Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Carbonate ion is the simplest form of oxocarbon anion. It is a polyatomic ion which has the formula CO32-. An ion is a net electrically charged atom or molecule. The charge of an electron is traditionally thought to be negative, and it is equal to and opposite the charge of a proton, which is traditionally thought to be positive. The term "carbonate" can refer to both carbonate minerals and carbonate rock (which is primarily made up of carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, CO32-. In this article, we will discuss the definition, formula, structure, uses, and sample questions of the topic Carbonate ion.
| Table of Contents |
Keyterms: Ion, Anion, Carbon, Oxocarbon, Atom, Proton, Minerals, Carbonate rock, Carbon dioxide, Oxygen, Salt, Carbonation, Calcium carbonate
What is Carbonate Ion?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A carbonate ion in chemistry refers to an ion having a carbon atom with three other oxygen atoms or a molecule having this carbonate ion species as an anion. The molecular formula for the carbonate ion is CO32-.
- Carbonation is the process of increasing the concentration of bicarbonate and carbonate ions in an aqueous solution to produce carbonated water. Carbonation is accomplished by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts or by injecting pressurized carbon dioxide gas.
- Carbonates also refer to carbonate rocks and minerals that contain carbonate ions in geology. Calcium carbonate, or CaCO3, is the most prevalent, and it's found in limestone and dolomite.
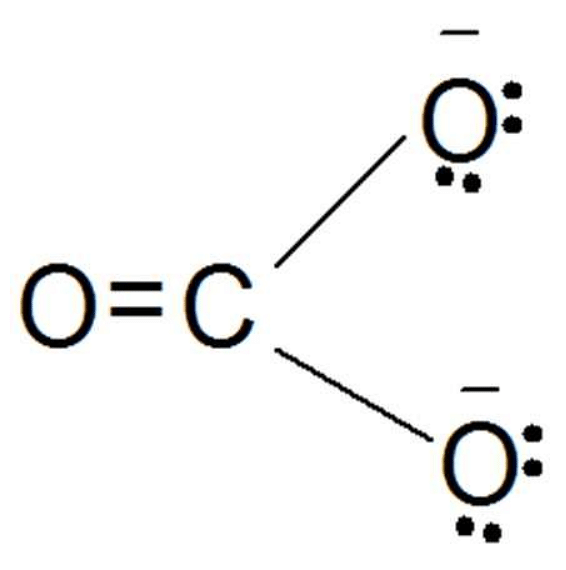
Carbonate Ion
Carbonate Ion Formula
Carbonate ion is an anion with a trigonal planar molecular structure. It is made up of one atom and three oxygen atoms. A Lewis base, by definition, draws protons in aqueous solutions.
- Chemical formula: CO32-
- Carbonate group C(=O)(O–)2
Localized Carbonate Ion
- It could be a relatively robust base. Alkali metals are frequently extracted from Na2CO3 or washing soda. Alkaline metal carbonates, except Li2CO3, are stable. Lithane was previously used to treat manic depressive patients.
- In the manufacture of glass, washing soda (soda ash) is utilized. Limestone is made of carbonate. Bicarbonate of soda is frequently isolated and sold, or heated to make washing soda.
Read More: Magnesium Carbonate
Structure of Carbonate Ion
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
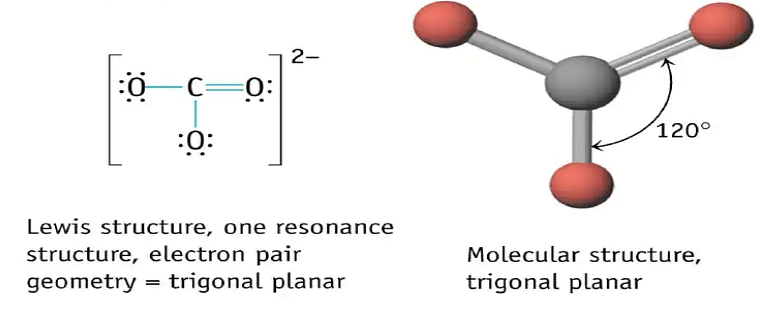
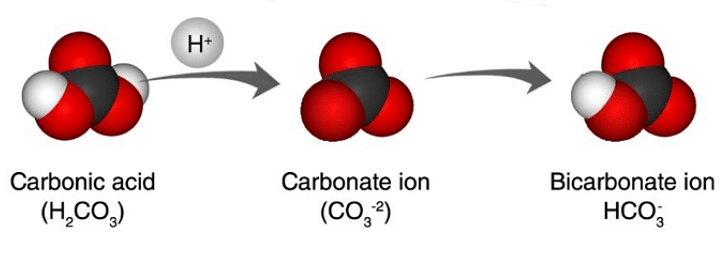
The carbonate ion is a polyatomic ion. One carbon atom and two oxygen atoms make up the simplest oxocarbon anion. With a molecular mass of 60 u, the ion exhibits a trigonal planar configuration. The formal charge of the carbonate ion is -2. It's a bicarbonate ion conjugate base (HCO-3), which is a carbonic acid conjugate base (H2CO3)
Now we'll take a closer look at the Lewis structure of the carbonate ion:
The anion has one double bond between a neutral oxygen atom and carbon in its Lewis structure. There are also two single bonds between two negatively charged oxygen atoms and carbon.
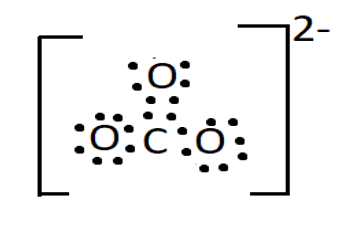
Lewis Structure of Carbonate Ion
Given the structure, one would assume that the two single bonds in the carbonate ion will be the same length and will be longer than the third bond, which is a double bond. However, it has been discovered that all three bonds are the same length, which is attributable to the resonance effect.
Carbonate ions have three resonant configurations, each with an identical bond length due to the interchangeability of double bonds.
Check out: Silver Carbonate
Properties of Carbonate Ion
The physical and chemical properties of carbonate ion are as given below:
Physical Properties
- Carbonates are solid at normal temperatures.
- Group-1 and group-2 carbonates are colorless, whereas transition element carbonates are colored.
- Carbonates that are present in group 2 are more covalent than those in group 1.
- The carbonate ion has a molar mass of 60.008 gmol-1 and a conjugate base of bicarbonate.
Chemical Properties
- Except for Li2CO3, all Group-1 carbonates are water-soluble.
- In water, Group-2 carbonates are only slightly soluble.
- In CO2 solutions, Group-2 carbonates are fairly soluble.
- Carbonates break down into oxide and carbon dioxide when heated.
- Group-1 and group-2 carbonates have greater thermal stability as they progress through the group.
Properties of Carbonate Ion
Carbonate Ion Reactions
All alkali metals form stable compounds when they react with their ions. Li2CO3 is an exception to the norm. Furthermore, the characteristics of lithium and magnesium are quite similar. A diagonal relationship is used to express their commonalities. It could be due to their similar sizes. As a result, lithium and its compounds do not react in the same way as other elements in Group 1.
Carbonate decomposes at temperatures above 840°C, producing carbon dioxide gas and leaving calcium oxide, a white solid.
CaCO3(s) → CO2(g) + Cao(s)
Carbonate, like all metal carbonates, interacts with acidic liquids to create CO2. This reaction is what causes limestone to fizz when weak hydrochloric acid is applied to its surface.
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) + CaCl2(aq)
- Calcination: CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
- Slaking: CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(s)
- Carbonation: Ca(OH)2(s) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Carbonate Ion Reactions
Uses of Carbonate
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Washing detergents contain carbonates such as potassium and sodium carbonates.
- Water softening agent
- Papers are made with these as raw ingredients.
- Used in the production of glass
- Carbonated water is created by dissolving CO2 in water under pressure.
Things to remember
- Alkali and alkaline earth metals are the most common elements utilized as carbonates.
- A trigonal planar structure consists of a carbon atom surrounded by three oxygen atoms.
- Metal carbonates disintegrate when heated, releasing carbon dioxide from the long-term carbon cycle into the short-term carbon cycle and leaving a metal oxide behind.
- Carbonates are carbonate rocks and minerals that contain carbonate ions in geology. Calcium carbonate, or CaCO3, is the most prevalent, and it's found in limestone and dolomite.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the process by which carbonate and water are produced from their ions? (3 marks)
Ans. As the hydrogen carbonates operate as both weak acids and weak bases, they are amphoteric. As a result, it behaves as an acid, reacting with soluble hydroxide solutions to produce carbonate and water.
KHCO3(aq) + KOH(aq) → K2CO3(aq) + H2O(aq)
Ques. What is the IUPAC name for Carbonate ion? (1 mark)
Ans. Trioxidocarbonate(2-) is the IUPAC designation for carbonate anion in a systematic additive sense.
Ques. What is carbonate ion? (2 marks)
Ans. A carbonate ion is made up of one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms. It has a negative charge of two units. The carbonate ion is referred to as a divalent ion since its charge is -2.
Ques. What is the reaction for calcination? (3 marks)
Ans. Calcination refers to the heating process of carbonate ores, solid chemical compounds to high temperatures in a limited supply or the absence of air. This is done to remove any impurities or volatile substances present for thermal decomposition.
Calcination: CaCO3(s) + CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Ques. What is the reaction to carbonation? (2 marks)
Ans. Carbonation is a reaction wherein the carbon dioxide undergoes a reaction to yield bicarbonates, carbonates, and carbonic acid.
Ca(OH)2(s) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Ques. What are the uses of carbonate ions? (5 marks)
Ans. The carbonate ions have multiple applications:
- Washing detergents contain carbonates such as potassium and sodium carbonates.
- Water softening agent
- Papers are made with these as raw ingredients.
- Used in the production of glass
- Carbonated water is created by dissolving CO2 in water under pressure.
Ques. What happens when 2+ ions interact with carbonate ions? (3 marks)
Ans. The 2+ Hexa aqua ions aren't acidic enough to release CO2. Similarly, you will continue to acquire a precipitate in these circumstances. It is, however, a precipitate of a substance known as "metal carbonate."
M2+(aq) + CO2−3(aq) → MCO3(s)
Also check:



Comments