MHT CET 2024 2 May Shift 1 question paper is available for download here. MHT CET 2024 question paper comprises 150 MCQs carrying a total weightage of 200 marks.
MHT CET 2024 2 May Shift 1 Question Paper for PCM is divided into three subjects- Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics with 50 questions for each section (10 questions from Class 11 and 40 questions from Class 12th syllabus).
MHT CET 2024 2 May Shift 1 Question Paper PDF Download
| MHT CET 2024 2 May Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer key | Check Solutions |
MHT CET 2024 2 May Shift 1 Question Paper Solution
Question 2:
Integrate the following function with respect to x:
∫ e^(3x) / (e^(3x) + 1) dx
Question 4:
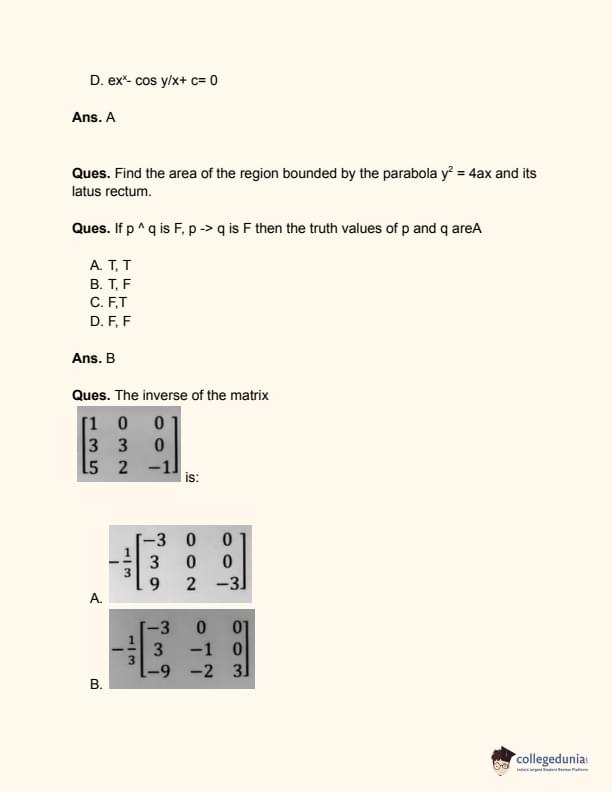
Find the area of the region bounded by the parabola:
y² = 4ax and its latus rectum.
Question 5:
If p ∧ q is False and p → q is False, then the truth values of p and q are:
Question 6:
Question 7:
What is the equivalent logic gate when the output of an AND gate is passed through a NOT gate?
Question 8:
In Young's double-slit experiment, if the distance between the slits is doubled while keeping the wavelength and the distance to the screen constant, the fringe spacing will:
Question 9:
In a series LCR circuit connected to an AC source, at resonance, the current is maximum because:
Question 11:
Which of the following techniques is most suitable for determining the size and morphology of nanoparticles?
Question 12:



Also Check:
MHT CET Previous Year Question Papers
| MHT CET 2023 Question Paper | MHT CET 2022 Question Paper |
| MHT CET 2021 Question Paper | MHT CET 2020 Question Paper |
| MHT CET 2019 Question Paper | MHT CET 2018 Question Paper |
Also Check:





Comments