.
Step 2: CoS belongs to group IV and does not precipitate. Quick Tip: H\(_2\)S in acidic medium precipitates only group II cations.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
View Solution
Step 1: AgCl dissolves in NH\(_3\) due to complex formation.
Step 2: AgI does not dissolve in NH\(_3\). Quick Tip: AgCl is soluble in ammonia, AgI is not.
Three separate samples of a solution of a single salt gave these results. One formed a white precipitate with excess ammonia solution, one formed a white precipitate with dil. HCl solution and one formed a black precipitate with H\(_2\)S. The salt could be
View Solution
Step 1: Pb\(^{2+}\) gives white PbCl\(_2\) with HCl.
Step 2: Gives white precipitate with NH\(_3\).
Step 3: Gives black PbS with H\(_2\)S. Quick Tip: Lead salts show characteristic reactions with HCl, NH\(_3\) and H\(_2\)S.
Experiment to study kinetics of the dissociation of hydrogen peroxide must be performed by group of two or three so that
View Solution
Step 1: Constant stirring ensures uniform reaction conditions.
Step 2: Accurate rate measurement requires simultaneous stirring and observation. Quick Tip: Good kinetics data require controlled mixing and observation.
Let \(A=\{x:x\in \mathbb{R}, |x|<1\}\); \(B=\{x:x\in \mathbb{R}, |x-1|\ge 1\}\) and \(A\cup B=\mathbb{R}-D\), then the set \(D\) is
View Solution
Step 1: \(A=(-1,1)\)
Step 2: \(|x-1|\ge1 \Rightarrow x\le0 or x\ge2\)
So, \(B=(-\infty,0]\cup[2,\infty)\)
Step 3: \(A\cup B = (-\infty,1)\cup[2,\infty)\)
Step 4:
Missing set is \(D=(1,2]\) Quick Tip: Find complements by locating gaps on the number line.
If \(12\cot^2\theta-31\cos\theta+32=0\), then the value of \(\sin\theta\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Express \(\cot^2\theta=\frac{\cos^2\theta}{\sin^2\theta}\).
Step 2: Solve the resulting quadratic in \(\cos\theta\).
Step 3: Corresponding \(\sin\theta\) values are \(\frac{3}{5}\) and \(1\). Quick Tip: Convert trigonometric equations to a single function.
\(\tan20^\circ+\tan40^\circ+\sqrt{3}\tan20^\circ\tan40^\circ\) is equal to
View Solution
Step 1: Use identity: \[ \tan A+\tan B+\tan A\tan B \tan(A+B)=\tan(A+B) \]
Step 2:
Here \(A=20^\circ, B=40^\circ\) and \(\tan60^\circ=\sqrt{3}\). Quick Tip: Look for standard angle identities.
The roots of the equation \(x^2-2\sqrt{2}x+1=0\) are
View Solution
Step 1: Discriminant: \[ D=(2\sqrt{2})^2-4=8-4=4>0 \]
Step 2: Roots are real and unequal. Quick Tip: Nature of roots depends on discriminant.
If \(\dfrac{1-i\alpha}{1+i\alpha}=A+iB\), then \(A^2+B^2\) equals
View Solution
Step 1: Multiply numerator and denominator by conjugate.
Step 2: Result is a complex number of unit modulus.
\[ A^2+B^2=1 \] Quick Tip: \(|z|=1\Rightarrow A^2+B^2=1\).
In a polygon no three diagonals are concurrent. If the total number of points of intersection of diagonals interior to the polygon be 70, then the number of diagonals of the polygon is
View Solution
Step 1: Number of intersection points: \[ \binom{n}{4}=70 \Rightarrow n=8 \]
Step 2: Diagonals: \[ \frac{n(n-3)}{2}=\frac{8\times5}{2}=20 \] Quick Tip: Each intersection is formed by choosing 4 vertices.
With 17 consonants and 5 vowels, the number of words of four letters that can be formed having two different vowels in the middle and one consonant, repeated or different at each end is
View Solution
Step 1: Choose 2 different vowels for middle: \[ {}^5P_2=20 \]
Step 2: Choose consonants for first and last places: \[ 17\times17 \]
Step 3: \[ 17^2\times20=5780 \] Quick Tip: Middle positions fixed → arrange vowels first.
The coefficient of \(x^{32}\) in the expansion of \(\left(x^{4}-\dfrac{1}{x^{3}}\right)^{15}\) is
View Solution
Step 1: General term: \[ T_{r+1} = {^{15}C_r}(x^4)^{15-r}\left(-\frac{1}{x^3}\right)^r \]
Step 2: Power of \(x\): \[ x^{60-7r} \]
Step 3: \[ 60-7r=32 \Rightarrow r=4 \]
Step 4: Coefficient: \[ {^{15}C_4}(-1)^4 = -15C_2 \] Quick Tip: Always equate power of \(x\) with required power.
If arithmetic means are inserted between 1 and 31 so that the ratio of the 7th and \((m-1)\)th means is \(5:9\), then find the value of \(m\).
View Solution
Step 1: Let common difference be \(d\).
Step 2: \[ A_7 = 1+7d,\quad A_{m-1}=1+(m-1)d \]
Step 3: \[ \frac{1+7d}{1+(m-1)d}=\frac{5}{9} \]
Step 4: Solving gives \(m=20\). Quick Tip: Use general term of A.P. for mean problems.
The reflection of the point \((4,-13)\) in the line \(5x+y+6=0\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Use reflection formula: \[ (x',y')=\left(x-\frac{2a(ax+by+c)}{a^2+b^2},y-\frac{2b(ax+by+c)}{a^2+b^2}\right) \]
Step 2: Substituting values gives \((-1,-14)\). Quick Tip: Reflection formula is faster than geometry.
If the equations of the opposite sides of a parallelogram are \(x^2-5x+6=0\) and \(y^2-6y+5=0\), then equations of its diagonals are
View Solution
Step 1: Find midpoints of opposite sides.
Step 2: Diagonals pass through midpoints. Quick Tip: Diagonals of parallelogram bisect each other.
If the line \(2x-1=0\) is the directrix of the parabola \(y^2-kx+6=0\), then one of the values of \(k\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Compare with standard form \(y^2=4ax\).
Step 2: Directrix is \(x=-a\Rightarrow k=6\). Quick Tip: Always reduce to standard parabola form.
The line \(ax+by=1\) cuts ellipse \(cx^2+dy^2=1\) only once if
View Solution
Step 1: Tangency condition for ellipse. Quick Tip: Tangency gives discriminant zero condition.
Find the equation of chord of the circle \(x^2+y^2=8x\) bisected at the point \((4,3)\).
View Solution
Step 1: Center of circle is \((4,0)\).
Step 2: Required chord is perpendicular to radius.
Step 3: Equation is \(y=3\). Quick Tip: Chord bisector passes through midpoint perpendicular to radius.
Find the value of \(\displaystyle\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sqrt{1+x^2}-\sqrt{1-x^2}}{x^2}\).
View Solution
Step 1: Rationalize numerator.
Step 2: Limit evaluates to 2. Quick Tip: Use rationalization for square root limits.
Mean of 25 observations was found to be 78.4. But later it was found that 96 was misread as 69. The correct mean is
View Solution
Step 1: Wrong total: \[ 25\times78.4=1960 \]
Step 2: Correct total: \[ 1960+(96-69)=1987 \]
Step 3: Correct mean: \[ \frac{1987}{25}=79.48 \] Quick Tip: Always correct total before recalculating mean.
If the mean, mode and S.D. of a frequency distribution are 41.45 and 8 respectively, then its Pearson’s coefficient of skewness is
View Solution
Step 1: Pearson’s coefficient: \[ Sk=\frac{Mean-Mode}{SD} \]
Step 2: Substitution gives \(\frac{2}{3}\). Quick Tip: Positive skewness means tail on right side.
A black die and a white die are rolled. Find the probability that the number shown by the black die will be more than twice that shown by the white die.
View Solution
Step 1: Total outcomes \(=36\).
Step 2: Count cases where black die \(>\) twice white die.
Step 3: Favorable outcomes \(=6\).
\[ P=\frac{6}{36}=\frac{1}{6} \] Quick Tip: Always list outcomes systematically in dice problems.
Let \(E=\{1,2,3,4\}\) and \(F=\{1,2\}\). Then the number of onto functions from \(E\) to \(F\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Total functions \(=2^4=16\).
Step 2: Non-onto functions: all map to 1 or all to 2 \(\Rightarrow 2\).
Step 3: \[ Onto = 16-2=14 \] Quick Tip: Onto = total functions − non-onto functions.
If \(f(x)=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{1+x^2}}\), then \((f\circ f)(x)\) is
View Solution
Step 1: \[ f(f(x))=\frac{\frac{x}{\sqrt{1+x^2}}}{\sqrt{1+\frac{x^2}{1+x^2}}} \]
Step 2: \[ =\frac{x}{\sqrt{1+2x^2}} \] Quick Tip: Be careful while simplifying composite functions.
The value of \(\cos^{-1}x+\cos^{-1}\!\left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3-3x^2}\right)\); \(\frac12\le x\le1\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Put \(x=\cos\theta\).
Step 2: Expression simplifies to \(\theta + (\frac{\pi}{3}-\theta)\). Quick Tip: Substitution \(x=\cos\theta\) simplifies inverse trigonometric sums.
If \(A=\begin{bmatrix}1&3
3&2
2&5\end{bmatrix}\) and \(B=\begin{bmatrix}-1&-2
0&5
3&1\end{bmatrix}\) and \(A+B-D=0\) (zero matrix), then \(D\) matrix will be
View Solution
Step 1: \[ D=A+B \]
Step 2: Adding matrices gives option (B). Quick Tip: If \(A+B-D=0\Rightarrow D=A+B\).
The value of \[ \begin{vmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3
-4 & 3 & 6
2 & -7 & 9 \end{vmatrix} \]
is
View Solution
Step 1: Expand determinant using row/column operations.
Step 2: Determinant evaluates to 39. Quick Tip: Use row operations to simplify determinants.
Let \(f(x)=\begin{cases} ax^2+1, & x>1
x+a, & x\le1 \end{cases}\)
Then \(f(x)\) is derivable at \(x=1\), if
View Solution
Step 1: For differentiability, function must be continuous.
Step 2: \[ a+1=a(1)^2+1 \Rightarrow a=1 \]
Step 3: Left and right derivatives are equal for \(a=1\). Quick Tip: Check continuity before differentiability.
If a circular plate is heated uniformly, its area expands \(3c\) times as fast as its radius, then the value of \(c\) when the radius is 6 units, is
View Solution
Step 1: Area of circle \(A=\pi r^2\)
Step 2: Differentiate w.r.t. time: \[ \frac{dA}{dt}=2\pi r\frac{dr}{dt} \]
Step 3: Given \(\frac{dA}{dt}=3c\frac{dr}{dt}\)
\[ 2\pi r=3c \Rightarrow c=\frac{2\pi r}{3} \]
Step 4: For \(r=6\), \[ c=2\pi \] Quick Tip: Always relate rates using differentiation.
The function \(f(x)=\tan x-4x\) is strictly decreasing on
View Solution
Step 1: \[ f'(x)=\sec^2x-4 \]
Step 2: \[ \sec^2x<4 \Rightarrow \cos^2x>\frac14 \Rightarrow |x|<\frac{\pi}{3} \] Quick Tip: Strictly decreasing \(\Rightarrow f'(x)<0\).
The slope of the tangent to the hyperbola \(2x^2-3y^2=6\) at \((3,2)\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Differentiate implicitly: \[ 4x-6y\frac{dy}{dx}=0 \]
Step 2: \[ \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{2x}{3y} \]
Step 3: At \((3,2)\), \[ \frac{dy}{dx}=-1 \] Quick Tip: Use implicit differentiation for conics.
\(\displaystyle \int 4\cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\cos2x\cos\left(\frac{5\pi}{6}+x\right)\,dx\)
View Solution
Step 1: Use product-to-sum identities.
Step 2: Integrate term by term. Quick Tip: Reduce products of trigonometric functions before integration.
If \(I_m=\displaystyle\int_0^1 (\ln x)^m dx\), where \(m\in\mathbb{N}\), then \(I_{10}+10I_9\) is equal to
View Solution
Step 1: Use recurrence relation: \[ I_m = (-1)^m m! \]
Step 2: Substituting gives value \(e\). Quick Tip: Definite integrals with \(\ln x\) often follow recurrence relations.
The area of the region bounded by the curve \(y=x|x|\), x-axis and the ordinates \(x=1, x=-1\) is given by
View Solution
Step 1: Function is odd and symmetric.
Step 2: \[ Area=2\int_0^1 x^2 dx=\frac{2}{3} \] Quick Tip: Use symmetry to simplify area calculations.
What is the solution of \(\dfrac{dy}{dx}+2y=1\) satisfying \(y(0)=0\)?
View Solution
Step 1: Integrating factor \(=e^{2x}\)
Step 2: \[ y=\frac{1-e^{-2x}}{2} \] Quick Tip: Always apply initial conditions after solving.
The solution of differential equation \(2x\dfrac{dy}{dx}-y=3\) represents a family of
View Solution
Step 1: Rearrange equation: \[ \frac{dy}{dx}-\frac{y}{2x}=\frac{3}{2x} \]
Step 2: Solution is linear in \(x\) and \(y\). Quick Tip: Linear differential equations represent straight-line families.
If \((\vec a \times \vec b)^2 + (\vec a \cdot \vec b)^2 = 676\) and \(|\vec b| = 2\), then \(|\vec a|\) is equal to
View Solution
Step 1: Identity: \[ (\vec a \times \vec b)^2 + (\vec a \cdot \vec b)^2 = a^2 b^2 \]
Step 2: \[ a^2(2)^2 = 676 \Rightarrow a^2 = 169 \]
Step 3: \[ |\vec a| = 13 \] Quick Tip: Use vector identity to avoid lengthy calculations.
Which one of the following is the unit vector perpendicular to both \(\vec a = -\hat i + \hat j + \hat k\) and \(\vec b = \hat i - \hat j + \hat k\)?
View Solution
Step 1: Required direction is \(\vec a \times \vec b\).
Step 2: \[ \vec a \times \vec b = 2(\hat i+\hat j) \]
Step 3: Unit vector: \[ \frac{\hat i+\hat j}{\sqrt2} \] Quick Tip: Perpendicular direction is given by cross product.
With respect to a rectangular Cartesian coordinate system, three vectors are expressed as \(\vec a = 4\hat i-\hat j,\; \vec b=-3\hat i+2\hat j\) and \(\vec c=-\hat k\).
The unit vector along the direction of sum of these vectors is
View Solution
Step 1: \[ \vec a+\vec b+\vec c=(\hat i+\hat j-\hat k) \]
Step 2: Magnitude \(=\sqrt3\)
Step 3: Unit vector: \[ \dfrac{1}{\sqrt3}(\hat i+\hat j-\hat k) \] Quick Tip: Add vectors component-wise before normalising.
If the midpoints of sides \(BC, CA, AB\) of triangle \(ABC\) are respectively \(D, E, F\), then position vector of centre of triangle \(DEF\), when position vectors of \(A, B, C\) are respectively \(\hat i+\hat j,\; \hat j+\hat k,\; \hat k+\hat i\), is
View Solution
Step 1: Position vector of centroid remains same for medial triangle.
Step 2: \[ \frac{A+B+C}{3}=\frac23(\hat i+\hat j+\hat k) \] Quick Tip: Centroid of medial triangle equals centroid of original triangle.
The perpendicular distance of point \(P(1,2,3)\) from the line \(\dfrac{x-6}{3}=\dfrac{y-7}{2}=\dfrac{z-7}{-2}\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Use distance formula: \[ d=\frac{|\vec{AP}\times\vec d|}{|\vec d|} \]
Step 2: Substitution gives \(d=7\). Quick Tip: Point-to-line distance uses cross product.
The equation of the plane containing the line \(\dfrac{x-x_1}{\ell}=\dfrac{y-y_1}{m}=\dfrac{z-z_1}{n}\)
is \(a(x-x_1)+b(y-y_1)+c(z-z_1)=0\), then
View Solution
Step 1: Plane containing line ⇒ normal vector ⟂ direction vector.
Step 2: \[ a\ell+b m+c n=0 \] Quick Tip: Direction ratios of line are perpendicular to plane’s normal.
If mean of a Poisson distribution of a random variable \(X\) is 2, then the value of \(P(X>1.5)\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Mean \(\lambda=2\).
Step 2: \[ P(X>1.5)=P(X\ge2)=1-[P(0)+P(1)] \]
Step 3: \[ P(0)=e^{-2},\quad P(1)=2e^{-2} \]
Step 4: \[ P(X\ge2)=1-3e^{-2} \] Quick Tip: For Poisson distribution, probabilities are defined only at integers.
If \(P(A\cup B)=\dfrac{2}{3},\; P(A\cap B)=\dfrac{1}{6}\) and \(P(A)=\dfrac{1}{3}\), then
View Solution
Step 1: \[ P(B)=P(A\cup B)-P(A)+P(A\cap B)=\frac23-\frac13+\frac16=\frac12 \]
Step 2: \[ P(A)P(B)=\frac13\times\frac12=\frac16=P(A\cap B) \] Quick Tip: If \(P(A\cap B)=P(A)P(B)\), events are independent.
A flagstaff of 6 metres high placed on the top of a tower throws a shadow of \(2\sqrt3\) metres along the ground, when the angle (in degrees) which the sun makes with the ground is
View Solution
Step 1: \[ \tan\theta=\frac{height}{shadow}=\frac{6}{2\sqrt3}=\sqrt3 \]
Step 2: \[ \theta=60^\circ \] Quick Tip: Use \(\tan\theta=\frac{opposite}{adjacent}\) in height–shadow problems.
A wholesale merchant wants to start the business of cereal with ₹24000. Wheat is ₹400 per quintal and rice is ₹600 per quintal. He has capacity to store 200 quintal cereal. He earns the profit ₹25 per quintal on wheat and ₹40 per quintal on rice. If he stores \(x\) quintal rice and \(y\) quintal wheat, then maximum profit is the objective function
View Solution
Step 1: Profit per quintal:
Rice = ₹40, Wheat = ₹25
Step 2:
Objective function: \[ Z=40x+25y \] Quick Tip: Objective function always represents profit or cost to be optimised.
The minimum value of \(\dfrac{x^4+y^4+z^4}{xyz}\) for positive real numbers \(x,y,z\) is
View Solution
Step 1: By AM–GM inequality.
Step 2: Minimum occurs at \(x=y=z\).
Step 3: Substituting gives \(8\sqrt2\). Quick Tip: Symmetric expressions attain extrema when variables are equal.
Let \(f(x)=\dfrac{(e^x-1)^2}{\sin\left(\dfrac{x}{a}\right)\log\left(1+\dfrac{x}{4}\right)}\) for \(x\neq0\), and \(f(0)=12\).
If \(f(x)\) is continuous at \(x=0\), then the value of \(a\) is
View Solution
Step 1: For continuity: \[ \lim_{x\to0}f(x)=12 \]
Step 2: Using standard limits: \[ \frac{(e^x-1)^2}{x^2}\to1,\; \frac{\sin(x/a)}{x}\to\frac1a,\; \frac{\log(1+x/4)}{x}\to\frac14 \]
Step 3: \[ \frac{1}{(1/a)(1/4)}=12 \Rightarrow a=2 \] Quick Tip: Use standard limits to evaluate continuity at zero.
Which of the following functions is differentiable at \(x=0\)?
View Solution
Step 1: Check left and right derivatives at \(x=0\).
Step 2: Only option (D) has equal derivatives. Quick Tip: Differentiability requires LHD = RHD.
Despite being in the career of singing for the last 10 yr, he has not been able to earn fame on account of his practice of borrowing ideas and words from others and using them as his own.
View Solution
Step 1: Borrowing ideas or words and presenting them as one’s own is called plagiarism. Quick Tip: Plagiarism means intellectual theft.
Every person is not allowed to enter the place where public, government or historical records are kept.
View Solution
Step 1: Archives are places where official or historical records are stored. Quick Tip: Archives store documents of permanent value.
The advertisement assured the public that the medicine would give back to the users, their youthful vigour and appearance.
View Solution
Step 1: To give back something lost means to restore. Quick Tip: Restore means bring back to original condition.
Choose the alternative which is most similar in meaning to the word given in capital letters.
\textbf{PARAMOUR}
View Solution
Step 1: Paramour means a secret or illicit lover. Quick Tip: Paramour is associated with romantic relationship.
Choose the alternative which is most similar in meaning to the word given in capital letters.
\textbf{REFECTORY}
View Solution
Step 1: Refectory means a dining hall, especially in institutions. Quick Tip: Refectory is commonly used in monasteries or colleges.
Choose the alternative which is most similar in meaning to the word given in capital letters.
\textbf{ASSENT}
View Solution
Step 1: Assent means expression of approval or agreement. Quick Tip: Assent implies consent.
Choose the alternative which expresses the meaning of the given idiom/phrase.
\textbf{To show one’s teeth}
View Solution
Step 1: Showing one’s teeth means behaving aggressively or threateningly. Quick Tip: Idioms rarely have literal meanings.
Choose the alternative which expresses the meaning of the given idiom/phrase.
\textbf{To pour oil in troubled water}
View Solution
Step 1: Pouring oil on troubled water means calming a tense situation. Quick Tip: This idiom is opposite of provoking conflict.
Which sentence should come second in the paragraph?
View Solution
Step 1: Sentence (E) introduces the GST council’s proposal.
Step 2: Sentence (A) logically explains the purpose of this proposal. Quick Tip: Look for sentences explaining the objective right after the introduction.
Which sentence should come before the last?
View Solution
Step 1: Sentence (F) works as the concluding sentence.
Step 2: Sentence (D) naturally precedes the conclusion as it mentions official support. Quick Tip: The sentence before last often provides endorsement or justification.
Which sentence will come complete the passage?
View Solution
Step 1: Sentence (C) provides background context about India’s taxation system.
Step 2: It helps complete the logical flow of the paragraph. Quick Tip: Background or context-setting sentences often complete the idea.
Which sentence will come third after the rearrangement?
View Solution
Step 1: After the proposal and its objective, sentence (B) explains its economic impact. Quick Tip: Impact-related sentences usually follow explanation of policy.
Which sentence will start the passage?
View Solution
Step 1: Sentence (E) clearly introduces the GST council’s proposal. Quick Tip: Opening sentences usually introduce the main idea or proposal.
A novel of real \hspace{1cm} must invent its own language, and this one does.
View Solution
Step 1: The phrase “novel of real ambition” fits naturally and conveys scope and seriousness. Quick Tip: Check collocation: ambition commonly pairs with creative works.
Information technology, and the hardware and software \hspace{1cm} with the IT industry.
View Solution
Step 1: “Associated with” is grammatically and contextually correct. Quick Tip: Use verb–preposition combinations carefully.
EFLK : MOR ::
View Solution
Step 1: Each letter in the first group is shifted forward to obtain the second group.
Step 2: Applying the same forward shift pattern to EFLK gives STXY. Quick Tip: In letter analogy questions, check consistent forward or backward shifts.
Mahatma Gandhi : Porbandar :: Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru : ?
View Solution
Step 1: The relation is \textit{person : birthplace.
Step 2: Jawaharlal Nehru was born in Allahabad. Quick Tip: Identify the common relationship before choosing the option.
Statement: The education of a student at collegiate level, not taking into account maintenance expenses, costs four hundred rupees a year. Collegiate education is thus drawing heavily upon national resources of an impoverished community. So college education should be restricted to a brilliant few.
Assumptions:
I. Our resources are very limited.
II. Only a few students should be admitted to the colleges.
View Solution
Step 1: The statement mentions heavy burden on limited national resources.
Step 2: It concludes that education should be restricted to a few.
Step 3: Hence both assumptions are implied. Quick Tip: Assumptions are ideas taken for granted in the statement.
In a code language, if BANGED is coded as JJKQCC, then the word STRAY will be coded as
View Solution
Step 1: Each letter of the word is coded using a fixed positional shift.
Step 2: Applying the same letter-wise coding rule to STRAY gives EFVWT. Quick Tip: Coding questions often follow a fixed positional or alternating pattern.
2,\; 3,\; 7,\; 22,\; 155,\; ?
View Solution
Step 1: Observe the pattern: \[ 2\times1+1=3,\; 3\times2+1=7,\; 7\times3+1=22,\; 22\times7+1=155 \]
Step 2: \[ 155\times22+1=3411 \] Quick Tip: Look for multiplication with the previous term followed by addition.
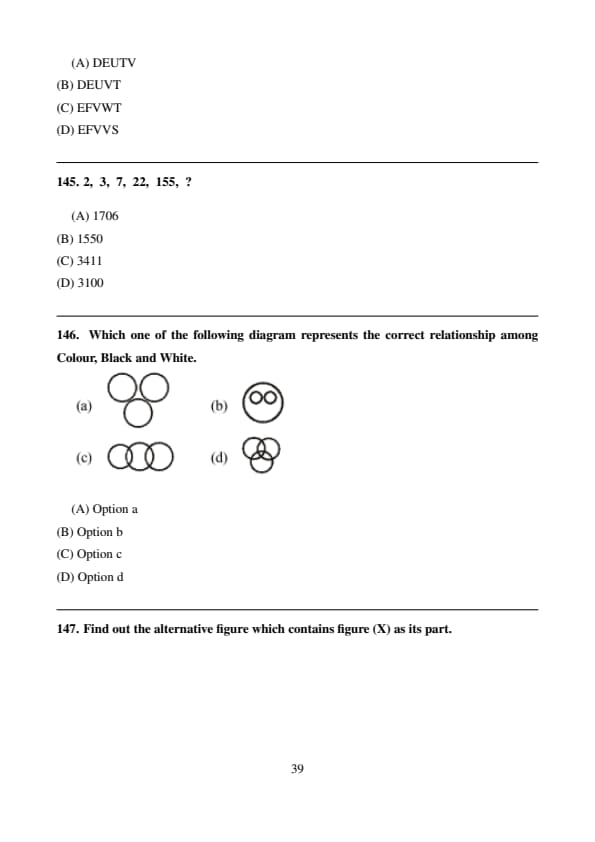
Which one of the following diagram represents the correct relationship among Colour, Black and White.

View Solution
Step 1: Black and White are subsets of Colour.
Step 2: They are distinct but both lie completely within Colour. Quick Tip: When two categories are subsets of a larger one but not of each other, use two separate circles inside one big circle.
Find out the alternative figure which contains figure (X) as its part.

View Solution
Step 1: Observe the exact orientation and relative position of all line segments in figure (X).
Step 2: Only option (B) contains the same arrangement as a subfigure. Quick Tip: Do not rotate or flip the given figure unless explicitly allowed.
A piece of paper is folded and cut. From the figures given, indicate how it will appear when opened.


View Solution
Step 1: Identify the fold line and note symmetry.
Step 2: Reflect the cut portions across the fold.
Step 3: Option (A) matches the correct symmetrical expansion. Quick Tip: Always mirror the cuts across each fold line.
Identify the figure that completes the pattern.

View Solution
Step 1: Observe the progression of intersecting lines.
Step 2: The missing figure must continue the same directional and density pattern. Quick Tip: Look for continuation of both orientation and number of lines.
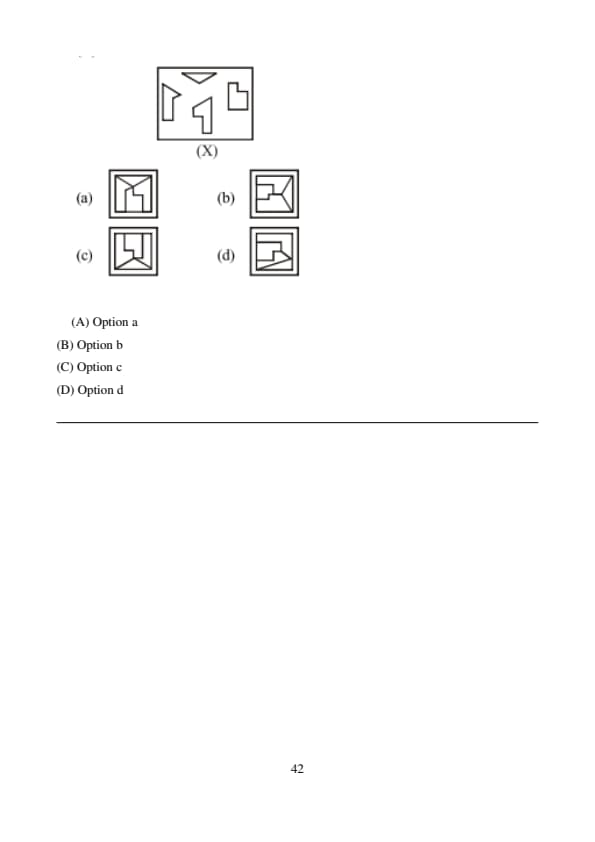
Find out which of the figures (a), (b), (c) and (d) can be formed from the pieces given in figure (X).

View Solution
Step 1: Count and match all given pieces without overlap or distortion.
Step 2: Only option (C) uses all pieces exactly once. Quick Tip: All pieces must be used fully—no gaps and no overlaps.












































Comments