Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
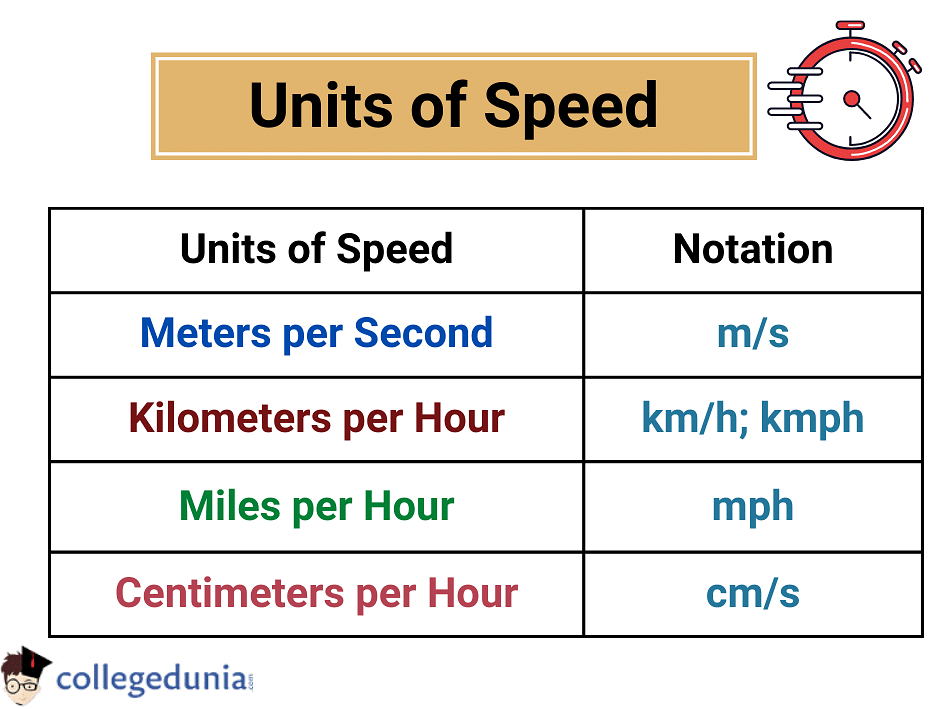
Unit of Speed is ‘meters per second’ (m/s). Speed is the rate of change in distance with time. SI unit of Speed is the combination of the standard units of distance and time. The unit of distance is meter (m) and the unit of time is second (s), thus, the SI unit of speed is meters per second (m/s).
- Speed is the distance covered by an object per unit of time.
- It is the ratio of the distance covered by the total time taken to cover that distance.
- Speed is a scalar quantity as it only has direction and no magnitude.
- The SI Unit of Speed is denoted as m/s or m.s-1.
- Other units of speed are kilometers per hour, feet per second, miles per hour, etc.
- Speed is calculated using the formula: Speed = Distance/Time
Read More: Measurement of Speed
Key Terms: Speed, SI Unit of Speed, Speed Formula, Distance, Time, Scalar, CGS Unit, Meters per Second, Magnitude, Unit Conversion
What is Speed?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Speed is the rate of change of position of an object moving in any direction.
- Speed is the ratio of the distance covered by an object to the time in which the distance was covered.
- It is a scalar quantity, with only magnitude and no associated direction.
Dimensional Analysis Video Explanation
Speed is the measurement of how fast an object moves to cover a distance.
- Speed can not have a negative value.
- The dimensional formula of Speed is M0.L1.T-1
- It is denoted by the symbol v and is measured in the units of meters per second (m/s).

Interesting Facts about Speed
|
SI Unit of Speed
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
SI Units are the standard units of measurement that are uniform throughout the world to avoid confusion. SI units of any physical quantity are laid out by the International System of Units (SI).
| The SI Unit of Speed is Meters per Second (m/s). |
- This standard unit of speed signifies how many meters an object can travel within a second.
- For instance, if an object travels 10 meters in a second, then, the speed of the object will be 10 m/s.
The SI unit of speed is derived from the standard units of Distance (meters) and Time (seconds). It can be understood as follows:
| \(Unit \hspace{1mm} of\hspace{1mm} Speed = \frac{Unit\hspace{1mm} of \hspace{1mm}Distance}{Unit \hspace{1mm}of \hspace{1mm}Time} = {m\over s}\) |
Read More:
Other Units of Speed
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Speed can be measured in various other units apart from its SI unit. In certain cases such as measuring a vehicle's speed, it is more sensible to use hours instead of seconds. Thus, kilometers per hour (kmph) or miles per hour are used to measure the speed of vehicles.
The different systems of measurement of speed are:
- CGS Unit of Speed: In the CGS system of units, length is measured in terms of centimeters and time in terms of seconds. Therefore we can derive the unit of speed as centimeters per second or cm/s.
- FPS Unit of Speed: FPS Units belong to the category of imperial units. Here, length is measured in terms of foot and time in terms of the second. Therefore, the unit of speed can be expressed as a foot per second or ft/s.
Read More: Difference Between Speed and Velocity
Conversion of Units of Speed
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
The unit conversion of the different units of speed from CGS to SI system and vice versa can be done with the help of the given table:
| Units | Conversion |
|---|---|
| Km to Cm | 1 km = 100000 cm |
| Km to M | 1 km = 1000m |
| Cm to m | 1 cm = 0.01m |
| M to mm | 1 m = 1000 mm |
| Cm to mm | 1cm = 10 mm |
| Hour to min | 1 h = 60 min |
| Min to sec | 1 min = 60 sec |
Speed Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
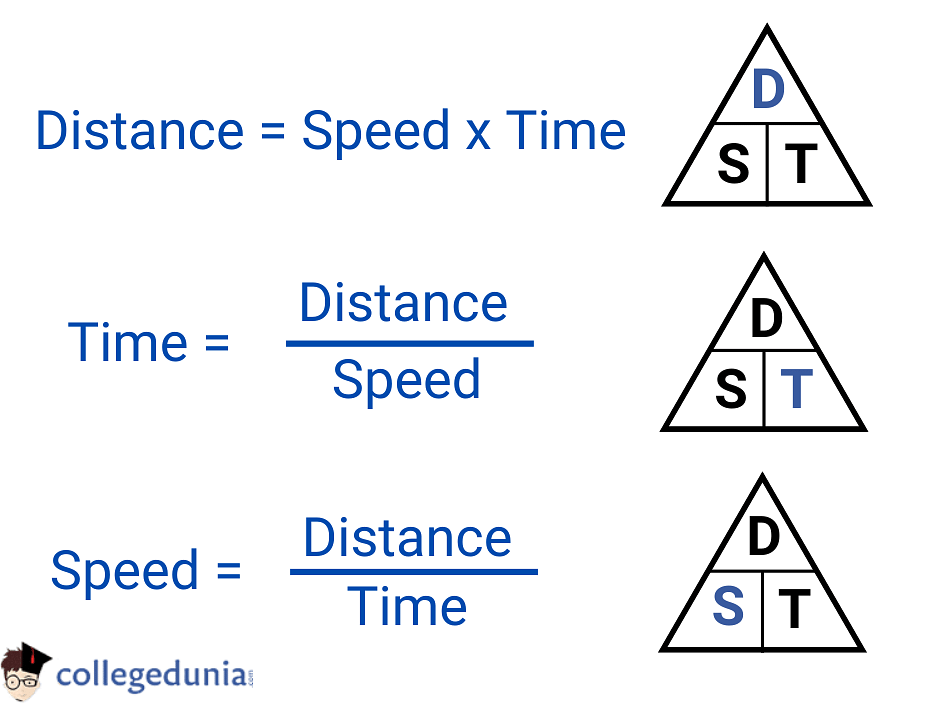
Speed is the ratio of the distance covered by an object to the time taken to cover that distance. Speed can be calculated using the given formula:
\(Speed = {Distance \over Time}\)
Using the appropriate symbols for all the physical quantities, the Speed Formula is expressed as:
| \(v = {d \over t}\) |
Where
- d is the Distance covered by an object measured in meters (m).
- t is the time taken to cover the distance measured in seconds (s).
- v denotes the Speed of an Object measured in m/s.
Speed, Distance, and Time Formula
Solved ExampleExample: A train covers a distance of 120 km in an hour. What will be the speed of the train in m/s? Solution: It is given that
Using the Speed Formula, Speed of Train = 120000/3600 = 33.3m/sec Thus, the speed of the train is 33.3 m/s. |
Things to Remember
- Speed is the rate at which an object travels over a certain distance.
- Speed is a scalar quantity with only direction and no magnitude.
- It is measured in terms of distance divided by time.
- Speed Formula is given as Speed = Distance/Time.
- The SI unit of Speed is meters per second (m/s).
- The CGS unit of speed is centimeters per second (cm/s).
- The FPS unit of speed is foot per second (ft/s).
- The speed of vehicles is always measured in terms of Kilometers per hour (kmph) or miles per hour (mph).
Previous Years’ Questions
- A block of mass of 1 kg is moving on the x-axis… [UPSEE 2017]
- If a body moves for 2 s with 15 m/s velocities towards the east and then moves… [JCECE 2006]
- A packet is dropped from a flight ascending with a velocity at a height of… [KEAM 2013]
- The position x of a particle with respect to time t along… [NEET 2007]
- The apparent frequency observed by a moving observer away from… [KEAM]
- The variation of speed (in m/s) of an object with time… [KEAM]
- The linear momentum p of a body varies with time and it is given by…
- The velocity of an object moving in a straight line path is given as…
- A child is swinging a swing. Minimum and maximum heights of swing from… [JCECE 2004]
- Hie equation of motion of a panicle is given by… [TS EAMCET 2018]
- The nature of a graph drawn for a freely falling body with time on… [TS EAMCET 2019]
- A body moving with uniform acceleration describes 40 m in the first… [COMEDK UGET 2004]
- The displacement time graph for two bodies A and B are straight lines… [COMEDK UGET 2004]
- What will be the ratio of speed in the first two seconds to the speed in the next…
- If a person sitting in a train moving with a constant velocity along a straight line…
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the SI Unit of Speed? (1 Mark)
Ans. The SI unit of Speed is meters per second (m/s). Speed is defined as the distance traveled per unit of time. Meter is the SI unit of distance, and the second is the SI unit of time, hence the SI unit of speed is m/s.
Ques. What is Speed? (1 Mark)
Ans. Speed is defined as the rate of change of distance with respect to time. It is the ratio of the distance covered by an object with respect to the time it takes to cover that distance. Speed is calculated using the given formula:
\(Speed = {Distance \over Time}\)
Ques. A car covers 20 km in 50 minutes. Find the speed of the car using the speed formula. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- Distance covered by Car = 20 km = 20×1000 = 20000 m
- Time Taken = 50 minutes = 50×60 = 3000 second
Using the Speed Formula,
Speed = Distance/Time
Speed of Car = 20000/3000 = 6.67m/s
Thus, the speed of the car is 6.67m/s.
Ques. What is the unit of speed of light? (1 Mark)
Ans. The units used to express the speed of light are the same as those used to express the speed of normal objects. The SI unit of speed is m/sec, although one may use miles per hour or any other speed unit.
Ques. Convert 60 km/h into m/sec. (2 Marks)
Ans. Given speed is 60 km/h.
- 1 km = 1000m
- 1 hour = 3600 seconds.
On conversion of the speed, we get
60 x 5/18
16.66 m/sec
Ques. What are the types of Speed? (2 Marks)
Ans. There are four main types of Speed which are as follows:
- Uniform Speed
- Variable Speed
- Average Speed
- Instantaneous Speed
Ques. Convert 150 m/s to km/h. (2 Marks)
Ans. Given speed is 150 m/s.
- 1 m = 1/1000 km
- 1 second = 1/3600 hours
On simplification, we get
150x 18/5
540 km/h
Ques. What do you mean by Uniform Speed? (1 Mark)
Ans. If an object covers an equal distance in an equal interval of time, then the object is said to be moving with a uniform speed. An example of uniform speed will be a body sliding on a frictionless surface with a constant speed.
Ques. Determine which is a higher speed:155 km/h or 75 m/s. (2 Marks)
Ans. To compare, we need to first convert 75 m/s into km/h.
Converting 75 m/s into km/h, we get
75 * 18/5
270 km/h
Now, between 155 km/h and 270 km/h, 270 km/h is a higher speed, because the distance covered in an hour is more than 155 km/h.
Ques. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have a zero displacement? If yes, support the answer with an example. (1 Mark)
Ans. Yes, the object in spite of moving through a distance can have a zero displacement. For example, if an object travels from point ‘A’ and reaches the same point ‘A’, then its displacement is zero as the initial and final positions of the object are the same.
Ques. Distinguish between speed and velocity. (2 Marks)
Ans. The difference between speed and velocity is as follows:
| Velocity | Speed |
|---|---|
| Velocity is the rate at which an object changes position in a particular direction. | Speed is the rate at which an object covers a certain distance per unit of time. |
| Velocity is a vector quantity as it has direction. | Speed is a scalar quantity as it does not have direction. |
| The velocity of an object can be zero, negative, or positive. | The speed of an object can never be negative or zero. |
Ques. It took 2s after lightning for the sound of thunder to reach a person. How far did the lightning strike? The speed of sound is 346 m/s in air. (3 Marks)
Ans. The speed of sound is 346 m/s in air.
- Time Given: 2s
- Distance Covered:?
We know that,
Speed = Distance/Time
- Distance = Speed x Time
- Distance = 346 x 2 = 692 m
Thus, the lightning struck 692 m away from the person.
Check-Out:





Comments