
Content Strategy Manager
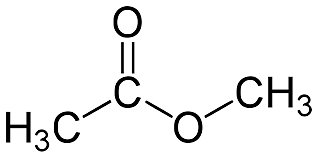
Methyl acetate is a carboxylate ester having the formula CH3 COOCH3. It is also known as MeOAc, acetic acid, methyl ester, or methyl ethanoate. It's a combustible liquid with a nice odor that reminds one of some glues and nail polish removers. Because it is weakly polar and lipophilic, methyl acetate is infrequently employed as a solvent, although its near cousin, ethyl acetate, is a more common solvent because it is less poisonous and less water-soluble. Let’s have a closer look at the topic.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Methyl acetate, Methyl, Carboxylate ester, Acetic acid, Methyl ester, Methyl ethanoate, Solvent, Flammability
What is Methyl Acetate?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
At normal temperature, methyl acetate is 25 percent soluble in water. It has a considerably greater solubility in water at higher temperatures. In the presence of strong aqueous bases or acids, methyl acetate is unstable. With a flashpoint of -10° C and a flammability value of 3, it is very flammable. Methyl acetate is a low-toxicity solvent often found in glues and nail polish removers. Apples, grapes, and bananas are among the fruits that contain methyl acetate.
Also Read:
| Chapter Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Acid Base Catalysis | Fischer Projection | Heterogeneous Reaction |
| Heterogeneous Catalyst | Tollen’s Test | Dialysis of Lyophilic and Lyophobic Sol |
Properties of Methyl Acetate
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some of the important properties of Methyl Acetate are tabulated below for your reference,
| IUPAC Name | Methyl Acetate |
| Chemical Formula | C3H6O2 |
| Molar Mass | 74.079 g mol-1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fragrant, fruity |
| Density | 0.932 g cm-3 |
| Melting Point | -98 oC |
| Boiling Point | 56.9 oC |
Uses of Methyl Acetate
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some of the key uses of Methyl Acetate are listed below for your reference,
Industrial Uses
- The reaction of carbonylation with methyl acetate to generate acetic anhydride is used in industry. It's also utilized as a solvent in paint, glue, nail polish, and graffiti removers, as well as lubricants, intermediates, and processing aids.
- Methyl acetate is also used as a chemical intermediate in the production of cellulose adhesives and perfumes, as well as the synthesis of chlorophacinone, diphacinone, fenfluramine, o-methoxy phenylacetone, p-methoxy phenylacetone, methyl cinnamate, methyl cyanoacetate, methyldopa, and phenylacetone.
Chemical Uses
- Methyl acetate is used as a flavoring agent in food additives for rum, brandy, and whisky, as well as in adhesives, cleaning products, personal care, and cosmetic products, lubricants, fast-drying paints like lacquers, motor vehicle coatings, furniture coatings, industrial coatings (low boiling point), inks, resins, oils, and electronic products. The paint, coatings, cosmetics, textiles, and automotive sectors are the primary end markets for this substance.
Preparation of Methyl Acetate
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Methyl acetate can be made in a variety of ways, some of them are listed below,
- Carbonylation is one method that is utilized in industry. Carbon monoxide substrates are brought together in these reactions. Methanol is burned with acetic acid in the presence of sulfuric acid to make methyl acetate.
- The esterification of methanol and acetic acid in the presence of a strong acid is another way of synthesis. This process likewise employs the use of sulfuric acid as a catalyst.
Handling
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Headaches, dizziness, sleepiness, and tiredness may occur if breathed or consumed. Irritation might occur if the product comes into contact with the eyes. Methyl Acetate has a flammability grade of 3 and may be ignited at most ambient temperatures due to its low flash point of -10 °C. When methyl acetate is ignited, it produces thick, unpleasant, and poisonous vapors that may travel long distances. These vapors are likewise explosive, and if they can return to the source of ignition, they risk exploding.
- When handling methyl acetate, personal protective equipment should be worn at all times to avoid contact with the skin, eyes, nose, and throat. If skin contact occurs, wash the contaminated area immediately and seek medical treatment. If you come into touch with your eyes, flush them with a lot of water right away. If you swallow anything, get medical help right away.
- Isolate the leak for at least 50 meters in all directions if methyl acetate is spilled. Because of the low flashpoint of methyl acetate, water extinguishers may be useless in the case of a fire. Alcohol-resistant foam extinguishers are useful for both minor and big flames.
Things to Remember
- Methyl acetate is a carboxylate ester having the formula CH3 COOCH3.
- Methyl acetate is a low-toxicity solvent often found in glues and nail polish removers.
- The reaction of carbonylation with methyl acetate to generate acetic anhydride is used in industry. It's also utilized as a solvent in paint, glue, nail polish, and graffiti removers, as well as lubricants, intermediates, and processing aids.
- Methyl acetate is used as a flavoring agent in food additives for rum, brandy, and whisky, as well as in adhesives, cleaning products, personal care, and cosmetic products, lubricants, fast-drying paints like lacquers, motor vehicle coatings, furniture coatings, industrial coatings (low boiling point), inks, resins, oils, and electronic products.
- Carbonylation is one method that is utilized in industry. Carbon monoxide substrates are brought together in these reactions. Methanol is burned with acetic acid in the presence of sulfuric acid to make methyl acetate.
- Isolate the leak for at least 50 meters in all directions if methyl acetate is spilled. Because of the low flashpoint of methyl acetate, water extinguishers may be useless in the case of a fire. Alcohol-resistant foam extinguishers are useful for both minor and big flames.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques: What is the IUPAC name of methyl acetate? (1 mark)
Ans: The IUPAC name of methyl acetate is Methyl ethanoate
Ques: Can methyl acetate form hydrogen bonds with water? (1 mark)
Ans: The chemical formula for methyl acetate is C3H6O2. Since it has no -OH bond, there is no bonding with water.
Ques: Which functional group is present in methyl acetate? (1 mark)
Ans: Methyl acetate has an ester functional group. RCOOR′ is the symbol for ester and carboxylic acids are used to make esters.
Ques: Does methyl acetate give a positive result for the Iodoform test? (3 marks)
Ans: The iodoform test yields a positive result for any chemical containing the CH3C=O or CH3CH(OH) groups. A pale yellow iodoform (triiodomethane) precipitate is produced when I2 and NaOH are combined with a chemical containing one of these groups. Because carboxylic acid and its derivatives do not pass the iodoform test, methyl acetate does not produce a positive result. This is because there is no free C=O group, which is necessary for the reaction, due to resonance.
Ques: What is the role of HCl in the hydrolysis of methyl acetate? (4 marks)
Ans: In the presence of an acid (HCl, for example), methyl acetate is hydrolyzed to produce acetic acid and methyl alcohol. Because two molecules are interacting in the presence of an acid, this reaction should be of second order. However, it is discovered to be first-class. Because there is so much water in the reaction, the active mass (molar concentration) is nearly constant throughout the process. As a result, the constant includes its active mass. As a result, just one concentration term determines the response rate (that is, by a single power of the concentration term only). As a result, the response is of the first order. Pseudo-first-order reactions are another name for these types of reactions.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments