
Content Curator
A chemical reaction is a process of molecular or ionic rearrangement of reactants that are simultaneously converted into one or more products. A chemical reaction occurs between either two atoms and molecules or ions.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Conservation of Mass, Chemical Equations, Combustion Reaction, Redox Reaction, Decomposition Reaction
What are Chemical Reactions?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Chemical reactions represent the chemical changes undergone by different elements and compounds. Quantitative study of the reactants required or the products formed is called stoichiometry.
There are 3 Key Concepts of Chemical Reactions: Conservation of Mass, Chemical Equations, Reversibility and Equilibrium.
Conservation of Mass
As per Law of Conservation of Mass, in a chemical reaction, mass is neither created nor destroyed. Chemical reactions do not change the number or type of leptons or baryons; thus, matter is conserved in chemical reactions.
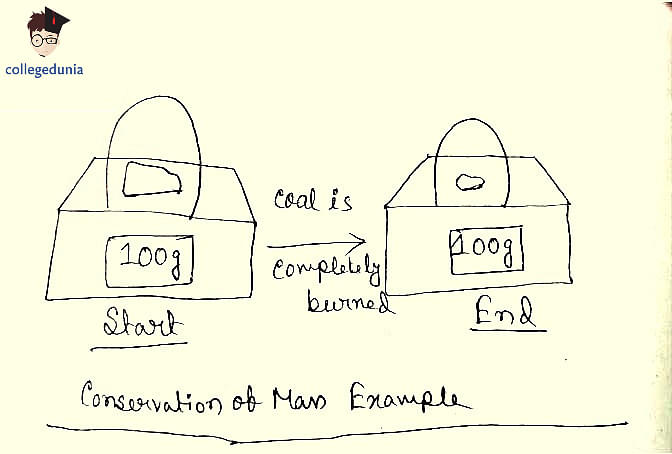
Conservation of Mass Example
Conservation of Mass: Frequently Asked Questions
Ques 1. What is Conservation of Mass? (1 Mark)
Ans. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. The mass of any one element at the beginning of a reaction is equivalent to the mass of that element at the end of the reaction.
Ques 2. What are the examples of Conservation of Mass? (1 Mark)
Ans. Example of Conservation of Mass: When wood burns, the mass of the soot, ashes, and gases equals the original mass of the charcoal and the oxygen when it first reacted.
Ques 3. What is the importance of the conservation of mass? (2 Marks)
Ans. The Law of conservation of mass has helped in understanding that substances do not disappear as result of a reaction (as they may appear to do); rather, they transform into another substance of equal mass.
Chemical Equations
Chemical equations describe a chemical reaction by determining identities and quantities of substances that are involved in a reaction. Chemical equations in chemical reactions show the starting compound (reactants) on the left and final compound (products) on the right, separated by an arrow.

Chemical Equations
Chemical Equations: Frequently Asked Questions
Ques 1. What are the 5 types of chemical equations? (2 Marks)
Ans. There are five basic categories of chemical equations: synthesis, combustion, decomposition, single and double replacement.
Ques 2. What is a basic chemical equation? (2 Marks)
Ans. A basic chemical equation shows the starting compound(s)—the reactants—on the left and the final compound(s)—the products—on the right, separated by an arrow. The numbers of atoms of each element and the total charge are the same on both sides of the equation.
Ques 3. What are the 3 rules for balancing equations? (2 Marks)
Ans. The rules followed for balancing equations are:
- All formulae in the equation should be correct.
- Only one element at a time should be worked with.
- Balancing is basically the addition of big numbers. You cannot change any of the small numbers in a chemical formula.
Reversibility and Equilibrium
In chemical reactions, reversibility occurs in products when upon formation, they react to produce the original reactants. Whereas, at equilibrium, two opposing reactions go on at equal rates, or velocities. Thus, there is no net change in the amounts of substances involved.

Reversible Reactions
Reversibility and Equilibrium: Frequently Asked Questions
Ques 1. Do reversible reactions reach dynamic equilibrium? (1 Mark)
Ans. When a reversible reaction happens in a closed container, it can achieve a dynamic equilibrium. At equilibrium: Forward and backward reactions are still happening.
Ques 2. Are all reversible reactions always equilibrium? (2 Marks)
Ans. The majority of reactions are reversible, i.e., a certain amount of reactant remains at the end of the reaction. Reversible reactions occur until equilibrium is established, meaning that they achieve a sort of balance between amounts of reactant and product.
Types of Chemical Reactions
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In a chemical reaction, the reacting substances are termed as reactants and the forming substances are termed as products.
Chemical reactions have been classified into six common categories:
- Combination Reaction
- Displacement Reaction
- Precipitation Reaction
- Neutralization Reaction
- Decomposition Reaction
- Combustion Reaction
Combination Chemical Reaction
A combination reaction is a reaction where two or more elements or compounds combine to form a single compound. These reactions are expressed by equations of the following form: X + Y → XY. Combination of two or more elements to form one compound is a combination reaction.
Displacement Chemical Reaction
Displacement chemical reaction is a reaction in which two compounds react and consequently, their anions and cations switch places forming two new products. Example: When iron is added to a copper sulphate solution, it displaces the copper metal.
Precipitation Chemical Reaction
Precipitation reaction can be defined as chemical reaction occurring in aqueous solution where two ionic bonds combine, resulting in formation of an insoluble salt. The insoluble salts formed in precipitation reactions are called precipitates.
Neutralization Chemical Reaction
Neutralization is a chemical reaction in which acid and a base react quantitatively with each other. In a reaction in water, the reaction’s product shows no excess of hydrogen or hydroxide ions in the solution.
Example: Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH), a base, reacts with Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sodium Chloride (NaCl) and Water are formed.
Decomposition Chemical Reaction
Decomposition reaction occurs when one reactant breaks down into two or more products. This process is expressed by the general equation: AB → A + B. Examples: Breakdown of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen, Breakdown of water to hydrogen and oxygen.
Combustion Chemical Reaction
Combustion reaction generates heat and light as it releases that energy. Burning wood in a fire is an example of a combustion reaction. Combustion reactions are a type of redox reaction. The classic chemistry class combustion reaction involves compounds of C and H reacting with O2 to form CO2 and H2O.
Types of Chemical Reactions: Frequently Asked Questions
Ques. What are the common types of chemical reactions?
Ans. On the basis of formation of different kinds of products or change in the condition of reactants, different types of chemical reactions are:
- Combustion reaction
- Neutralization reaction
- Decomposition reaction
- Redox Reaction
- Double-Displacement Reaction or Precipitation
Ques. Explain the reaction: 2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl.
Ans. The reaction 2Na + Cl2 = 2NaCl is an example of a Combination reaction. Decomposition reaction will occur when one reactant breaks down into two or more products, e.g. AB => A + B. In Combination Reaction, two or more elements/compounds combine to form a single compound, e.g. A + B => AB.
Ques. What type of reaction is AB → A + B?
Ans. This is an example of Decomposition Reaction. These are the same number of synthesis reactions, with the format AB → A + B.
Here are the different types of chemical reactions and their general reaction expressions:
| Types of Chemical Reactions | Basic Reaction |
|---|---|
| Combination Chemical Reaction | A + B → AB |
| Displacement Chemical Reaction | A + BC → AC + B |
| Precipitation Chemical Reaction | A + Soluble salt B → Precipitate + soluble salt C |
| Neutralization Chemical Reaction | Acid + Base → Salt + Water |
| Decomposition Chemical Reaction | AB → A + B |
| Combustion Chemical Reaction | A + O2 → H2O + CO2 |
Class-wise Chemical Reaction Topics
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Class-wise important chemical reaction topics have been provided in the following sections:
Class 12 Chemical Reaction Important Topics
Class 12 Chemical Reaction important topics include First order reactions, Rate of reaction, Coupling reaction.
Check out:
Class 11 Chemical Reaction Important Topics
Important chemical reaction topics covered in Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus are listed below:
Class 10 Chemical Reaction Important Topics
Class 10 important chemical reaction topics are:
Frequently Asked Questions
Ques. How to identify a chemical reaction? (2 Marks)
Ans. Chemical reaction is accompanied by easily observed physical effects including emission of heat and light, formation of a precipitate, evolution of gas, or a color change.
Ques. What are some examples of chemical reactions in everyday life? (2 Marks)
Ans. Examples of chemical reactions in everyday life are rust, photosynthesis, baking, combustion, digestion, fermentation, chemical batteries, and washing with soap and water.
Ques. How do we classify each chemical reaction? (2 Marks)
Ans. Chemical reactions can be classified as an acid–base reaction, an exchange reaction, a condensation reaction and its reverse, a cleavage reaction, and an oxidation–reduction (or redox) reaction. To keep track of electrons in chemical reactions, oxidation states are assigned to atoms in compounds.
Ques. What are basic chemical reactions? (2 Marks)
Ans. Chemical reactions involve changes of reactants into products. Basic chemical reactions have been classified based on types of changes that are occuring during the reaction. There are five basic categories - synthesis, decomposition, combustion, single replacement, and double replacement.
Ques. Give an example of a chemical reaction in the body. (3 Marks)
Ans. Digestion in the human body is also an example of decomposition reactions. Starch decomposes into sugar in the body and proteins get decomposed into smaller substances called amino acids.
Trillions of chemical reactions occur simultaneously in the body. They drive processes that keep a human body 'alive'. Collectively, they are known as metabolism. Metabolism is made up of numerous metabolic pathways.
Ques. What are the common observations of a chemical reaction? (3 Marks)
Ans. Common observations of Chemical Reactions are:
- Change of gas
- Variation of temperature
- Formation of precipitation
- Color changes
- Change of state of matter
Ques. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation for process of photosynthesis.
(ii) When do desert plants take up carbon dioxide and perform photosynthesis? [Short Answer Type Questions (2 Marks) -Year 2015]
Ans. (i) \(6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}(g)+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(l) \stackrel{\text { Sunlight }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}(s)+6 \mathrm{O}_{2}(g)\)
(ii) In desert plants, stomata are open at night. They take CO2 at night which is stored in the form of acid and is used during day time for photosynthesis.
Ques. (a) Define a balanced chemical equation. Why should an equation be balanced?
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reaction:
(i) Phosphorus burns in presence of chlorine to form phosphorus pentachloride.
(ii) Burning of natural gas.
(iii) The process of respiration. [Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks) -Year 2015]
Ans. (a) Balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products. According to law of conservation of mass, matter can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
(b)
- P4 (s) + 10Cl2 (g) ———> 4PCl5 (S)
- CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) ———> CO2 (g) + 2H2O(l) + heat energy
- C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2 (g) + 6H2O ———> 6CO2 (aq) + 12H2O (l) + energy
Also Check:
Also Read:





Comments