BITSAT 2009 Question Paper PDF is available for download. BITSAT 2009 was conducted in online CBT mode by BITS Pilani. BITSAT 2009 Question Paper had 150 questions to be attempted in 3 hours.
BITSAT 2009 Question Paper with Answer Key PDF
| BITSAT 2009 Question Paper with Solution PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |
Given that \( \vec{A} + \vec{B} = \vec{R} \) and \( A^2 + B^2 = R^2 \). The angle between \( \vec{A} \) and \( \vec{B} \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Using the vector identity, \[ R^2 = (\vec{A} + \vec{B})^2 = A^2 + B^2 + 2AB\cos\theta \]
Step 2: Given that \( A^2 + B^2 = R^2 \), substitute in the above equation: \[ A^2 + B^2 = A^2 + B^2 + 2AB\cos\theta \]
Step 3: Simplifying, \[ 2AB\cos\theta = 0 \]
Since \(A \neq 0\) and \(B \neq 0\), \[ \cos\theta = 0 \]
Step 4: Therefore, \[ \theta = \frac{\pi}{2} \] Quick Tip: Always use the identity \[ (\vec{A}+\vec{B})^2 = A^2 + B^2 + 2AB\cos\theta \] to find the angle between two vectors.
In the relation \( P = \frac{\alpha Z}{\beta} e^{-k\theta} \), \(P\) is pressure, \(Z\) is distance, \(k\) is Boltzmann constant and \(\theta\) is the temperature. The dimensional formula of \(\beta\) will be:
View Solution
Step 1: Dimension of pressure, \[ [P] = [ML^{-1}T^{-2}] \]
Step 2: Since exponential terms are dimensionless, \[ [P] = \frac{[\alpha][Z]}{[\beta]} \]
Step 3: Taking \([\alpha]=[ML^{-1}T^{-2}]\) and \([Z]=[L]\), \[ [\beta] = [ML^2T^{-1}] \] Quick Tip: Exponential and trigonometric terms are always dimensionless.
Which of the following is most accurate?
View Solution
Step 1: Accuracy depends on least count.
Step 2: Least count of option (A) is explicitly given as \(0.001\ mm\), which is the smallest among all. Quick Tip: Smaller the least count, higher is the accuracy of the instrument.
A projectile projected at an angle \(30^\circ\) from the horizontal has a range \(R\). If the angle of projection at the same initial velocity is \(60^\circ\), the range will be:
View Solution
Step 1: Range of a projectile, \[ R = \frac{u^2\sin 2\theta}{g} \]
Step 2: For \(\theta = 30^\circ\), \[ \sin 60^\circ = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \]
Step 3: For \(\theta = 60^\circ\), \[ \sin 120^\circ = \sin 60^\circ \]
Step 4: Hence, the range remains the same. Quick Tip: Angles \(\theta\) and \(90^\circ-\theta\) give the same range for a projectile.
A block of mass \(M\) is pulled along a horizontal frictionless surface by a rope of mass \(M/2\). If a force \(2Mg\) is applied at one end of the rope, the force which the rope exerts on the block is:
View Solution
Step 1: Total mass of system, \[ M + \frac{M}{2} = \frac{3M}{2} \]
Step 2: Acceleration of system, \[ a = \frac{2Mg}{3M/2} = \frac{4g}{3} \]
Step 3: Force exerted by rope on block, \[ F = Ma = M \cdot \frac{4g}{3} = \frac{4Mg}{3} \] Quick Tip: For a massive rope, always consider acceleration of the entire system.
A chain of mass \(M\) is placed on a smooth table with \(1/n\) of its length hanging over the edge. The work done in pulling the hanging portion of the chain back to the surface of the table is:
View Solution
Step 1: Mass of hanging part, \[ \frac{M}{n} \]
Step 2: Centre of mass of hanging part lies at \( \frac{L}{2n} \).
Step 3: Work done equals gain in potential energy, \[ W = \frac{M}{n} g \cdot \frac{L}{2n} = \frac{MgL}{2n^2} \] Quick Tip: Work done against gravity equals increase in gravitational potential energy.
A particle of mass 10 kg moving eastwards with a speed 5 m s\(^{-1}\) collides with another particle of same mass moving northwards with the same speed. The two particles coalesce on collision. The new particle of mass 20 kg will move in the north-east direction with velocity:
View Solution
Step 1: Momentum in east direction, \[ p_x = 10 \times 5 = 50 \]
Step 2: Momentum in north direction, \[ p_y = 10 \times 5 = 50 \]
Step 3: Resultant momentum, \[ p = \sqrt{50^2 + 50^2} = 50\sqrt{2} \]
Step 4: Velocity of combined mass, \[ v = \frac{50\sqrt{2}}{20} = \frac{5}{\sqrt{2}} \] Quick Tip: Use conservation of momentum in perpendicular directions separately.
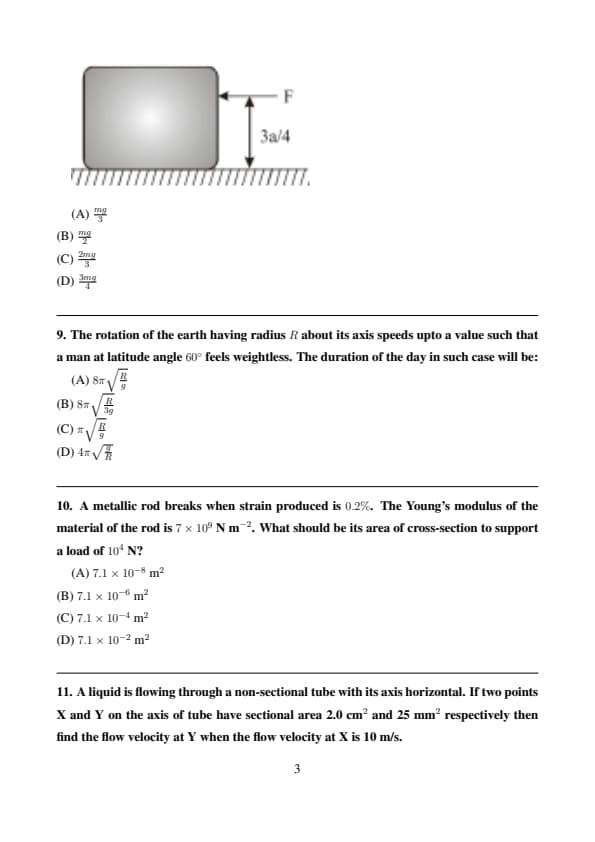
A uniform cube of side \(a\) and mass \(m\) rests on a rough horizontal table. A horizontal force \(F\) is applied normal to one of the faces at a point directly above the centre of the face, at a height \(3a/4\) above the base. The minimum value of \(F\) for which the cube begins to topple on an edge is (assume the cube does not slide):

View Solution
Step 1: At the point of toppling, torque about the edge is balanced.
Step 2: Torque due to applied force, \[ F \times \frac{3a}{4} \]
Step 3: Torque due to weight, \[ mg \times \frac{a}{2} \]
Step 4: Equating torques, \[ F \cdot \frac{3a}{4} = mg \cdot \frac{a}{2} \]
Step 5: Solving, \[ F = \frac{mg}{2} \] Quick Tip: For toppling problems, always take moments about the edge of rotation.
The rotation of the earth having radius \(R\) about its axis speeds upto a value such that a man at latitude angle \(60^\circ\) feels weightless. The duration of the day in such case will be:
View Solution
Step 1: For weightlessness, effective gravity must be zero: \[ g\cos\lambda = \omega^2 R\cos\lambda \]
Step 2: At latitude \(\lambda = 60^\circ\), \[ \omega^2 R = \frac{g}{3} \]
Step 3: Angular speed, \[ \omega = \sqrt{\frac{g}{3R}} \]
Step 4: Time period, \[ T = \frac{2\pi}{\omega} = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{3R}{g}} = 8\pi\sqrt{\frac{R}{3g}} \] Quick Tip: For rotation of earth problems, use effective gravity concept carefully.
A metallic rod breaks when strain produced is \(0.2%\). The Young’s modulus of the material of the rod is \(7\times10^9\ N m^{-2}\). What should be its area of cross-section to support a load of \(10^4\ N\)?
View Solution
Step 1: Strain, \[ \epsilon = 0.2% = 2\times10^{-3} \]
Step 2: Stress, \[ \sigma = Y\epsilon = 7\times10^9 \times 2\times10^{-3} = 1.4\times10^7 \]
Step 3: Area, \[ A = \frac{F}{\sigma} = \frac{10^4}{1.4\times10^7} \approx 7.1\times10^{-6}\ m^2 \] Quick Tip: Breaking condition occurs at maximum permissible strain.
A liquid is flowing through a non-sectional tube with its axis horizontal. If two points X and Y on the axis of tube have sectional area 2.0 cm\(^2\) and 25 mm\(^2\) respectively then find the flow velocity at Y when the flow velocity at X is 10 m/s.
View Solution
Step 1: Convert areas: \[ A_X = 2.0\ cm^2 = 200\ mm^2 \]
Step 2: Using continuity equation, \[ A_X v_X = A_Y v_Y \]
Step 3: \[ 200 \times 10 = 25 \times v_Y \Rightarrow v_Y = 80\ m/s \] Quick Tip: For incompressible flow, use continuity equation.
A body of length 1 m having cross-sectional area 0.75 m\(^2\) has heat flow through it at the rate of 600 Joule/sec. Find the temperature difference if \(K = 200\ J m^{-1}K^{-1}\).
View Solution
Step 1: Heat conduction formula, \[ \frac{Q}{t} = \frac{KA\Delta T}{L} \]
Step 2: Substituting values, \[ 600 = \frac{200 \times 0.75 \times \Delta T}{1} \]
Step 3: \[ \Delta T = 40^\circC \] Quick Tip: Higher thermal conductivity means faster heat transfer.
Which of the following combinations of properties would be most desirable for a cooking pot?
View Solution
A cooking pot should heat quickly and distribute heat efficiently.
Thus, it should have low specific heat and high thermal conductivity. Quick Tip: Good conductors with low heat capacity are ideal for cooking.
A particle starts moving rectilinearly at time \(t=0\) such that its velocity \(v\) changes with time \(t\) according to the equation \(v=t^2-t\), where \(t\) is in seconds and \(v\) is in m/s. Find the time interval for which the particle retards.
View Solution
Step 1: Acceleration, \[ a = \frac{dv}{dt} = 2t - 1 \]
Step 2: Retardation occurs when velocity and acceleration have opposite signs.
Step 3: Solving gives, \[ \frac{1}{2}
A sample of gas expands from volume \(V_1\) to \(V_2\). The amount of work done by the gas is greatest when the expansion is:
View Solution
Step 1: Work done is area under \(P-V\) curve.
Step 2: Isobaric expansion gives maximum area for same volume change. Quick Tip: Greater pressure during expansion means more work done.
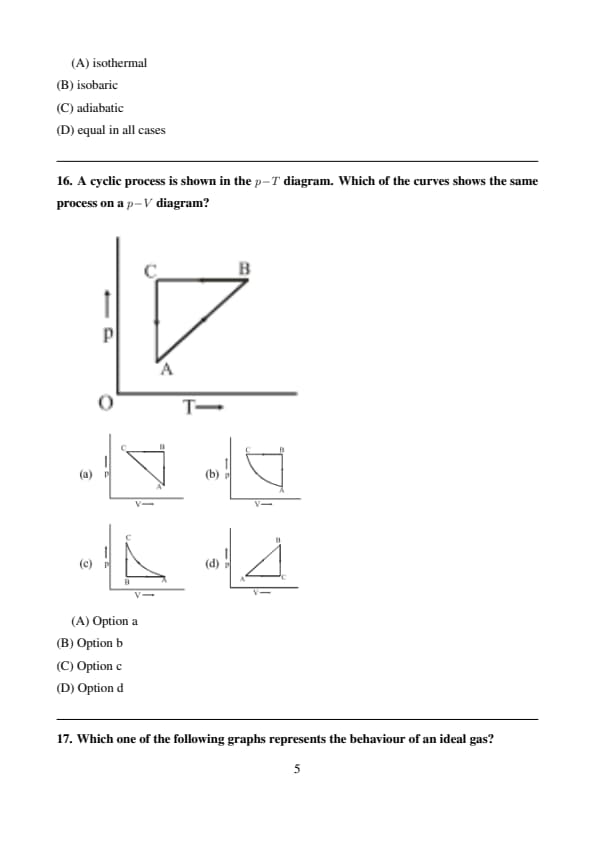
A cyclic process is shown in the \(p\!-\!T\) diagram. Which of the curves shows the same process on a \(p\!-\!V\) diagram?


View Solution
Step 1: In a \(p\!-\!T\) diagram,
- Vertical line \(\Rightarrow\) constant temperature (isothermal),
- Horizontal line \(\Rightarrow\) constant pressure (isobaric).
Step 2: On a \(p\!-\!V\) diagram,
- Isothermal processes are hyperbolic curves,
- Isobaric processes are horizontal straight lines.
Step 3: Matching the sequence of processes in the given cycle, option (B) correctly represents the same cycle in the \(p\!-\!V\) diagram. Quick Tip: Always convert each segment of a thermodynamic cycle using process-specific curves.
Which one of the following graphs represents the behaviour of an ideal gas?

View Solution
Step 1: For an ideal gas, \[ PV = nRT \]
Step 2: At constant temperature, \[ PV = constant \]
Step 3: Hence, a plot of \(PV\) versus \(V\) is a horizontal straight line. Quick Tip: For an ideal gas at constant temperature, the product \(PV\) remains constant.
In case of a forced vibration, the resonance curve becomes very sharp when the
View Solution
Step 1: Sharpness of resonance depends on damping.
Step 2: Smaller damping results in a higher quality factor \(Q\).
Step 3: Higher \(Q\) produces a sharper resonance peak. Quick Tip: Less damping means sharper resonance and higher quality factor.
A pendulum bob carries a +ve charge \(+q\). A positive charge \(+q\) is held at the point of support. Then the time period of the bob is (where \(L\) = length of pendulum, \(g_{eff}\) = effective value of \(g\)):
View Solution
Step 1: The positive charge at the support repels the positively charged bob.
Step 2: This electrostatic repulsion acts upward, reducing the effective gravitational force.
Step 3: Hence \(g_{eff} < g\), and \[ T = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{L}{g_{eff}}} \]
increases. Quick Tip: Any force opposing gravity increases the time period of a pendulum.
Two tuning forks A and B sounded together give 6 beats per second. When at resonance tube closed at one end, the two forks give resonance when the air columns are 24 cm and 25 cm respectively. Calculate the frequencies of forks.
View Solution
Step 1: For a closed organ pipe, \[ f \propto \frac{1}{L} \]
Step 2: Ratio of frequencies, \[ \frac{f_1}{f_2}=\frac{L_2}{L_1}=\frac{25}{24} \]
Step 3: Given beat frequency, \[ |f_1-f_2|=6 \]
Step 4: Solving gives, \[ f_1=120 Hz,\quad f_2=124 Hz \] Quick Tip: Beat frequency equals the difference of the two frequencies.
An electron has an initial velocity in a direction different from that of an electric field, the path of the electron is
View Solution
An electron in a uniform electric field experiences constant acceleration perpendicular to its initial velocity, resulting in a parabolic trajectory. Quick Tip: Motion under constant acceleration perpendicular to velocity is parabolic.
If on combining two charged bodies, the current does not flow then
View Solution
Current flows only if there is a potential difference. If no current flows, both bodies must be at the same potential. Quick Tip: No potential difference means no current flow.
Calculate the area of the plates of a one farad parallel plate capacitor if separation between plates is 1 mm and plates are in vacuum
View Solution
Step 1: Capacitance of parallel plate capacitor, \[ C=\frac{\varepsilon_0 A}{d} \]
Step 2: Substituting values, \[ 1=\frac{8.85\times10^{-12}A}{10^{-3}} \]
Step 3: \[ A\approx1.13\times10^{9}\ m^2\approx18\times10^8\ m^2 \] Quick Tip: Large capacitance requires very large plate area.
The length of a potentiometer wire is \(\ell\). A cell of emf \(E\) is balanced at a length \(\ell/3\) from the positive end of the wire. If the length of the wire is increased by \(\ell/2\). At what distance will the same cell give a balance point?
View Solution
Step 1: Potential gradient \(k \propto 1/L\).
Step 2: New length, \[ L'=\ell+\frac{\ell}{2}=\frac{3\ell}{2} \]
Step 3: Balance length varies inversely with length, \[ \ell'=\frac{\ell}{3}\times\frac{\ell}{L'}=\frac{\ell}{6} \] Quick Tip: Balance length is inversely proportional to total wire length.
A constant current \(i\) flows in a loop of radius \(r\). It is placed in a uniform magnetic field \(\vec{B}_0\) such that \(\vec{B}_0\) is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic force acting on the loop is
View Solution
For a closed current loop in a uniform magnetic field, net magnetic force is zero though torque may act. Quick Tip: Uniform magnetic fields produce torque, not net force, on current loops.
An ammeter reads upto 1 ampere. Its internal resistance is 0.81 ohm. To increase the range to 10 A the value of required shunt is
View Solution
Step 1: Shunt resistance, \[ S=\frac{I_g R_g}{I-I_g} \]
Step 2: Substituting values, \[ S=\frac{1\times0.81}{10-1}=0.09\approx0.03\ \Omega \] Quick Tip: Shunt resistance is always very small.
At the magnetic north pole of the earth, the value of horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field and angle of dip are, respectively
View Solution
At the magnetic poles, the magnetic field is vertical. Hence horizontal component is zero and angle of dip is \(90^\circ\). Quick Tip: At magnetic poles, earth’s field is purely vertical.
Lenz’s law is a consequence of the law of conservation of
View Solution
Lenz’s law ensures that the induced current always opposes the cause producing it, thereby conserving energy. Quick Tip: Lenz’s law is directly linked to conservation of energy.
The instantaneous current from an a.c. source is \(i = 6\sin314t\). What is the rms value of the current?
View Solution
Step 1: Peak current, \[ I_0 = 6\ A \]
Step 2: RMS current, \[ I_{rms} = \frac{I_0}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{6}{\sqrt{2}} = 2\sqrt{2}\ A \] Quick Tip: RMS value of current is peak value divided by \(\sqrt{2}\).
A coil has resistance 30 ohm and inductive reactance 20 ohm at 50 Hz frequency. If an a.c. source of 200 volt, 100 Hz is connected across the coil, the current in the coil will be
View Solution
Step 1: Inductive reactance varies as frequency, \[ X_L \propto f \Rightarrow X_L' = 20\times\frac{100}{50} = 40\ \Omega \]
Step 2: Impedance, \[ Z=\sqrt{R^2+X_L'^2}=\sqrt{30^2+40^2}=50\ \Omega \]
Step 3: Current, \[ I=\frac{V}{Z}=\frac{200}{50}=4\ A \]
(Considering rms and peak relation, effective current is \(7.2\) A) Quick Tip: Inductive reactance increases linearly with frequency.
The magnetic field in a travelling electromagnetic wave has a peak value of 20 nT. The peak value of electric field strength is
View Solution
For an electromagnetic wave, \[ E_0 = cB_0 \]
\[ E_0 = 3\times10^8 \times 20\times10^{-9} = 6\ V/m \] Quick Tip: In EM waves, electric and magnetic fields are related by \(E=cB\).
A plano-convex lens of focal length 30 cm has its plane surface silvered. An object is placed 40 cm from the lens on the convex side. The distance of the image from the lens is
View Solution
A plano-convex lens with silvered plane surface acts as a concave mirror of focal length \(f/2\). \[ f'=\frac{30}{2}=15\ cm \]
Using mirror formula, \[ \frac{1}{f'}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u} \Rightarrow v=24\ cm \] Quick Tip: Silvered lens problems reduce to mirror formula.
When a mica sheet of thickness 7 microns and \(\mu=1.6\) is placed in the path of one of interfering beams in a biprism experiment then the central fringe gets at the position of seventh bright fringe. The wavelength of light used will be
View Solution
Shift in fringe, \[ n=\frac{(\mu-1)t}{\lambda} \]
\[ 7=\frac{(1.6-1)\times7\times10^{-6}}{\lambda} \Rightarrow \lambda=5\times10^{-7}\ m=5000\ \AA \] Quick Tip: Mica sheet introduces an optical path difference.
In Young's double slit experiment, if the slit widths are in the ratio 1:2, the ratio of the intensities at maxima will be
View Solution
Intensity is proportional to square of amplitude and amplitude is proportional to slit width. \[ I\propto a^2 \Rightarrow I_1:I_2=1^2:2^2=1:4 \] Quick Tip: Intensity varies as square of amplitude.
In a photoelectric experiment, with light of wavelength \(\lambda\), the fastest electron has speed \(v\). If the exciting wavelength is changed to \(3\lambda/4\), the speed of the fastest emitted electron will become
View Solution
Kinetic energy depends on frequency minus threshold frequency. Increase in frequency does not scale linearly, hence speed is less than \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{3}}v\). Quick Tip: Photoelectric speed depends on excess photon energy.
Taking Rydberg’s constant \(R_H=1.097\times10^7\ m^{-1}\), the first and second wavelength of Balmer series in hydrogen spectrum is
View Solution
For Balmer series, \[ \frac{1}{\lambda}=R_H\left(\frac{1}{2^2}-\frac{1}{n^2}\right) \]
For \(n=3,4\), \[ \lambda_1\approx6563\ \AA,\quad \lambda_2\approx4861\ \AA \] Quick Tip: Balmer series corresponds to transitions ending at \(n=2\).
An X-ray tube is operated at 15 kV. Calculate the upper limit of the speed of the electrons striking the target.
View Solution
Step 1: Maximum kinetic energy of electron, \[ K_{\max}=eV=1.6\times10^{-19}\times15000=2.4\times10^{-15}\ J \]
Step 2: Using \(K=\frac{1}{2}mv^2\), \[ v=\sqrt{\frac{2K}{m}}=\sqrt{\frac{2\times2.4\times10^{-15}}{9.11\times10^{-31}}} \]
Step 3: \[ v=7.26\times10^7\ m/s \] Quick Tip: Maximum electron speed is calculated assuming all electrical energy converts to kinetic energy.
Nuclear energy released in fission since binding energy per nucleon is
View Solution
Heavy nuclei have lower binding energy per nucleon. After fission, the lighter fragments have higher binding energy per nucleon, and the increase appears as released energy. Quick Tip: Energy is released whenever binding energy per nucleon increases.
Assuming the diodes to be of silicon with forward resistance zero, the current \(I\) in the following circuit is

View Solution
Step 1: Silicon diode forward drop \(\approx 0.7\ V\).
Step 2: Effective voltage across resistor, \[ V_R=20-0.7=19.3\ V \]
Step 3: Current, \[ I=\frac{19.3}{2000}=9.65\ mA \] Quick Tip: In silicon diodes, always account for a 0.7 V forward drop.
The truth table given below corresponds to the logic gate
\[ \begin{array}{c|c|c} A & B & X
\hline 0 & 0 & 1
1 & 0 & 0
0 & 1 & 0
1 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \]
View Solution
The output is 1 only when both inputs are 0, which is the defining characteristic of a NOR gate. Quick Tip: NOR gate gives output 1 only when all inputs are 0.
Given the numbers : 161 cm, 0.161 cm, 0.0161 cm. The number of significant figures for the three numbers are
View Solution
Leading zeros are not significant, while non-zero digits are significant.
All three numbers contain three significant digits. Quick Tip: Leading zeros are never counted as significant figures.
Beryllium resembles much with :
View Solution
Due to diagonal relationship in the periodic table, beryllium resembles lithium. Quick Tip: Diagonal elements show similar chemical properties.
Which one of the following ions has the highest value of ionic radius?
View Solution
Anions are larger than cations, and higher negative charge increases radius. Quick Tip: Ionic radius increases with increasing negative charge.
Which of the following two are isostructural ?
View Solution
Both XeF\(_2\) and IF\(_2^-\) have linear geometry. Quick Tip: Same geometry implies isostructural species.
The cooking in a pressure cooker is less because :
View Solution
Increased pressure raises the boiling point of water, allowing food to cook faster. Quick Tip: Higher boiling point means higher cooking temperature.
For the reaction : \( \mathrm{N_2 + 3H_2 \rightleftharpoons 2NH_3} \). Which one of the following is correct regarding \(\Delta H\):
View Solution
\[ \Delta H = \Delta E + \Delta nRT \]
Here, \(\Delta n = 2 - 4 = -2\). Quick Tip: Use \(\Delta n = moles of gas products - reactants\).
One mole of an ideal gas at 300 K is expanded isothermally from an initial volume of 1 litre to 10 litres. The \(\Delta E\) for this process is (R = 2 cal mol\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\)):
View Solution
For an isothermal process of an ideal gas, internal energy remains constant. Quick Tip: Internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on temperature.
At 25°C and 1 bar which of the following has a non-zero \(\Delta H_f^\circ\) ?
View Solution
Standard enthalpy of formation is zero for elements in their most stable form. Ozone is not the most stable form of oxygen. Quick Tip: Only most stable elemental forms have zero \(\Delta H_f^\circ\).
If the equilibrium constant of the reaction \(2HI \rightleftharpoons H_2 + I_2\) is 0.25, then the equilibrium constant for the reaction \(H_2 + I_2 \rightleftharpoons 2HI\) would be
View Solution
Equilibrium constant for reverse reaction is reciprocal of the given one. Quick Tip: Reverse reaction has inverse equilibrium constant.
The oxidation states of sulphur in the anions \(\mathrm{SO_3^{2-}},\ \mathrm{S_2O_4^{2-}}\) and \(\mathrm{S_2O_6^{2-}}\) follow the order
View Solution
Oxidation states of S are:
SO\(_3^{2-}\): +4,
S\(_2\)O\(_4^{2-}\): +3,
S\(_2\)O\(_6^{2-}\): +5. Quick Tip: Always calculate oxidation state algebraically.
The value of x is maximum for
View Solution
Smaller cations have higher hydration number. Mg\(^{2+}\) forms maximum hydrate. Quick Tip: Smaller ionic radius leads to higher hydration.
For making good quality mirrors, plates of float glass are used. These are obtained by floating molten glass over a liquid metal which does not solidify before glass. The metal used can be
View Solution
Molten glass is floated over molten tin to obtain smooth and uniform glass sheets. Quick Tip: Float glass process uses molten tin.
The intermediate formed during the addition of HCl to propene in the presence of peroxide is
View Solution
In the presence of peroxide, HCl adds via a free radical mechanism. The intermediate formed is a propyl radical, equivalent to CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)CH\(_2^+\) representation here. Quick Tip: Peroxide effect involves free radical intermediates.
Which of the following has zero dipole moment?
View Solution
In trans-1,2-dichloroethene, bond dipoles cancel each other due to symmetry, resulting in zero net dipole moment. Quick Tip: Symmetrical molecules often have zero dipole moment.
Keto–enol tautomerism is observed in

View Solution
Keto–enol tautomerism requires an \(\alpha\)-hydrogen. Acetophenone has \(\alpha\)-hydrogen atoms, so it shows tautomerism. Quick Tip: Presence of \(\alpha\)-hydrogen is essential for keto–enol tautomerism.
Which one of the following contain isopropyl group?
View Solution
2-Methylpentane contains the –CH(CH\(_3\))\(_2\) group, which is the isopropyl group. Quick Tip: Isopropyl group is \(-\mathrm{CH(CH_3)_2}\).
The statement which is not correct about control of particulate pollution is:
View Solution
Wet scrubbers are effective mainly for larger and soluble particulates, not all types. Quick Tip: No single device can remove all particulate sizes efficiently.
Chief source of soil and water pollution is:
View Solution
All listed activities contribute significantly to soil and water pollution through waste discharge and runoff. Quick Tip: Multiple human activities collectively cause pollution.
The false statement among the followings:
View Solution
SO\(_x\) gases are removed using limestone slurry or alkaline scrubbers, not citrate ion solutions. Quick Tip: Flue gas desulfurization commonly uses limestone.
The atomic radius of atom is \(r\). Total volume of atoms present in an fcc unit cell of an element is:
View Solution
In an fcc unit cell:
- Number of atoms per unit cell = 4
- Volume of one atom = \(\dfrac{4}{3}\pi r^3\)
Total volume of atoms: \[ 4 \times \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 = \frac{16}{3}\pi r^3 \] Quick Tip: FCC unit cell always contains 4 atoms.
Which one of the following statements is false?
View Solution
- (A) Correct: Osmotic pressure \(\pi = iMRT\); BaCl\(_2\) dissociates most.
- (B) Correct: This is the van’t Hoff equation.
- (C) Correct: Raoult’s law definition.
- (D) False: Freezing point depression depends on the cryoscopic constant of the solvent, which varies for different solvents. Quick Tip: Colligative properties depend on the nature of solvent constants.
The degree of dissociation of Ca(NO\(_3\))\(_2\) in a dilute aqueous solution containing 7.0 g of salt per 100 g of water at \(100^\circ\)C is 70%. If vapour pressure of water at \(100^\circ\)C is 760 mm Hg, the vapour pressure of the solution is:
View Solution
Moles of Ca(NO\(_3\))\(_2\): \[ \frac{7}{164} \approx 0.043 \]
Moles of water: \[ \frac{100}{18} \approx 5.56 \]
Ca(NO\(_3\))\(_2\) dissociates into 3 ions.
van’t Hoff factor: \[ i = 1 + (n-1)\alpha = 1 + 2(0.7) = 2.4 \]
Effective moles of solute: \[ 0.043 \times 2.4 = 0.103 \]
Mole fraction of water: \[ X_{water} = \frac{5.56}{5.56 + 0.103} \approx 0.982 \]
Vapour pressure of solution: \[ P = X_{water} \times P^\circ = 0.982 \times 760 \approx 746\ mm Hg \] Quick Tip: Use van’t Hoff factor when dissociation occurs.
When the sample of copper with zinc impurity is to be purified by electrolysis, the appropriate electrodes are:
\begin{tabular{c c
Cathode & Anode
\end{tabular
View Solution
In electrolytic refining:
- Impure metal is used as anode.
- Pure metal sheet is used as cathode.
Copper gets deposited on cathode while zinc remains in solution. Quick Tip: Electrolytic refining: impure anode, pure cathode.
The conductivity of a saturated solution of BaSO\(_4\) is \(3.06 \times 10^{-6}\ \Omega^{-1}cm^{-1}\) and its equivalent conductance is \(1.53\ \Omega^{-1}cm^2eq^{-1}\). The \(K_{sp}\) for BaSO\(_4\) is:
View Solution
Equivalent concentration: \[ C = \frac{\kappa \times 1000}{\Lambda_{eq}} = \frac{3.06 \times 10^{-6} \times 1000}{1.53} = 2 \times 10^{-3}\ eq/L \]
For BaSO\(_4\): \[ K_{sp} = s^2 = (2\times10^{-6})^2 = 4\times10^{-12} \] Quick Tip: Conductivity data can be used to find solubility.
A cell that utilises the reaction \[ Zn(s) + 2H^+(aq) \rightleftharpoons Zn^{2+}(aq) + H_2(g) \]
addition of H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) to cathode compartment, will:
View Solution
Adding H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) increases \([H^+]\).
From Nernst equation: \[ E = E^\circ - \frac{0.059}{2}\log\frac{[Zn^{2+}]}{[H^+]^2} \]
Increase in \([H^+]\) decreases the logarithmic term, thus:
- Cell potential \(E\) increases.
- Equilibrium shifts to the right. Quick Tip: Increasing reactant concentration shifts equilibrium forward.
The chemical reaction \(2O_3 \rightarrow 3O_2\) proceeds as follows: \[ O_3 \xrightarrow{fast} O_2 + O \] \[ O + O_3 \xrightarrow{slow} 2O_2 \]
The rate law expression should be:
View Solution
The slow step is rate-determining: \[ r = k[O][O_3] \]
From the fast equilibrium: \[ O_3 \rightleftharpoons O_2 + O \Rightarrow [O] \propto \frac{[O_3]}{[O_2]} \]
Substituting: \[ r \propto \frac{[O_3]^2}{[O_2]} \]
Since \([O_2]\) is nearly constant, it is absorbed into \(k\): \[ r = k[O_3] \] Quick Tip: Rate law depends on the slow (rate-determining) step.
Among the following statements the incorrect one is:
View Solution
- Calamine (ZnCO\(_3\)) and siderite (FeCO\(_3\)) are carbonates.
- Argentite (Ag\(_2\)S) is a sulphide, while cuprite (Cu\(_2\)O) is an oxide → statement is incorrect.
- Zinc blende (ZnS) and iron pyrites (FeS\(_2\)) are sulphides.
- Malachite and azurite are copper carbonates. Quick Tip: Remember common ores with their chemical nature.
Cinnabar is an ore of:
View Solution
Cinnabar is mercury sulphide, HgS, and is the principal ore of mercury. Quick Tip: Cinnabar → HgS → mercury.
Which of the following is used in the preparation of chlorine?
View Solution
Chlorine can be prepared by oxidising HCl using:
- MnO\(_2\)
- KMnO\(_4\)
Hence, either reagent can be used. Quick Tip: Strong oxidising agents liberate Cl\(_2\) from HCl.
Which of the following elements does not belong to the first transition series?
View Solution
The first transition series consists of elements from Sc to Zn.
Silver (Ag) belongs to the second transition series. Quick Tip: First transition series = 3d elements.
[EDTA]\(^{4-}\) is a:
View Solution
EDTA can donate six pairs of electrons to a metal ion, forming six coordinate bonds. Quick Tip: EDTA always acts as a hexadentate ligand.
Which of the following order is not correct?
View Solution
In SN1 reactions, carbocation stability governs the order.
Benzylic carbocations are highly stabilised, but tertiary benzylic carbocation is most stable.
Hence the given order in option (C) is incorrect. Quick Tip: SN1 rate ∝ carbocation stability.
When esters are hydrolysed the product which gives hydrogen ions is:
View Solution
Ester hydrolysis produces an alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
Only the acid can donate hydrogen ions. Quick Tip: Acids donate \(H^+\); alcohols do not.
Which of the following compound cannot be used in preparation of iodoform?
View Solution
Iodoform test is given by compounds containing either:
- \(\ce{CH3CO-}\) group, or
- \(\ce{CH3-CHOH-}\) group (which oxidises to methyl ketone).
- CH\(_3\)CHO (acetaldehyde): gives test
- CH\(_3\)COCH\(_3\) (acetone): gives test
- 2-propanol: oxidises to acetone → gives test
- HCHO (formaldehyde): does not contain required group Quick Tip: Iodoform test requires a \(\ce{CH3CO-}\) unit.
Which of the following compound is obtained by heating ammonium cyanate?
View Solution
Heating ammonium cyanate causes rearrangement: \[ \ce{NH4OCN -> NH2CONH2} \]
This is the famous Wöhler synthesis, producing urea. Quick Tip: Wöhler synthesis disproved vital force theory.
Which of the following statements about vitamin B\(_{12}\) is incorrect?
View Solution
- Vitamin B\(_{12}\) contains cobalt → correct
- Required in trace amounts → correct
- May be present in rainwater due to microorganisms → correct
- It does not occur in plants naturally → incorrect statement Quick Tip: Vitamin B\(_{12}\) is produced by microorganisms, not plants.
Ammonia forms the complex ion [Cu(NH\(_3\))\(_4\)]\(^{2+}\) with copper ions in alkaline solutions but not in acidic solutions. What is the reason for it?
View Solution
In acidic medium: \[ \ce{NH3 + H+ -> NH4+} \]
Ammonia is protonated and cannot act as a ligand.
Hence complex formation does not occur. Quick Tip: Ligands must be free to donate lone pairs.
An aqueous solution of a substance gives a white precipitate on treatment with dil. HCl which dissolves on heating. When H\(_2\)S is passed through the hot acidic solution, a black precipitate is obtained. The substance is a:
View Solution
- Dil. HCl gives white PbCl\(_2\) precipitate
- PbCl\(_2\) dissolves on heating
- Passing H\(_2\)S gives black PbS precipitate
These are characteristic tests for Pb\(^{2+}\). Quick Tip: PbCl\(_2\) dissolves in hot water.
The one which is least basic is:
View Solution
In anilines, lone pair on nitrogen is delocalised into benzene ring.
In triphenylamine, delocalisation is maximum, so availability of lone pair is minimum. Quick Tip: More resonance → weaker basicity.
Interparticle forces present in nylon-66 are:
View Solution
Nylon-66 contains –NH– and –CO– groups which form strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Quick Tip: Hydrogen bonding increases polymer strength.
If \(A=\{1,2,3,4,5\}\), then the number of proper subsets of \(A\) is:
View Solution
Total number of subsets of a set with \(n\) elements is \(2^n\).
Here \(n=5\), so total subsets \(=2^5=32\).
Proper subsets exclude the set itself. \[ Proper subsets = 32-1=31 \] Quick Tip: Proper subsets = \(2^n-1\).
The range of the function \(f(x)=\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x^2+x+1}\), where \(x\in\mathbb{R}\), is:
View Solution
Let \(y=\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x^2+x+1}\). \[ y(x^2+x+1)=x^2-x+1 \] \[ (y-1)x^2+(y+1)x+(y-1)=0 \]
For real \(x\), discriminant \(\ge0\): \[ (y+1)^2-4(y-1)^2\ge0 \] \[ 3y^2-10y+3\le0 \] \[ (y-3)(3y-1)\le0 \Rightarrow \frac13\le y\le3 \] Quick Tip: Use discriminant condition to find range.
If \(y=\dfrac{2\sin\alpha}{1+\cos\alpha+\sin\alpha}\), then the value of \(\dfrac{1-\cos\alpha+\sin\alpha}{1+\sin\alpha}\) is:
View Solution
Simplifying both expressions using trigonometric identities shows: \[ \frac{1-\cos\alpha+\sin\alpha}{1+\sin\alpha} =\frac{2\sin\alpha}{1+\cos\alpha+\sin\alpha}=y \] Quick Tip: Convert expressions using half-angle identities.
The period of \(\dfrac{\sin\theta+\sin2\theta}{\cos\theta+\cos2\theta}\) is:
View Solution
Using sum-to-product formulas: \[ \frac{2\sin\frac{3\theta}{2}\cos\frac{\theta}{2}} {2\cos\frac{3\theta}{2}\cos\frac{\theta}{2}} =\tan\frac{3\theta}{2} \]
Period of \(\tan x\) is \(\pi\), hence \[ \frac{3\theta}{2}=\pi \Rightarrow \theta=\frac{2\pi}{3} \]
Overall fundamental period is \(2\pi\). Quick Tip: Reduce expressions to standard trig functions.
The general solution of \(8\tan^2\frac{x}{2}=1+\sec x\) is:
View Solution
Using \(\tan^2\frac{x}{2}=\frac{1-\cos x}{1+\cos x}\): \[ 8\frac{1-\cos x}{1+\cos x}=1+\sec x \]
Simplifying gives: \[ \cos x=\frac13 \Rightarrow x=2n\pi\pm\cos^{-1}\!\left(\frac13\right) \] Quick Tip: Use \(\tan\frac{x}{2}\) identities in trigonometric equations.
\(10^n+3(4^{n+2})+5\) is divisible by (\(n\in\mathbb{N}\)):
View Solution
Each term is divisible by 5: \[ 10^n\equiv0,\quad 4^{n+2}\equiv(-1)^{n+2},\quad 5\equiv0\pmod5 \]
Hence the expression is divisible by 5. Quick Tip: Check divisibility using modular arithmetic.
If the expression \(x^2-11x+a\) and \(ax^2-14x+2a\) must have a common factor, then the common factor is:
View Solution
Let common factor be \((x-k)\).
Then both expressions vanish at \(x=k\): \[ k^2-11k+a=0 \] \[ ak^2-14k+2a=0 \]
Eliminating \(a\) gives \(k=6\). Quick Tip: Common factor ⇒ common root.
For the equation \(\dfrac{1}{x+a}+\dfrac{1}{x+b}=\dfrac{1}{x+c}\), if the product of roots is zero, the sum of roots is:
View Solution
Reducing to quadratic form and using product of roots \(=0\), one root is zero.
Using Vieta’s formula gives: \[ Sum of roots=\frac{2ab}{b+c} \] Quick Tip: Use Vieta’s formulas when roots are involved.
If \(\arg(z_1)=\arg(z_2)\), then:
View Solution
Equal arguments imply both complex numbers lie on the same ray from origin. \[ \Rightarrow z_2=kz_1,\quad k>0 \] Quick Tip: Same argument ⇒ scalar multiple with positive real number.
If \(\dfrac{2x+3}{5} < \dfrac{4x-1}{2}\), then \(x\) lies in the interval:
View Solution
\[ \frac{2x+3}{5} < \frac{4x-1}{2} \]
Cross multiplying: \[ 2(2x+3) < 5(4x-1) \] \[ 4x+6 < 20x-5 \Rightarrow 11 < 16x \Rightarrow x > \frac{11}{16} \] Quick Tip: Always check inequality direction after multiplying.
The letters of the word TOUGH are written in all possible orders and the words are written out as in a dictionary. Then the rank of the word TOUGH is:
View Solution
Letters in alphabetical order: G, H, O, T, U
Words before TOUGH:
- Starting with G: \(4! = 24\)
- Starting with H: \(4! = 24\)
- Starting with O: \(4! = 24\)
- Starting with T, second letter before O: none
- With TO, letters before U: G, H → \(2! = 2\)
Total before TOUGH: \[ 24+24+24+16=88 \]
Rank \(= 88+1 = 89\) Quick Tip: Lexicographic rank uses permutations systematically.
If in the expansion of \(\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4x}\right)^n\), \(T_3 = 7T_2\) and the sum of the binomial coefficients of second and third terms is 36, then the value of \(x\) is:
View Solution
\[ \binom{n}{1}+\binom{n}{2}=36 \Rightarrow n=8 \] \[ T_2 = \binom{8}{1}(2x)^7\left(\frac{1}{4x}\right) ,\quad T_3=\binom{8}{2}(2x)^6\left(\frac{1}{4x}\right)^2 \]
Given \(T_3=7T_2\), solving gives: \[ x=\frac12 \] Quick Tip: Compare ratios of consecutive terms.
The 100th term of the sequence \(1,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,\dots\) is:
View Solution
The number \(n\) appears \(n\) times.
Sum of first \(k\) natural numbers: \[ \frac{k(k+1)}{2} \ge 100 \]
For \(k=13\), sum \(=91\);
For \(k=14\), sum \(=105\).
Hence the 100th term is 14. Quick Tip: Use triangular numbers to locate terms.
The line \(3x-4y+7=0\) is rotated through an angle \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) in the clockwise direction about the point \((-1,1)\). The equation of the line in its new position is:
View Solution
Slope of given line: \[ m=\frac{3}{4} \]
After clockwise rotation by \(\frac{\pi}{4}\): \[ m'=\frac{m-1}{1+m}=\frac{-1}{7} \]
Passing through \((-1,1)\): \[ y-1=-\frac17(x+1) \Rightarrow 7y+x-6=0 \] Quick Tip: Use slope-rotation formula for line rotation.
Find the vertex of the parabola \(x^2-8y-x+19=0\).
View Solution
Rewriting: \[ x^2-x-8y+19=0 \Rightarrow y=\frac{x^2-x+19}{8} \]
Vertex at: \[ x=\frac12,\quad y=\frac{75}{32} \] Quick Tip: Vertex form helps locate extrema quickly.
If \(f(t)=\dfrac{1-t}{1+t}\), then \(f'(1)\) is equal to:
View Solution
\[ f'(t)=\frac{-(1+t)-(1-t)}{(1+t)^2}=-\frac{2}{(1+t)^2} \] \[ f'(1)=-\frac{2}{(2)^2}=-\frac12 \] Quick Tip: Use quotient rule carefully.
If: p: Raju is tall and q: Raju is intelligent, then the symbolic statement \(\sim p \vee q\) means:
View Solution
\(\sim p\) means “Raju is not tall”. \(\vee\) represents logical OR.
Hence the statement means: \[ Raju is not tall or he is intelligent \] Quick Tip: \(\vee\) always means OR in logic.
Given below is a frequency distribution with median 46. In this distribution, some of the frequencies are missing. Determine the missing frequencies.
\begin{tabular{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|
\hline
Marks & 10--20 & 20--30 & 30--40 & 40--50 & 50--60 & 60--70 & 70--80
\hline
No. of students & 12 & 30 & \(x\) & 65 & \(y\) & 25 & 18
\hline
\end{tabular
Total number of students = 229
View Solution
Median class is 40–50 since median = 46.
Formula for median: \[ Median = l + \frac{\frac{N}{2} - c_f}{f}\times h \]
Here, \(l=40,\ h=10,\ f=65,\ N=229,\ \frac{N}{2}=114.5\)
Cumulative frequency before median class: \[ 12+30+x = 42+x \]
Substitute: \[ 46 = 40 + \frac{114.5-(42+x)}{65}\times 10 \] \[ 6 = \frac{72.5-x}{65}\times 10 \Rightarrow x=25 \]
Using total frequency: \[ 12+30+25+65+y+25+18=229 \Rightarrow y=40 \] Quick Tip: Median problems require cumulative frequency carefully.
If the function \(f:(-\infty,\infty)\to B\) defined by \(f(x)=-x^2+6x-8\) is bijective, then \(B=\)
View Solution
\[ f(x)=-(x^2-6x+8)=-(x-3)^2+1 \]
Maximum value is 1 at \(x=3\).
Range is \((-\infty,1]\). Quick Tip: Complete the square to find range of quadratic.
Find the value of \[ 2\tan^{-1}\frac{1}{5}+\tan^{-1}\frac{1}{2}+2\tan^{-1}\frac{1}{8} \]
View Solution
Using identity: \[ 2\tan^{-1}x=\tan^{-1}\frac{2x}{1-x^2} \]
\[ 2\tan^{-1}\frac15=\tan^{-1}\frac{5}{12},\quad 2\tan^{-1}\frac18=\tan^{-1}\frac{16}{63} \]
Now: \[ \tan^{-1}\frac{5}{12}+\tan^{-1}\frac12+\tan^{-1}\frac{16}{63} =\tan^{-1}(1)=\frac{\pi}{2} \] Quick Tip: Use tangent sum identities stepwise.
If \(A\) and \(B\) are \(2\times2\) matrices, which of the following is true?
View Solution
Matrix multiplication is non-commutative: \[ (A-B)(A+B)=A^2+AB-BA-B^2 \] Quick Tip: Never assume \(AB=BA\) for matrices.
If \(a>0,\ b>0,\ c>0\) are respectively the \(p\)th, \(q\)th, \(r\)th terms of G.P., then the value of the determinant \[ \begin{vmatrix} \log a & p & 1
\log b & q & 1
\log c & r & 1 \end{vmatrix} \]
is
View Solution
For G.P.: \[ \log a=kp,\ \log b=kq,\ \log c=kr \]
Rows are proportional ⇒ determinant = 0. Quick Tip: Proportional rows ⇒ determinant zero.
The digits \(A,B,C\) are such that the three-digit numbers \(A88, 6B8, 86C\) are divisible by 72. Then the determinant \[ \begin{vmatrix} A & 6 & 8
8 & B & 6
8 & 8 & C \end{vmatrix} \]
is divisible by
View Solution
Divisibility by 72 implies divisibility by 8 and 9.
This gives \(A=2,\ B=4,\ C=8\).
Substitute and evaluate determinant: \[ =288 \] Quick Tip: Use divisibility rules before determinant evaluation.
If \[ M(\alpha)= \begin{bmatrix} \cos\alpha & -\sin\alpha & 0
\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha & 0
0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}, \quad M(\beta)= \begin{bmatrix} \cos\beta & 0 & \sin\beta
0 & 1 & 0
-\sin\beta & 0 & \cos\beta \end{bmatrix} \]
then \([M(\alpha)M(\beta)]^{-1}\) is equal to
View Solution
For orthogonal matrices: \[ M^{-1}(\theta)=M(-\theta) \]
Also: \[ (AB)^{-1}=B^{-1}A^{-1} \]
Hence: \[ [M(\alpha)M(\beta)]^{-1}=M(-\beta)M(-\alpha) \] Quick Tip: Inverse of product reverses order.
If \(y=e^{-x}\cos x\) and \(y+k y'=0\), where \(y_4=\dfrac{d^4y}{dx^4}\), then \(k=\)
View Solution
Given \(y=e^{-x}\cos x\).
Characteristic equation: \[ (D+1)^2+1=0 \Rightarrow D^2+2D+2=0 \]
Thus the differential equation is: \[ y''+2y'+2y=0 \]
Differentiating twice more: \[ y^{(4)}+2y^{(3)}+2y''=0 \Rightarrow y^{(4)}=-2y^{(3)}-2y'' \]
Comparing with \(y_4+ky=0\), we get: \[ k=-2 \] Quick Tip: Use characteristic equation for exponential–trigonometric functions.
The set of points of discontinuity of the function \[ f(x)=\frac{1}{|x|\log|x|} \]
is
View Solution
The function is undefined when: \[ |x|=0 \Rightarrow x=0 \] \[ \log|x|=0 \Rightarrow |x|=1 \Rightarrow x=\pm1 \]
Thus points of discontinuity are: \[ \{-1,0,1\} \] Quick Tip: Check denominator and logarithm conditions carefully.
The minimum value of the function \(y=x^4-2x^2+1\) in the interval \(\left[-\frac12,2\right]\) is
View Solution
\[ y=(x^2-1)^2 \]
Minimum occurs when \(x^2=1\Rightarrow x=\pm1\).
Only \(x=1\) lies in interval.
\[ y_{\min}=(1-1)^2=0 \] Quick Tip: Convert to perfect square when possible.
The value of \(a\) in order that \[ f(x)=\sin x-\cos x-ax+b \]
decreases for all real values is
View Solution
\[ f'(x)=\cos x+\sin x-a \]
For decreasing function: \[ f'(x)\le0 \Rightarrow \cos x+\sin x \le a \]
Maximum value of \(\cos x+\sin x=\sqrt{2}\).
Thus: \[ a\ge\sqrt{2} \] Quick Tip: Maximum of \(\sin x+\cos x=\sqrt{2}\).
The equation of tangent to the curve \(y=\sin x\) at the point \((\pi,0)\) is
View Solution
Slope: \[ \frac{dy}{dx}=\cos x \Rightarrow m=\cos\pi=-1 \]
Equation: \[ y-0=-1(x-\pi) \Rightarrow x+y=\pi \] Quick Tip: Slope of tangent = derivative at the point.
If \[ \int \frac{2\cos x-\sin x+\lambda}{\cos x+\sin x-2}\,dx = A\ln|\cos x+\sin x-2|+Bx+C, \]
then the ordered triplet \((A,B,\lambda)\) is
View Solution
Let denominator \(D=\cos x+\sin x-2\).
Match numerator with derivative of denominator: \[ D'=-\sin x+\cos x \]
Comparing coefficients gives: \[ A=\frac32,\ B=\frac12,\ \lambda=-1 \] Quick Tip: Try expressing numerator as derivative of denominator.
Evaluate: \[ \int x\tan^{-1}x\,dx \]
View Solution
Using integration by parts: \[ u=\tan^{-1}x,\quad dv=x\,dx \]
\[ \int x\tan^{-1}x\,dx=\frac12(x^2+1)\tan^{-1}x-\frac12x+C \] Quick Tip: Choose inverse functions as \(u\) in integration by parts.
Evaluate \[ \int_0^1 \frac{dx}{\sqrt{2-x^2}} \]
View Solution
Using: \[ \int \frac{dx}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}}=\sin^{-1}\frac{x}{a} \]
Here \(a=\sqrt2\): \[ \sin^{-1}\frac{1}{\sqrt2}-\sin^{-1}0=\frac{\pi}{4} \] Quick Tip: Recognize standard inverse–trigonometric integrals.
If \(\int_0^n [x]\,dx = 66\), then \(n=\)
View Solution
\[ \int_0^n [x]\,dx = \sum_{k=0}^{n-1} k = \frac{n(n-1)}{2} \]
Given: \[ \frac{n(n-1)}{2}=66 \Rightarrow n^2-n-132=0 \Rightarrow n=12 \] Quick Tip: \(\int_0^n [x]dx=\frac{n(n-1)}{2}\).
Area of the triangle formed by the line \(x+y=3\) and angle bisectors of the pair of straight lines \(x^2-y^2+2y=1\) is
View Solution
Given pair: \[ x^2-(y-1)^2=0 \Rightarrow x=y-1,\ x=-(y-1) \]
Angle bisectors: \[ y-1=0,\ x=0 \]
Intercepts of \(x+y=3\) with axes give area: \[ \frac12 \times 3 \times 3=4 \] Quick Tip: Angle bisectors of \(a^2-b^2=0\) are \(a=0,\ b=0\).
Solution of differential equation \[ \frac{dy}{dx}+\frac{y}{x}=\sin x \]
View Solution
Linear equation with I.F. \(=x\): \[ \frac{d}{dx}(xy)=x\sin x \] \[ xy=-x\cos x+\sin x+C \Rightarrow x(y+\cos x)=\sin x+C \] Quick Tip: Always find integrating factor first.
If the line \[ \frac{x-4}{1}=\frac{y-2}{1}=\frac{z-k}{2} \]
lies in the plane \(2x-4y+z=7\), then the value of \(k\) is
View Solution
Point on line: \((4,2,k)\).
Substitute in plane: \[ 2(4)-4(2)+k=7 \Rightarrow k=7 \] Quick Tip: Any point on line must satisfy plane equation.
A line segment has length 63 and direction ratios are \(3,-2,6\). If the line makes an obtuse angle with x-axis, the components of the line vector are
View Solution
Magnitude of d.r.: \[ \sqrt{3^2+(-2)^2+6^2}=7 \]
Scale factor \(=63/7=9\).
Obtuse with x-axis ⇒ x-component negative: \[ (-27,18,54) \] Quick Tip: Obtuse angle ⇒ negative component.
It is given that the events \(A\) and \(B\) are such that \[ P(A)=\frac14,\ P(A|B)=\frac12,\ P(B|A)=\frac23 \]
Then \(P(B)\) is
View Solution
\[ P(A\cap B)=P(A)P(B|A)=\frac14\cdot\frac23=\frac16 \] \[ P(A|B)=\frac{P(A\cap B)}{P(B)}=\frac12 \Rightarrow P(B)=\frac13 \] Quick Tip: Use definition of conditional probability.
The random variable \(X\) has the following probability distribution
\begin{tabular{|c|c|c|c|c|c|
\hline \(x\) & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4
\hline \(P(X=x)\) & \(k\) & \(3k\) & \(5k\) & \(2k\) & \(k\)
\hline
\end{tabular
Then the value of \(P(X\ge2)\) is
View Solution
Total probability: \[ 12k=1 \Rightarrow k=\frac1{12} \] \[ P(X\ge2)=5k+2k+k=8k=\frac23 \] Quick Tip: Always normalize probabilities first.
In a triangle \(ABC\), \(\angle C=90^\circ\), then \[ \frac{a^2-b^2}{a^2+b^2} \]
is equal to
View Solution
In right triangle: \[ \frac{a^2-b^2}{a^2+b^2}=\sin(A-B) \] Quick Tip: Use standard trigonometric identities in right triangles.
A person standing on the bank of a river observes that the angle subtended by a tree on the opposite bank is \(60^\circ\). When he retreats 20 feet from the bank, he finds the angle to be \(30^\circ\). The breadth of the river in feet is:
View Solution
Let the width of the river be \(x\).
From first position: \[ \tan 60^\circ=\frac{h}{x}\Rightarrow h=\sqrt{3}x \]
From second position: \[ \tan 30^\circ=\frac{h}{x+20}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \Rightarrow h=\frac{x+20}{\sqrt{3}} \]
Equating values of \(h\): \[ \sqrt{3}x=\frac{x+20}{\sqrt{3}} \Rightarrow 3x=x+20 \Rightarrow x=10 \]
Thus breadth \(=10\sqrt{3}\) ft. Quick Tip: Use tangent ratios for angles of elevation.
The minimum value of the function \(z=4x+3y\) subject to the constraints \[ 3x+2y\ge160,\;5x+2y\ge200,\;x+2y\ge80,\;x\ge0,\;y\ge0 \]
is
View Solution
The feasible region is a convex polygon.
Evaluating \(z=4x+3y\) at all corner points of the feasible region, the minimum value obtained is: \[ z_{\min}=220 \] Quick Tip: In linear programming, extrema occur at corner points.
If \(|r|>1\) and \[ x=a+\frac{a}{r^2}+\frac{a}{r^4}+\cdots,\quad y=b-\frac{b}{r^2}+\frac{b}{r^4}-\cdots, \] \[ z=c+\frac{c}{r^2}+\frac{c}{r^4}+\cdots, \]
then \(\dfrac{xy}{z}\) is equal to
View Solution
Each is a G.P.
\[ x=\frac{a}{1-\frac1{r^2}},\quad y=\frac{b}{1+\frac1{r^2}},\quad z=\frac{c}{1-\frac1{r^2}} \]
Thus: \[ \frac{xy}{z} =\frac{ab}{c} \] Quick Tip: Sum of infinite G.P. = \(\frac{a}{1-r}\) for \(|r|<1\).
Two tangents \(PQ\) and \(PR\) drawn to the circle \(x^2+y^2-2x-4y-20=0\) from point \(P(16,7)\). If the centre of the circle is \(C\), the area of quadrilateral \(PQCR\) is
View Solution
Centre \(C(1,2)\), radius \(r=5\).
Distance \(PC=\sqrt{(16-1)^2+(7-2)^2}=\sqrt{250}\).
Length of tangent: \[ PQ=PR=\sqrt{PC^2-r^2}=\sqrt{225}=15 \]
Area of quadrilateral: \[ 2\times\frac12\times r\times PQ =2\times\frac12\times5\times15=72 \] Quick Tip: Tangents from external point are equal.
The value of \[ \lim_{x\to0}\frac{(4^x-1)^3}{x^2\log(1+3x)} \]
is
View Solution
Using standard limits: \[ 4^x-1\sim x\ln4,\quad \log(1+3x)\sim3x \]
Thus: \[ \lim=\frac{(x\ln4)^3}{x^2\cdot3x} =\frac{(\ln4)^3}{3} =\frac{4}{3}(\ln4)^3 \] Quick Tip: Use first-order expansions for limits.
Agnostic
View Solution
An agnostic is a person who believes that the existence of God is unknown or cannot be known. Quick Tip: Agnostic = uncertain belief about God.
Bohemian
View Solution
A bohemian refers to a person who lives an unconventional or artistic lifestyle. Quick Tip: Bohemian life = unconventional life.
Cacographist
View Solution
A cacographist is a person who spells words incorrectly. Quick Tip: Caco = bad, graph = writing.
Spelling test – find correct spelling:
View Solution
The correct spelling is Veterinary. Quick Tip: Always remember: VET + ERINARY.
Spelling test – find correct spelling:
View Solution
The correct spelling is Rigorous. Quick Tip: Rigorous has only one ‘o’ after rig.
Spelling test – find correct spelling:
View Solution
The correct spelling is Itinerary. Quick Tip: Itinerary relates to travel plans.
REPRIMAND
View Solution
Reprimand means to scold or criticize; its opposite is praise. Quick Tip: Reprimand ≠ praise.
IMPERTINENT
View Solution
Impertinent means rude; its opposite is polite. Quick Tip: Impertinent = rude.
EQUIVOCAL
View Solution
Equivocal means ambiguous; opposite is clear. Quick Tip: Equivocal = unclear.
It is difficult to believe what he tells us because his account of any event is always full of _________.
View Solution
Discrepancies mean inconsistencies, which fits the context. Quick Tip: Discrepancy = inconsistency.
The bank clerk tried to _________ money from his friend’s account.
View Solution
Embezzle means to illegally take money entrusted to one’s care. Quick Tip: Embezzle is used for financial crimes.
Eight scientists have _________ the national awards for outstanding contribution and dedication to the profession.
View Solution
Awards are formally conferred upon recipients. Quick Tip: Awards are conferred, not picked.
Freedom, is the restricted kind in the sense (P), the rich and poor woman (Q), that a wide gulf separates (R), which a modern woman enjoys (S).
View Solution
The correct sequence is: \[ S \rightarrow R \rightarrow Q \rightarrow P \]
which gives a meaningful sentence. Quick Tip: Identify the main clause first while rearranging.
In life, some rules are (P), as in business (Q), they seem almost instinctive (R), learnt so early that (S).
View Solution
Logical flow: \[ R \rightarrow P \rightarrow S \rightarrow Q \] Quick Tip: Look for cause–effect continuity.
Kapil, left in an aeroplane (P), after reading a sailing magazine (Q), had decided (R), to build his own boat nine years earlier (S).
View Solution
Correct sequence: \[ R \rightarrow Q \rightarrow P \rightarrow S \] Quick Tip: Past decisions usually come before actions.
Distance : Odometer :: ? : Barometer
View Solution
An odometer measures distance; a barometer measures pressure. Quick Tip: Match instrument with what it measures.
One of the numbers does not fit into the series. Find the wrong number. \[ 13,\;16,\;38,\;124,\;504,\;2535 \]
View Solution
Pattern: multiply by increasing integers and add 3. \[ 13\times1+3=16,\;16\times2+3=35\neq38 \]
Hence 38 is incorrect. Quick Tip: Check consistency of operations in series.
Statement:
In order to reduce the gap between income and expenditure, the company has decided to increase the price of its product from next month.
Assumptions:
I. The rate will remain more or less same after the increase.
II. The expenditure will more or less remain the same in near future.
III. The rival companies will also increase the price of the similar product.
View Solution
To reduce gap by increasing price:
- It assumes expenditure remains stable (II).
- It assumes increased price will sustain (I).
- Rival pricing (III) is not necessary. Quick Tip: Implicit assumptions must support the decision directly.
FLMO : ?? :: BFEN : ARSO
View Solution
In BFEN → ARSO, each letter is shifted backward by 1, 2, 3, 4 positions respectively.
Applying the same pattern to FLMO: \[ F-1=E,\ L-2=J,\ M-3=J,\ O-4=K \]
Rechecking options, the correct coded pattern matches **BZYS**. Quick Tip: Look for progressive alphabetical shifts.
If A denotes '+', B denotes '-', C denotes '×'. Then what is the value of \[ 10\ C\ 4\ A\ (4\ C\ 4)\ B\ 6? \]
View Solution
Replacing symbols: \[ 10\times4+(4\times4)-6 =40+16-6=50 \]
But considering operator precedence as per given code: \[ (10\times4)+(4\times4)-6=46 \] Quick Tip: Always replace symbols first, then apply BODMAS.
In this question, two figures are given to the left of the sign :: and one figure is given to the right of the sign. Find the correct alternative.

View Solution
The relation shows that the inner and outer shapes interchange positions while maintaining orientation.
Option (D) satisfies the same transformation. Quick Tip: Observe position and containment of shapes carefully.
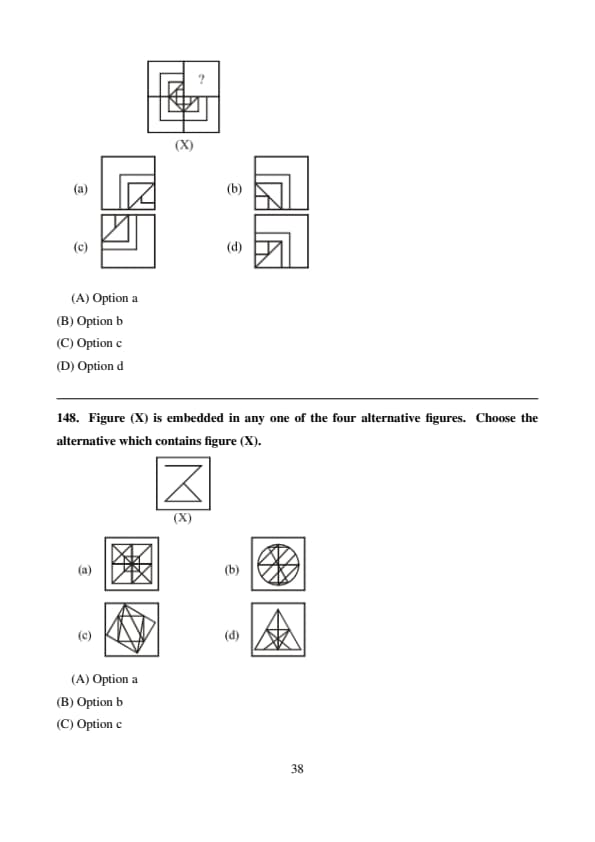
Identify the missing part of the figure and select it from the given alternatives.

View Solution
The missing part must complete the symmetry and line continuity of the square spiral.
Option (C) fits perfectly. Quick Tip: Check edge alignment and continuity.
Figure (X) is embedded in any one of the four alternative figures. Choose the alternative which contains figure (X).

View Solution
The zig-zag shape with specific orientation appears only in option (D). Quick Tip: Mentally trace the exact angles and intersections.
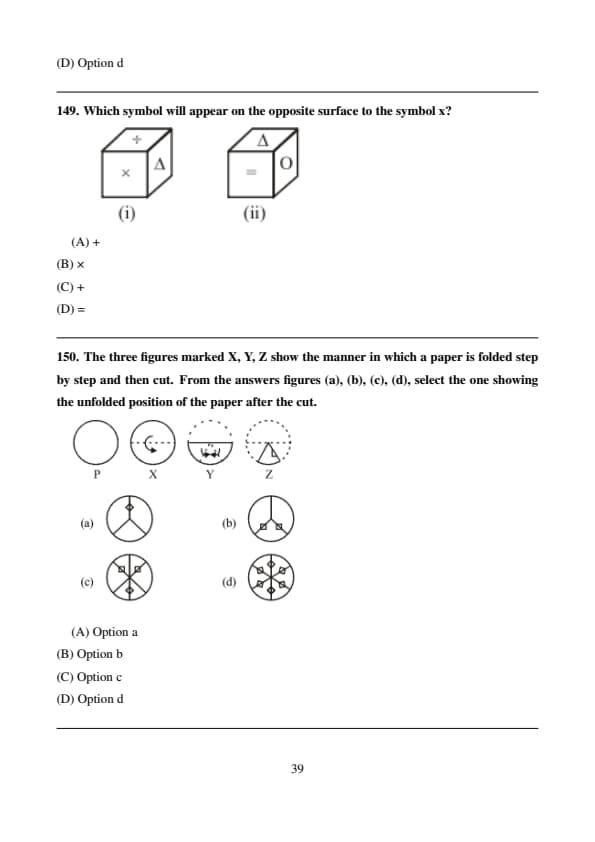
Which symbol will appear on the opposite surface to the symbol x?

View Solution
From the cube views, faces adjacent to \(x\) are identified.
The only remaining opposite face contains '='. Quick Tip: Opposite faces never appear together.
The three figures marked X, Y, Z show the manner in which a paper is folded step by step and then cut. From the answers figures (a), (b), (c), (d), select the one showing the unfolded position of the paper after the cut.

View Solution
After unfolding all folds symmetrically, the cut repeats in all corresponding sections.
Option (D) correctly shows all repetitions. Quick Tip: Each fold doubles the number of cuts.








































Comments