Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Wheel and axle is a simple machine that works on the application of force and uses the concept of mechanical advantage. The system of the machine changes the force applied by changing or managing the distance over which we apply the force. Let us say if the input force is 1/3rd of the output force, then the force is applied about three times the distance. The machine amplifies the force that is applied on its one side such that if we apply a small force at the boundary of the wheel, the axle can be used to lift huge loads.
Read More: Mechanical Properties of Solids
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Wheel, Axle, Load Force, Tangential Force, Mechanical Advantage, Fulcrum, Friction, Locking Mechanism, Rotation
What is Wheel and Axle?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Wheel and axle is a machine that has a wheel attached to an axle. Both the axle and the wheel rotate together, so the force is transferred to each other. The rotation is enabled by a bearing. When little force is applied to the axle, huge loads can be lifted by the axle.
The driving force can be tangentially applied to the perimeter of the wheel while on the axle, the load force can be applied. There is a hinge that balances these two tangential and load forces, known as the fulcrum.
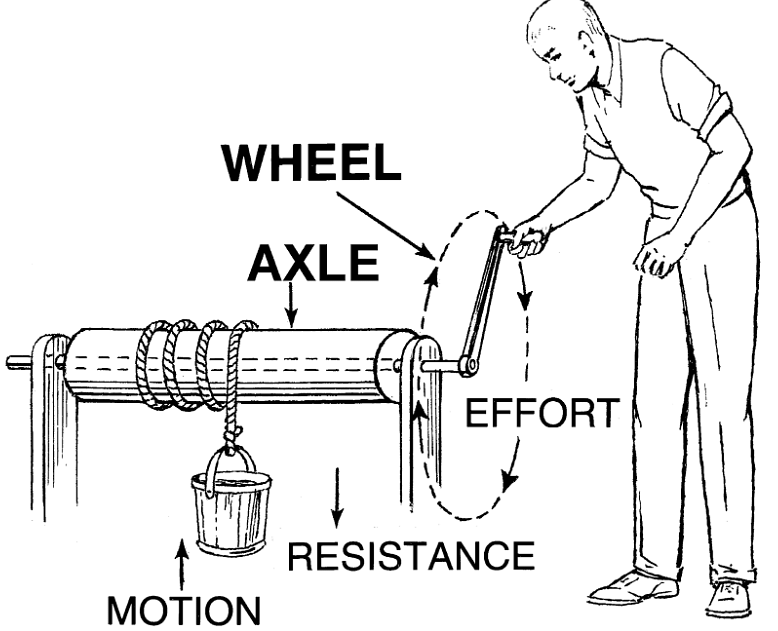
Wheel and Axle
When a tangential force is applied to the larger disk, it provides a large force on the weight that is linked to the axle thereby promoting mechanical advantage. No energy is stored in the wheel and axle. So, no elasticity or friction is produced. The power output at the axle is equivalent to the input force that is exerted on the wheel.
The wheel and axle are assembled together through two-cylinder disks having different diameters. Both of them are mounted on an axis from where they are rotated. Axle is the thin rod that rotates while the wider object that is linked to the axle is known as the wheel. Wheel and axle is a simple machine, made up of two parts which are:
- Wheel: Wheel can be understood as the round disc that is located on the external part of the machine
- Axle: Axle refers to the rod-like part or a rounded cylinder that is placed on the inside of the machine. The axle is further attached to the wheel and it helps to promote the movement.
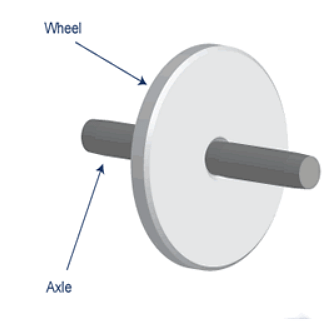
Components of a Wheel and Axle Machine
The common examples of wheel and axle systems are Ferris Wheel, Bicycle, Analog clocks, Winch, Fan, etc.
Also Check: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Types of Wheel and Axle Machine
[Click Here for Previous Year's Questions]
Wheel and Axle machine are further classified into two categories depending on where the force is being applied:
Force is applied to the axle
- In these machines, the force is applied to the axle of the machine and therefore the wheel rotates at a rapid rate.
- The motion that is started from the axle gets transferred to the wheel.
- Some examples of this type of machine are Ferris wheel, bicycle, etc.
Force is applied to the wheel
- In these machines, the force is applied to the wheel of the machine and therefore the axle is rotated at a higher speed.
- The motion of the machine starts from the wheel which builds pressure on the axle in large amounts.
- Examples of this machine are pizza cutter, drill machine, windmill, etc.
Also Check:
Mechanical Advantage of Wheel and Axle
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Machines are used by us in various aspects of life to make our work easier. When huge work is done with the help of just a small amount of energy, it is referred to as mechanical advantage. It refers to the force ratio of the output (the force the machine generates) to the input (the force supplied to the machine using a human being).
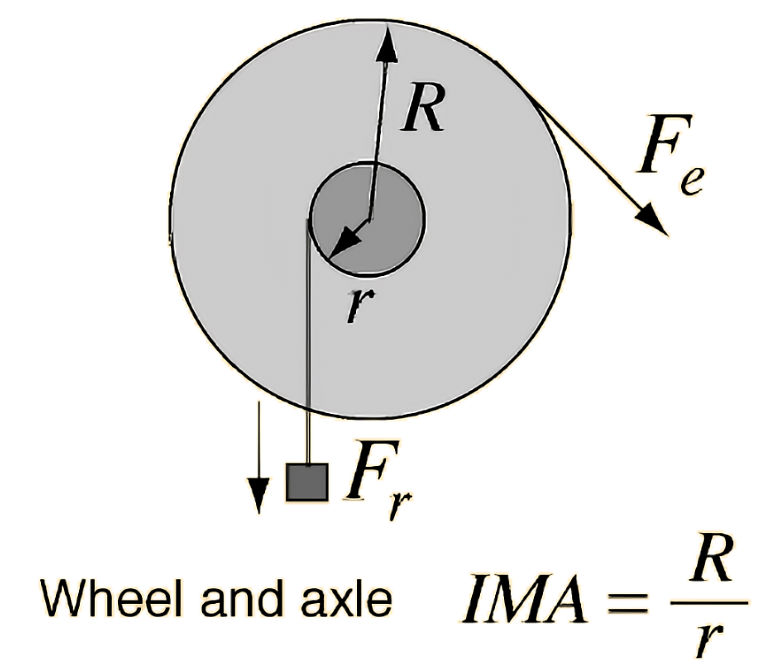
Mechanical Advantage of Wheel Mechanism
The wheel and axle is one simple machine amongst the other machines such as a lever, wedge, pulley, screw, and inclined plane. These kinds of machines are used for their mechanical advantage so that more work can be done with a little force. The Mechanical Advantage can be represented as:
| MA = a/b = FA/FB |
Here,
- a and b refer to the distances from the centre of a bearing to the edges of the axle (represented by A and a wheel represented by B).
- FA refers to the input force that we apply to the boundary of the wheel A
- FB refers to the output force generated on the edge of the axle.
- a/b denotes the ratio of velocities of the two points A and B.
Therefore,
⇒ Mechanical Advantage = Radius of Wheel / Radius of Axle
Solved Example Related to Wheel and AxleExample: Determine the mechanical advantage of load 40 N, while the required force to lift it is 15 N. Solution: As given in the question, Mechanical Advantage = 40 N Required Force = 15 N Thus, following the formula of mechanical advantage, MA = \({{Load} \over Effort}\) = \({{40} \over 15}\) = 2.7 \(\therefore\) It is generally seen that MA is a ratio of two same quantities, which makes it not have any unit. It is considered a constant for the given system. |
Working Mechanism of Wheel and Axle
[Click Here for Previous Year's Questions]
Wheel and axle is a simple machine in which the exerted force and the force of friction are in opposite directions. Due to this, the object is able to move forward with the minimum amount of resistance. The friction that is produced between the wheel and the axle results in displacement that causes the motion of the object.
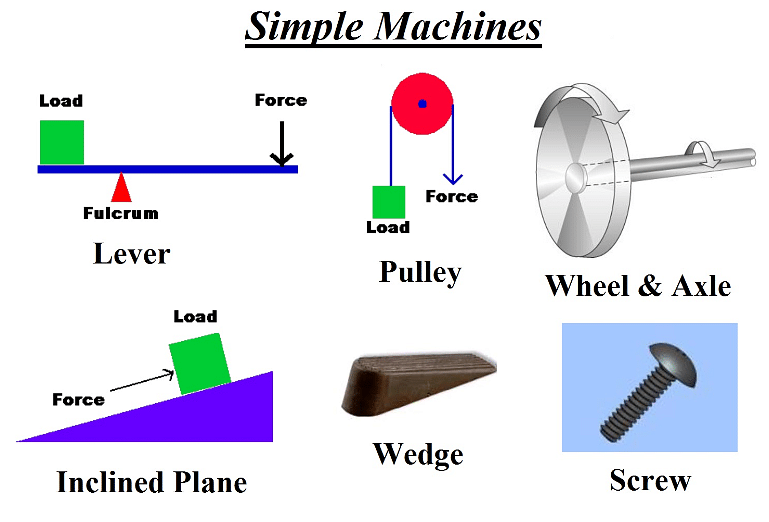
Other Simple Machines
Examples of Wheel and Axle
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Now, let us take a look at some daily examples of the concept of wheel and axle in use:
- In a screwdriver, when we apply a force to the handle of the screwdriver (the wheel), the handle spins and multiplies the force and effort so that the output force of the shaft (axle) is greater.
- The locking mechanism of a door also uses the wheel and axle machine concept. The doorknob has its mechanism inside the door which can be controlled by the knob only. Since, we can’t turn the axle to open the door, we instead turn the wheel and that helps us operate the mechanism.

Examples of Wheel and Axle
In some cases, the force is applied on the axle, so that the force to the wheel is multiplied and it covers a great distance as the wheel is larger in size than the axle.
- For example, in the case of a windmill, the force is applied on the axle and a greater force is generated on the wheel (blades).
- A ceiling fan works on the same principle. As we turn the axle, the large wheel i.e. the blades of the fan are powered and the desired output is obtained.
- Turbines and fans also make use of the wheel and axle mechanism.
- When we turn the steering wheel of the car, the axle multiplies our effort and hence the wheels of the car are turned more.
Also Read:
Previous Year Questions
- Two discs are rotating about their axes, normal to the discs … [NEET 2013]
- A crowbar of length 120 cm has its fulcrum …
- Two discs of same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis … [NEET 2017]
- When a mass is rotating in a plane about a fixed point … [NEET 2012]
- Moment of Inertia of a thin uniform rod rotating about the perpendicular axis … [KCET 2015]
- The propulsion of a rocket is based on the principle of conservation of … [KEAM]
- A thin circular ring of mass m and radius R is rotating about … [KEAM]
- A solid sphere and a hollow sphere, both of the same size … [KEAM]
- A solid cylinder rolls down an inclined plane of height 3 m … [KEAM]
- From a circular ring of mass MM and radius R … [KEAM]
- If the angular momentum of a particle of mass … [KEAM]
- A ball of radius 11 cm and mass 8 kg rolls from rest down a ramp …
- The angular momentum of a rotating body changes …
- A child is standing with folded hands at the centre of a platform rotating …
- Five particles of mass …
- A sphere of diameter 0.2 m and mass 2 kg is rolling on an inclined plane …
Things to Remember
- The wheel and axle is a simple machine that has a wheel attached to an axle and that makes use of the concept of mechanical advantage.
- The driving force can be tangentially applied to the perimeter or the boundary of the wheel while on the axle, the load force can be applied.
- When huge work is done with the help of just a small amount of energy, it is referred to as a mechanical advantage. It is the ratio of the output to the input.
- The friction that is produced between the wheel and the axle results in displacement that causes the motion of the object.
- The wheel and axle is one simple machine amongst the other machines such as a lever, wedge, pulley, screw, and inclined plane.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is a wheel and axle? (3 marks)
Ans. A wheel and axle is a simple machine wherein the components of the machine that is the wheel and the axle changes the direction of the force applied so that the resulting motion is in a straight line.
- The Wheel is the round disc that is located on the external part of the machine
- Axle is a rod-like part or a rounded cylinder that is placed on the inside of the machine. The axle is further attached to the wheel and it helps to promote the movement.
Ques. Give some examples of wheel and axle. (5 marks)
Ans. The wheel and axle mechanism is used in our everyday life in a variety of objects. Some of them are:
- Analog Clock: The minute, hour, and second hands of a clock are attached to a cylindrical pin that is located at the center. The pin acts as an axle while the hands of the clock resemble a pin.
- Tires of car: The steering wheel acts as an axle. When force is applied on them, the tires of the car turn, producing motion.
- Bicycle: The force applied on the axle here initiates the motion in wheels of the cycle.
- Ferris wheel: The central point of the ferris wheel is the axle, the force of which initiates the motion of the wheel.
- Electric Fan: The force generated by the motor of the fan reaches the hub and helps in the movement of the blades of the electric fan.
Ques. State the working of wheel and axle. (3 marks)
Ans. Wheel and axle is a machine where the wheel is attached to a smaller axle so that the force is transferred from one body to another when these two machines rotate. The machine can be understood as a kind of lever wherein a drive force is tangentially applied to the boundary of the wheel and a load force is applied on the axle so that both the forces are balanced around a hinge known as the fulcrum. The wheel here is attached to the axle.
Ques. Answer the following questions: (5 marks)
a) What are simple machines?
b) Name some simple machines.
c) Name the three parts of a lever
Ans. a) Simple machines are simple tools that help us by completing the work or moving a load with very less force applied by a human. The force that is applied is known as effort.
- b) Wedge, screw, pulley, and inclined plane are some types of simple machines.
- c) The three parts of a lever are fulcrum, load, and effort.
Ques. What are the two types of wheel and axle machines? (3 marks)
Ans. The two types of wheel and axle machine are as follows:
- Machines where the force is applied to the axle:- In these machines, the force is applied to the axle of the machine, and therefore the wheel rotates at a rapid rate. The motion that is started from the axle gets transferred to the wheel. Some examples of this type of machine are ferris wheel, bicycle, etc.
- Machines where the force is applied to the wheel:- In these machines, the force is applied to the wheel of the machine and therefore the axle is rotated at a higher speed. Examples of this machine are pizza cutter, drill machine, windmill, etc.
Ques. What is the purpose of an axle? (3 marks)
Ans. An axle is a shaft or a rod that helps in the rotation of the wheels. The axle is the part that mainly supports the weight of the car. As the axles conduct the power which plays an important role in turning wheels of a vehicle, they are a necessary component in any vehicle.
Ques. How are wheels useful in daily life? (3 marks)
Ans. Wheels are the basis of vehicles as they help in transportation. Wheels can be used to move heavy machinery or loads from one place to another. As the wheels make use of rolling friction, the amount of force that is to be applied is comparatively less and therefore the motion takes place smoothly.
Ques. What is the mechanism of a wheel and axle machine? (3 marks)
Ans. In a wheel or axle machine, generally, there is some kind of force applied that either makes the wheel move or the axle. This applied force causes motion which brings the machine into play. The wheel of the machine rotates around an axle, or a fulcrum so that the motion continues. The friction between the axle and the wheel can be reduced by applying grease to the axle.
When both wheel and axle rub together against each other, such as when a heavy log slides across each other. The wheels eliminate or reduce the friction that is generated. Now, as the friction is reduced comparatively, it is easier to move and stay in motion.
Ques. Explain the mechanical advantage of a simple machine. (3 marks)
Ans. Now, as we know that power is the product of the force and velocity of an object.
Let us assume that a and b are the distances from the bearing wheels’ center to the edges of the wheel, represented as A, and edges of the axle, represented as B.
Let FA be the force that is applied to the edge of wheel A that is known as the input force while FB is the force that is generated at the outer edge of the axle B.
a/b then refers to the ratio of velocities of points A and B.
Therefore, the ratio of the output force to the input force, referred as mechanical advantage, is given by the following formula:
Mechanical Advantage = a/b = FA/FB
Ques. State the advantages and disadvantages of friction. (5 marks)
Ans. The advantages and disadvantages of friction are as stated below:
Advantages
Friction is beneficial in the following ways:
- Due to the presence of friction between the pen and the paper or chalk on the board, it becomes easier for us to write on paper or the board.
- The friction that exists between our feet and the ground makes it easier for us to walk and even run on the ground below us without falling.
Disadvantages
Despite of its many advantages, friction also have numerous disadvantages:
- In machines, as a result of friction, heat gets produced which is a type of waste of energy.
- Friction also results in the wear and tear of various parts in machines that are constantly in motion. Soles of the shoes also are weared out due to the friction that is generated between the shoes and the ground.
Ques. What are simple and compound machines? (5 marks)
Ans. The two types of machines are simple and compound machines. They can be understood as:
- A Simple Machine is a mechanical device that changes the magnitude or direction of a force. Generally, they are simple mechanisms that make use of mechanical advantage or leverage in order to multiply the force that is applied to make the motion easier. The simple machines either have few or no moving parts at all that can contribute to modifying force and motion. Some examples of simple machines are wheel and axle, the inclined plane, pulley, lever, screw, and wedge.
- Compound machines refer to a device that is formed from the combination of either two or more simple machines. An example of a compound machine is wheelbarrow. In a wheelbarrow, the functionality of a single wheel and axle is combined with the functionality of a lever. From these six basic simple machines, multiple compound machines can be formed by a combination of two or more. Examples of compound machines are a jack, shovel, and a can opener.
Also Read:



Comments