Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
Average Speed is the total distance traveled by an object in a particular interval of time. Average Speed is calculated when the speed of a moving object is not always constant and varies across a period of time. It is a scalar quantity as it has magnitude only and no direction. Average Speed is calculated when the total distance covered is divided by the total time taken. With the help of average speed, we can find a single value to represent the entire motion using the values of total time and the total distance covered in the case of varying speeds. The SI unit of average speed is m/s (meters per second).
| Average Speed = Total Distance Traveled / Total Time Taken |
Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Motion in a Straight Line
Key Terms: Average Speed, Speed, Distance, Time, Displacement, Velocity, Average Velocity, Motion, Average Speed Formula
What is Average Speed?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Average Speed is defined as the total distance traveled by an object to the total time taken. The speed of an object keeps on changing throughout the journey. In such cases, the average speed is calculated to find a uniform rate that describes the entire motion.
- Average speed is a scalar quantity with only magnitude.
- Average speed is the ratio of the total distance traveled by the body to the time taken to cover that distance.
- The SI unit of Average Speed is m/s.
- Average Speed is denoted by the symbol ‘S’.
Motion in a Straight Line Video Explanation
Read More:
Average Speed Formula
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Average Speed Formula is used to calculate the uniform rate in a situation with varying speeds during the course of a journey. Average speed has no direction and is indicated by the magnitude.
Average Speed Formula is given by dividing the total distance traveled by the body by the time taken to cover that distance.
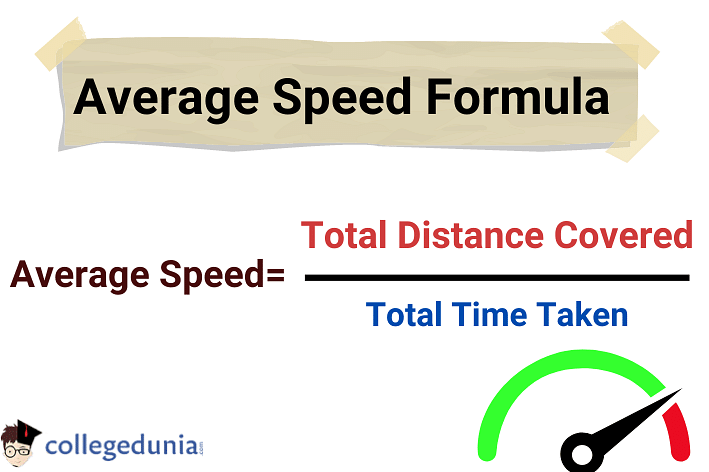
| \(Average\, Speed = {Total\,Distance\,Covered\over Total\,Time\,Taken}\) |
Mathematically, Average Speed Formula is given as:
| \(S_{avg} = {D_{Total} \over T_{Total}}\) |
Average Speed Formula
Solved ExampleExample: A bus travels at a speed of 300 km/hr for 2 hours and then slows down to 220 km/hr for the next 2 hours. Calculate the average speed of the train. Solution: First, we will calculate the total distance,
Using the average speed formula, Average Speed of Bus = Total Distance Travelled (D) / Total Time Taken (T) Average Speed of Bus = 1040/4 = 260 m/s |
Read More: Motion in a Straight Line
Average Speed Formula Derivation
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Consider that a boy walks up to his school at varying speeds say v1, v2, v3, …., and so on, over time intervals of t1, t2, t3,…, and so on. Thus,
- Total Distance Travelled = v1t1 + v2t2 + v3t3 + …. Vntn
- Total Time Taken = t1 + t2 + t3 + ….. + tn
To calculate a uniform speed to describe his motion, the average speed at which the boy covers the distance will be
Vavg = (v1t1 + v2t2 + v3t3 + . . . . + vntn) / (t1 + t2 + t3 +. . .+ tn)
Thus, the average speed formula is derived by dividing the total distance covered by an object by the total time taken to cover that distance.
Read More: Motion in a Straight Line Important Questions
Average Speed Formula Solved Examples
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Here are a few examples of Average Speed Formula to understand the concept better:
Example 1: An object moves with a speed of 4m/s for 20 seconds and then again moves with a speed of 6m/s for another 20 seconds and finally moves with a speed of 8m/s for the next 20s. What will be the average speed of the object?
Solution: We know that,
Distance = Speed x Time
- Distance Travelled in First 20s, D1 = 20s × 4 m = 80 m
- Distance Travelled in Next 20s, D2 = 20 × 6 m = 120 m
- Distance Travelled in the Last 20s, D3 = 20 × 8 m =100 m
- Total Distance Travelled D = 80 + 120 + 160 m = 360 ms
- Total Time Taken, T = 20 × 3 = 60s
Using the Average Speed Formula,
- Average Speed = Total Distance Travelled (D) / Total Time Taken (T)
- Average Speed of Object = 360/60 m/s = 60 m/s
Thus, the average speed of the object is 60 m/s.
Example 2: A ball moves from Point A to Point B in 10s and returns back in 8s. If the distance between points A and B is 36m, what will be the average speed of the person?
Solution: Given that,
- Total Distance Covered = 2 x 36 = 72m
- Total Time Taken = 10 + 8 = 18 s
Using the Average Speed Formula,
- Average Speed = Total Distance Travelled (D) / Total Time Taken (T)
- Average Speed of the Ball = 72/18 = 4 m/s.
Thus, the average speed of the ball is 4 m/s.
Average Speed Formula Special Cases
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Average Speed Formula is applicable in different cases which are described as below:
Case 1
For an object traveling with a speed of s1 for time t1, and the speed of s2 for time t2, the average speed formula is given below. The distance is given by the product of s1×t1, and s2×t2.
\(S_{avg} = {s_1 \times {t_1} + s_2 \times {t_2}\over t_1 + t_2}\)
Case 2
When 'n' different speeds, s1, s2, s3,...sn are given for 'n' respective time intervals, t1, t2, t3,...tn respectively, the average speed formula is given as
\(S_{avg} = {s_1t_1 + s_2 t_2 + ....+s_nt_n\over t_1 + t_2+....+t_n}\)
Case 3
When different distances, d1, d2,d3,...dn, are covered for different intervals of time, t1,t2,t3,...tn, the average speed formula is given as:
\(S_{avg} = {d_1+d_2 + d_3 +....+d_n\over t_1 + t_2+t_3+....+t_n}\)
Case 4
When different speeds, s1, s2, s3,...sn, are given for different distances, d1,d2,d3,...dn respectively, average speed formula is given as
\(S_{avg} = {d_1+d_2 + d_3 +....d_n\over {d_1\over s_1} +{d_2\over s_2} + {d_3\over s_3}+....+{d_n\over s_n}}\)
Case 5
When two or more speeds are given (s1, s3, s3,...sn) such that those speeds were traveled for the same amount of time (t1 = t2 = t3 =...tn = t) is given, the average speed formula is given as
\(S_{avg} = {s_1t_1 + s_2 t_2 + ....+s_nt_n\over t\times n} = {s_1+ s_2 + ....+s_n\over n}\)
Check More:
Difference between Average Speed and Average Velocity
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Here are the key differences between Average Speed and Average Velocity:
| Average Speed | Average Velocity |
|---|---|
| Average Speed is the ratio of total distance traveled to total time covered. | Average Velocity is the ratio of displacement and total time taken. |
| It is a scalar quantity as it has magnitude only. | It is a vector quantity as it has both direction and magnitude. |
| Average Speed is always positive. | Its value can be zero and both positive and negative. |
| Average speed is always more than the quantity of average velocity. | Average velocity cannot be greater than the average distance. |
Difference between Distance and Displacement
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The key differences between Distance and Displacement have been tabulated below:
| Distance | Displacement |
|---|---|
| Distance is the total length or magnitude of the path from the initial point to the final point. | Displacement is the shortest distance from the initial to the final points. |
| Distance is a scalar quantity which means it has magnitude only. | Displacement is a vector quantity which means it has both magnitude and direction. |
| Distance is always a positive value. | Its value can be zero and both positive and negative. |
Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 Handwritten Notes
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Given below are the handwritten notes on Motion in a Straight Line and related concepts:




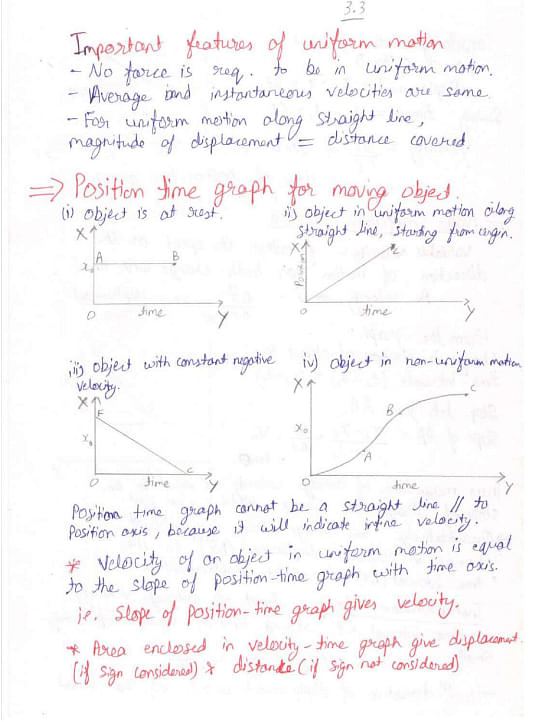



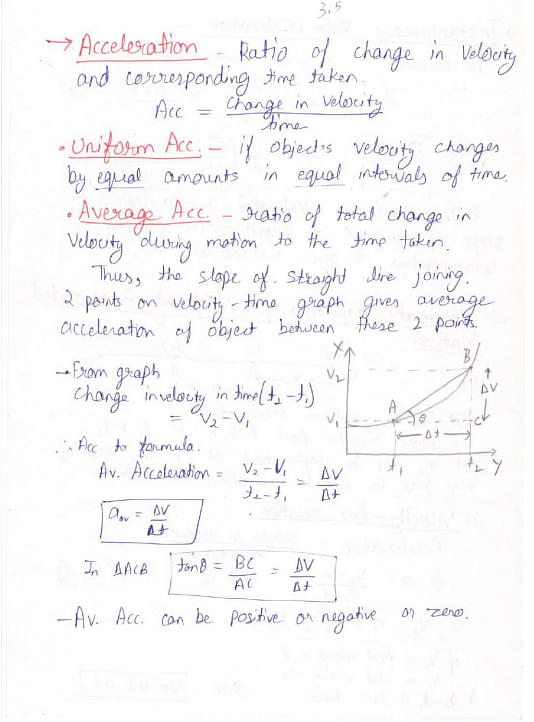







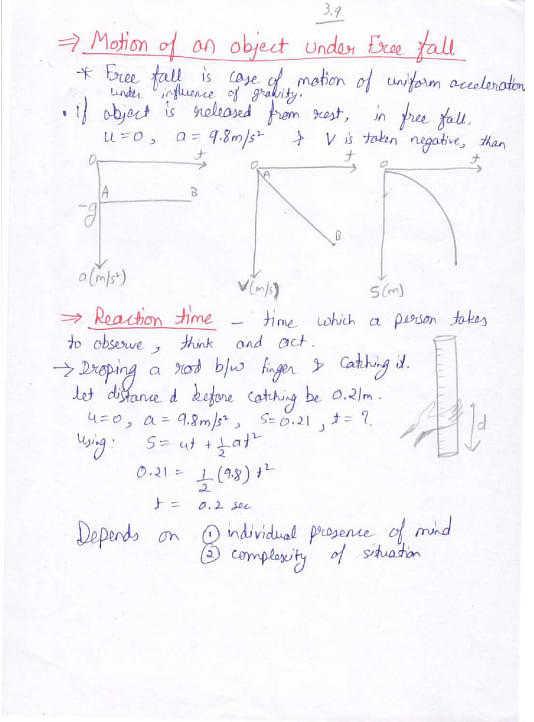
Things to Remember
- Average Speed is defined as the mean value of the speed of an object over a period of time.
- It is a scalar quantity with only magnitude and no direction.
- Average Speed is calculated by dividing the total distance covered by the total time taken.
- Average Speed Formula = Total Distance Covered / Total Time Taken
- The value of average speed can never be zero or negative.
- Speed is measured through a device called an odometer.
Previous Years’ Questions
- A body is traveling towards East with a speed of… (JKCET 2015)
- A man can swim at a speed of 4 km/h…
- A vehicle travels half the distance L with speed…
- A bullet of mass 40g moving with a speed of…
- The ratio of angular speed of a second-hand to the hour-hand… (KCET 2015)
- A wheel has a speed of 1200 revolutions per minute and is made…
- The motion of a particle in a straight line is an example of… (JKCET 2013)
- A particle is moving along a straight line path according to the…
- For a particle moving in a straight line, the displacement of the particle… (NTA Abhyas 2020)
- A particle moving in a straight line covers half the distance with speed… (KEAM)
Sample Questions
Ques. In a journey from Delhi to Lucknow, a car travels a distance of 70 km in its first hour and a distance of 65 km in its second hour. Find the average speed of the car during the entire journey. (3 Marks)
Ans. Using the average speed formula,
Average Speed = Total Distance Covered / Total Time Taken
Given,
- Distance traveled by car in first hour = 70 km
- Distance traveled by car in the second hour = 65 km
Therefore, the total distance covered by the car = 70 + 65 =135
Total time taken = 1h + 1h = 2h
Thus, Average Speed = 135/2 = 67.5 km/h
Ques. What is the relationship between average speed, total distance covered, and total time? (2 Marks)
Ans. The average speed formula is given as
Average Speed = Total distance covered / Total Time taken
The formula implies that average speed is directly proportional to the total distance covered and inversely proportional to the total time taken.
Ques. On a roundtrip from Goa to Mumbai, a bus driver of a tourist bus covers 600 km with a speed of 70km/h traveling from Mumbai to Goa, and on returning it covers the same distance at the speed of 80km/h. Find the average speed of the tourist bus. (5 Marks)
Ans. We know that,
Speed = Distance/Time
So, Time = Distance/Speed
Let us individually calculate the time duration taken by the bus in individual cases
Case 1: Distance travelled from Mumbai to Goa (D1) = 600km (given)
Speed (S1) = 70km/h (given)
Therefore, Time taken (T1) = distance/time(given)
= 600/70 = 8.5h
Case 2: Distance travelled from goa to Mumbai (D2) = 600(given)
Speed (S2) = 80km/h(given)
Therefore, time taken (T2) = 600/80 =7.5h
Now, the average speed of the tourist bus is = total distance covered / total time taken
= D1+D2/T1+T2
= 600+600/8.5+7.5 = 1200/16 = 75km/h
Hence, the average speed of the tourist bus for a round trip from Mumbai to Goa is 75km/h.
Ques. In a long journey of 1000 km, a bus travels the first 500 km at the speed of 50km/h. What should be the average speed of the bus so that it covers the distance of the next 500 km in 8h? Also, find the average speed of the bus for the entire journey. (3 Marks)
Ans. Case 1: Distance Traveled = 500 km (Given)
Speed = 50km/h(given)
We know that speed = distance/time
Therefore, time taken= 500/50 =10h
Case 2: Distance Traveled = 500km (Given)
Speed = Distance/Time = 500/8 = 62.5km/h
Average Speed = Total Distance Covered/ Total Time Taken = 1000/18 = 55.5km/h
Ques. What is Average speed? Give its formula. (2 Marks)
Ans. Average speed is defined as the total distance covered divided by the total time taken to cover that distance. The average speed formula is given as:
Average Speed = Total distance covered / Total Time taken
Ques. A car travels at a speed of 45 km/hr for 5 hours and then slows down to 40 km/hr for the next 2 hours. What will be the average speed using the average speed formula? (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- Distance 1 = 45 × 5 = 225 miles
- Distance 1 = 40 × 2 = 80 miles
Total Distance D = Distance 1 + Distance 2
D = 225 + 80 = 305 miles
Using the Average Speed Formula,
Average Speed = Total distance traveled ÷ Total time taken
Average Speed = 305 ÷ 7 = 43.57 m/s.
Thus, the average speed of a car is 43.57 m/s.
Ques. In 24h an artificial satellite covers a certain distance when revolving in a circular orbit of radius 42250 km. Find the average speed of the satellite. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given,
- The radius of circular orbit = 42250km
- Time taken = 24h
Distance covered by the satellite in 24 hours is:
We know that distance covered by a satellite = Circumference of the circular orbit
= 2πR = 2 x 3.14 x 42250
= 265330 km
we know that average speed = total distance covered/ total time taken
Therefore, the average speed of the satellite becomes = 265330/24 = 11055km/h
Ques. At the start of a trip, a taxi driver notes the reading of the odometer of the car, which is 15000km. At the end of the journey, the driver notices that the reading of the odometer reads as 1550km. Find the average speed of a taxi in km/h and m/s if the complete duration of the journey is 20h. (3 Marks)
Ans. Initial distance=15000km
Final distance= 20000km
Total Distance covered =final distance - initial distance =1550-1500
= 500km or 500000 meters
Total time taken = 10 h(given)
We know that average speed =
Total distance covered/Total time consumed
Therefore, average speed of taxi in km/h = 500/10 = 50km/h (km/h)
Average speed of taxi in m/s = 500000/60 = 8333m/s (m/s)
Ques. Define the term displacement. (2 Marks)
Ans. Displacement is the vector quantity, where a person can calculate both its direction as well as magnitude. It is the shortest distance calculated from the starting point and the endpoint. It is to be noted that the value of displacement can be 0, positive, or even negative.
Ques. Is average speed a scalar or a vector quantity? (1 Mark)
Ans. Average Speed is a scalar quantity as it has only magnitude.
Check-Out:




Comments