KCET 2024 Physics Question Paper is available for download here.. KCET Physics question paper was conducted on April 19, 2024 from 10.30 AM to 11.50 PM by Karnataka Examination Authority (KEA). KCET 2024 Physics question paper consists of 60 questions to be attempted in 80 minutes for a total of 60 marks.
KCET 2024 Physics Question Paper with Solution PDF
| KCET 2024 Physics Question Paper with Answer Key | Check Solutions |
KCET 2024 Physics Question Paper with Solution
Question 1:
The ratio of molar specific heats of oxygen is
(A) 1.4
(B) 1.67
(C) 1.33
(D) 1.28
View Solution
For a particle executing simple harmonic motion (SHM), at its mean position:
(A) Velocity is zero and acceleration is maximum
(B) Velocity is maximum and acceleration is zero
(C) Both velocity and acceleration are maximum
(D) Both velocity and acceleration are zero
View Solution
A motor-cyclist moving towards a huge cliff with a speed of 18 km/h, blows a horn of source frequency 325 Hz. If the speed of the sound in air is 330 m/s, the number of beats heard by him is
(A) 5
(B) 4
(C) 7
(D) 6
View Solution
A body has a charge of −3.2µC. The number of excess electrons it has is
(A) 1.2 × 1015
(B) 5 × 1010
(C) 3.2 × 1016
(D) 5.12 × 1013
View Solution
A point charge A of +10µC and another point charge B of + 20µC are kept 1 m apart in free space. The electrostatic force on A due to B is F1, and the electrostatic force on B due to A is F2. Then
(A) F2 = 2F1
(B) F1 = -F2
(C) 2F1 = −F2
(D) F1 = F2
View Solution
A uniform electric field E = 3 × 103 N/C is acting along the positive Y-axis. The electric flux through a rectangle of area 10 m × 30 m, where the plane of the rectangle is parallel to the Z-X plane is
(A) 12 × 103 Vm
(B) 9 × 103 Vm
(C) 15 × 103 Vm
(D) 18 × 103 Vm
View Solution
The total electric flux through a closed spherical surface of radius *r* enclosing an electric dipole of dipole moment 2*aq* is (Give ∈₀ = permittivity of free space)
(A) Zero
(B) q/∈₀
(C) 2q/∈₀
(D) 8πr²q/∈₀
View Solution
Under electrostatic condition of a charged conductor, which among the following statements is true?
(A) The electric field on the surface of a charged conductor is σ/∈₀, where σ is the surface charge density
(B) The electric potential inside a charged conductor is always zero
(C) Any excess charge resides on the surface of the conductor
(D) The net electric field is tangential to the surface of the conductor
View Solution
A cube of side 1 cm contains 100 molecules each having an induced dipole moment of 0.2 × 10⁻¹⁶ C⋅m in an external electric field of 4 × 10⁴ N/C. The electric susceptibility of the materials is
(A) 50
(B) 5
(C) 0.5
(D) 0.05
View Solution
A capacitor of capacitance 5μF is charged by a battery of emf 10V. At an instant of time, the potential difference across the capacitors is 4V and the time rate of change of potential difference across the capacitor is 0.6 V/s. Then the time rate at which energy is stored in the capacitor at the instant is
(A) 12μW
(B) 3μW
(C) Zero
(D) 30μW
View Solution
Ê is the electric field inside a conductor whose material has conductivity σ and resistivity ρ. The current density inside the conductor is J. The correct form of Ohm's law is
(A) J = σÊ
(B) J = ρÊ
(C) J = σÊ
(D) J = ρÊ
View Solution
In the circuit shown, the end A is at potential V₀, and end B is grounded. The electric current indicated in the circuit is
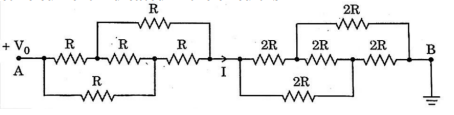
(A) V₀/2R
(B) V₀/R
(C) V₀/3R
(D) V₀/R
View Solution
The electric current flowing through a given conductor varies with time as shown in the graph below. The number of free electrons which flow through a given cross-section of the conductor in the time interval 0 ≤ t ≤ 20 s is

(A) 3.125 × 1019
(B) 1.6 × 1019
(C) 6.25 × 1018
(D) 1.625 × 1019
View Solution
The I-V graph for a conductor at two different temperatures 100°C and 400°C is as shown in the figure. The temperature coefficient of resistance of the conductor is about (in per degree Celsius)

(A) 3 × 10-7
(B) 6 × 10-7
(C) 9 × 10-7
(D) 12 × 10-7
View Solution
An electric bulb of 60 W, 120 V is to be connected to a 220 V source. What resistance should be connected in series with the bulb, so that the bulb glows properly?
(A) 50 Ω
(B) 100 Ω
(C) 200 Ω
(D) 288 Ω
View Solution
In an experiment to determine the temperature coefficient of resistance of a conductor, a coil of wire X is immersed in a liquid. It is heated by an external agent. A meter bridge set up is used to determine resistance of the coil X at different temperatures. The balancing points measured at temperatures t₁ = 0°C and t₂ = 100°C are 50 cm and 60 cm respectively. If the standard resistance taken out is S = 4 Ω in both trials, the temperature coefficient of the coil is
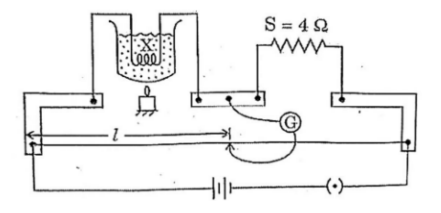
(A) 0.05 °C⁻¹
(B) 0.02 °C⁻¹
(C) 0.005 °C⁻¹
(D) 2.0 °C⁻¹
View Solution
A moving electron produces
(A) Only electric field
(B) Both electric and magnetic field
(C) Only magnetic field
(D) Neither electric nor magnetic field
View Solution
A coil having 9 turns carrying a current produces a magnetic field B₁ at the centre. Now the coil is rewound into 3 turns carrying the same current. Then the magnetic field at the centre B₂ is:
(A) B₁/9
(B) 3B₁
(C) 2B₁
(D) B₁/3
View Solution
A particle of specific charge α/m is projected from the origin towards the positive x-axis with the velocity 10 m/s in a uniform magnetic field B = −2k̂ T. The velocity v of the particle after time t = 5 ms will be (in m/s)
(A) 5î + 5ĵ
(B) 5î - 5ĵ
(C) 5î + 5k̂
(D) 5î - 5k̂
View Solution
The magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil of radius R carrying current I is 64 times the magnetic field at a distance x on its axis from the centre of the coil. Then the value of x is
(A) R/√15
(B) R/4
(C) R
(D) R/√3
View Solution
Magnetic hysteresis is exhibited by magnetic materials.
(A) only para
(B) only dia
(C) only ferro
(D) both para and ferro
View Solution
Magnetic susceptibility of Mg at 300 K is 1.2 × 10⁻⁵. What is its susceptibility at 200 K?
(A) 18 × 10⁻⁵
(B) 180 × 10⁻⁵
(C) 1.8 × 10⁻⁵
(D) 0.18 × 10⁻⁵
View Solution
A uniform magnetic field of strength B = 2mT exists vertically downwards. These magnetic field lines pass through a closed surface as shown in the figure. The closed surface consists of a hemisphere S₁, a right circular cone S₂, and a circular surface S₃. The magnetic flux through S₁ and S₂ are respectively

(A) Φ₁ = -20 Wb, Φ₂ = +20 Wb
(B) Φ₁ = +20 Wb, Φ₂ = -20 Wb
(C) Φ₁ = -40 Wb, Φ₂ = +40 Wb
(D) Φ₁ = +40 Wb, Φ₂ = -40 Wb
View Solution
In the figure, a conducting ring of certain resistance is falling towards a current-carrying straight long conductor. The ring and conductor are in the same plane. Then the

(A) induced electric current is zero
(B) induced electric current is anticlockwise
(C) induced electric current is clockwise
(D) ring will come to rest
View Solution
An induced current of 2 A flows through a coil. The resistance of the coil is 100 Ω. What is the change in magnetic flux associated with the coil in 1 ms?
(A) 2 × 10⁻² Wb
(B) 2 × 10⁻³ Wb
(C) 22 × 10⁻² Wb
(D) 2 × 10⁻⁴ Wb
View Solution
A square loop of side length a is moving away from an infinitely long current-carrying conductor at a constant speed v as shown. Let x be the instantaneous distance between the long conductor and side AB. The mutual inductance M of the square loop - long conductor pair changes with time t according to which of the following graphs?

View Solution
Which of the following combinations should be selected for better tuning of an LCR circuit used for communication?
(A) R = 20 Ω, L = 1.5 H, C = 35 μF
(B) R = 25 Ω, L = 2.5 H, C = 45 μF
(C) R = 25 Ω, L = 1.5 H, C = 45 μF
(D) R = 15 Ω, L = 3.5 H, C = 30 μF
View Solution
In an LCR series circuit, the value of only capacitance C is varied. The resulting variation of resonance frequency f₀ as a function of C can be represented as

View Solution
The figure shows variation of R, XL, and XC with frequency f in a series LCR circuit. Then for what frequency point is the circuit capacitive?

(A) B
(B) C
(C) D
(D) A
View Solution
Electromagnetic waves are incident normally on a perfectly reflecting surface having surface area A. If I is the intensity of the incident electromagnetic radiation and c is the speed of light in vacuum, the force exerted by the electromagnetic wave on the reflecting surface is
(A) 2IA/c
(B) IA/c
(C) IA/2c
(D) I/2Ac
View Solution
The final image formed by an astronomical telescope is
(A) real, erect and diminished
(B) virtual, inverted and diminished
(C) real, inverted and magnified
(D) virtual, inverted and magnified
View Solution
If the angle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle of a prism for an equilateral prism, then the speed of light inside the prism is
(A) 3 × 10⁸ ms⁻¹
(B) 2 × 10⁸ ms⁻¹
(C) √3 × 10⁸ ms⁻¹
(D) (3/2) × 10⁸ ms⁻¹
View Solution
A luminous point object O is placed at a distance 2R from the spherical boundary separating two transparent media of refractive indices n₁ and n₂, where R is the radius of curvature of the spherical surface. If n₁ = 4/3, n₂ = 3/2, and the image is obtained at a distance from P equal to

(A) 30 cm in the rarer medium
(B) 30 cm in the denser medium
(C) 18 cm in the rarer medium
(D) 18 cm in the denser medium
View Solution
An equiconvex lens of radius of curvature 14 cm is made up of two different materials. Left half and right half of vertical portion is made up of material of refractive index 1.5 and 1.2 respectively as shown in the figure. If a point object is placed at a distance of 40 cm, calculate the image distance.

(A) 25 cm
(B) 50 cm
(C) 35 cm
(D) 40 cm
View Solution
A galaxy is moving away from the Earth so that a spectral line at 6000 Å is observed at 6300 Å. Then the speed of the galaxy with respect to the Earth is
(A) 500 km/s
(B) 150 km/s
(C) 200 km/s
(D) 1500 km/s
View Solution
Question 36:
Three polaroid sheets are co-axially placed as indicated in the diagram. Pass axes of the polaroids 2 and 3 make 30° and 90° with pass axes of polaroid sheet 1. If I₀ is the intensity of the incident unpolarised light entering sheet 1, the intensity of the emergent light through sheet 3 is
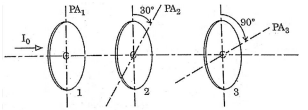
View Solution
In Young's double slit experiment, an electron beam is used to produce interference fringes of width β₁. Now the electron beam is replaced by a beam of protons with the same experimental setup and same speed. The fringe width obtained is β₂. The correct relation between β₁ and β₂ is
View Solution
Light of energy E falls normally on a metal of work function W₀. The kinetic energies K of the photoelectrons are
View Solution
The photoelectric work function for photo metal is 2eV. Among the four wavelengths, the wavelength of light for which photoemission does not take place is
View Solution
In alpha particle scattering experiment, if v is the initial velocity of the particle, then the distance of closest approach is
View Solution
The ratio of area of first excited state to ground state of orbit of hydrogen atom is
View Solution
The ratio of volume of Al²⁷ nucleus to its surface area is (Given R₀ = 1.2 × 10⁻¹⁵ m)
View Solution
Consider the nuclear fission reaction n¹ + U²³⁵ → Ba¹⁴⁴ + Kr⁸⁹ + 3 n. Assuming all the kinetic energy is carried away by the fast neutrons only and total binding energies of U²³⁵, Ba¹⁴⁴, and Kr⁸⁹ to be 1800 MeV, 1200 MeV, and 780 MeV respectively, the average kinetic energy carried by each fast neutron is (in MeV)
View Solution
The natural logarithm of the activity R of a radioactive sample varies with time t as shown. At t = 0, there are N₀ undecayed nuclei. Then N₀ is equal to [Take e² = 7.5]
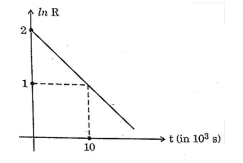
View Solution
Depletion region in an unbiased semiconductor diode is a region consisting of
View Solution
The upper level of valence band and lower level of conduction band overlap in the case of
View Solution
In the diagram shown, the Zener diode has a reverse breakdown voltage Vz. The current through the load resistance Rʟ is Iʟ. The current through the Zener diode is
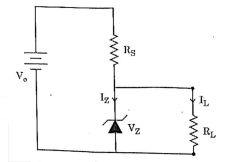
View Solution
A p-n junction diode is connected to a battery of emf 5.7 V in series with a resistor 5k Ω such that it is forward biased. If the barrier potential of the diode is 0.7 V, neglecting the diode resistance, the current in the circuit is
View Solution
An athlete runs along a circular track of diameter 80m. The distance travelled and the magnitude of displacement of the athlete when he covers ¾ of the circle is (in m)
View Solution
Among the given pair of vectors, the resultant of two vectors can never be 3 units. The vectors are
View Solution
A block of certain mass is placed on a rough inclined plane. The angle between the plane and the horizontal is 30°. The coefficients of static and kinetic frictions between the block and the inclined plane are 0.6 and 0.5 respectively. Then the magnitude of the acceleration of the block is [Take g = 10 m/s²]
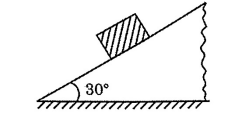
View Solution
A particle of mass 500 g is at rest. It is free to move along a straight line. The power delivered to the particle varies with time according to the following graph:
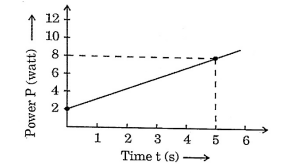
View Solution
Dimensional formula for activity of a radioactive substance is
View Solution
A ceiling fan is rotating around a fixed axle as shown. The direction of angular velocity is along
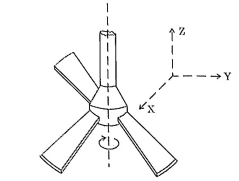
View Solution
A body of mass 1 kg is suspended by a weightless string which passes over a frictionless pulley of mass 2 kg as shown in the figure. The mass is released from a height of 1.6m from the ground. With what velocity does it strike the ground?
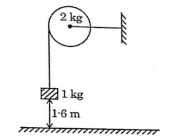
View Solution
What is the value of acceleration due to gravity at a height equal to half the radius of the Earth, from its surface?
View Solution
A thick metal wire of density ρ and length L is hung from a rigid support. The increase in length of the wire due to its own weight is
View Solution
Water flows through a horizontal pipe of varying cross-section at a rate of 0.314 m³/s. The velocity of water at a point where the radius of the pipe is 10 cm is
View Solution
A solid cube of mass m at a temperature θ₀ is heated at a constant rate. It becomes liquid at temperature θ₁, and vapor at temperature θ₂. Let s₁ and s₂ be specific heats in its solid and liquid states respectively. If Lf and Lᵥ are latent heats of fusion and vaporization respectively, then the minimum heat energy supplied to the cube until it vaporises is
View Solution
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is taken round the cyclic process MNOM. The work done by the gas is
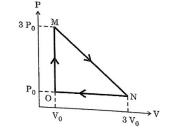
View Solution
Also Check:
KCET Previous Year Question Papers
| KCET 2023 Question Paper | KCET 2022 Question Paper | KCET 2021 Question Paper |
| KCET 2020 Question Paper | KCET 2019 Question Paper | KCET 2018 Question Paper |




Comments