Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Formal charge is a charge assigned to an individual atom in a molecule of covalent bonding. It is assumed that the chemical bonds are distributed equally between the atoms without considering relative electronegativity. The difference between the valence electron of an atom of a polyatomic molecule in the state of the element and the assigned number of electrons in the atom with Lewis structure is known as the formal charge of an ion or an atom of a polyatomic molecule.
Read About: Carbonate Ion Formula
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Formal charge, electron, atom, molecule, covalent bonding, electronegativity, valance
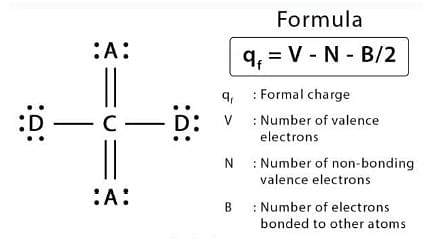
Formal charge formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Formal charge = (number of valence electrons in neutral atom) – (non-bonded electrons + number of bonds)
Or
F.C = [total number of valence e- in free state] – [ total number of e- assigned in lewis structure]
Or
F.C = [total number of valence e- in free state] – [ total number of non-bonding pair e- (lone pair)] – ½ [total number of bonding e- ]

How To Calculate Formal Charge
Read More: Magnesium Carbonate
The importance of formal charge
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- The formal charge doesn’t give any specific information about the real charge separation in the molecules as it is a theoretical concept
- Calculating the formal charges is important as it plays a crucial role in determining the minimum energy configuration among various possible Lewis structures in a molecule.
- The information about the minimum energy structure helps anticipate the important product of a reaction as well as elaborates a lot about the process.
- The structure with minimum energy consists of the least formal charge and the one where the total charge is mostly distributed.
Formal Charge
Read More: Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Significance of formal charge
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Molecular structure: a molecule in order to have the most stable state because of the lowest energy, should have a formal charge of zero.
- Resonance: When similar various molecular structures exist, it becomes difficult for the formal charge to indicate a molecule's preferred structure. If the arrangements of bonds are different in the molecules but they have similar atom arrangements, then the resonance structure can be helpful.
- Reactivity: the behaviour of a molecule during a process is determined by the formal charge of a molecule. An atom will be a nucleophile or a source of electrons in a reaction if it is a negative formal charge whereas an atom will be electrophile or is more like to take electrons if it has a positive formal charge.
Read More: Difference Between An Atom And Molecule
Things to remember
- FC = V – N - B2 Where V = no of valence electrons, N = number of non-bonding valence electrons, B = total number of electrons shared in bonds.
- Formal charges are a way of analyzing the electron distributions in a Lewis dot structure rather than indicating them as real changes
- The lone pair of electrons is known as unshared pairs or non-bonding pairs.
- The formal charge is the charge carried by an atom of a molecule presuming the electrons in the chemical bonding are equally shared among the atoms.
- A molecule should have a formal charge of zero in order to have the lowest energy state.
Sample questions
Ques. Calculate the formal charge on O atoms of O3. (2 Marks)
Ans: formal charge on O1 :
6- 6/2 – 2 = +1
Formal charge on O2:
6 – 4/2 – 4 = 0
Formal charge on O3:
6 – 2/2- 6 = -1
Ques. Calculate the formal charge on (i) Cl atom in HCIO4- ion (ii) S atom in HSO4- ion (2 Marks)
Ans: formal charge on
- Cl atom in HCIO4- ion
= 7 – 8/2 – 0 = 3
- S atom in HSO4- ion
= 6 – 8/2 – 0 = 2
Ques. Show the formal charge calculation of SO42- (4 Marks)
Ans: sulphur (S) atom:
Valence e- in Free State = 6
Number of non-bonding e- in Lewis structure = 0
No of bonding pairs in Lewis structure = 12
Formal charge = 6- 0- 12/2
= 6-6 = 0
Oxygen (O) -1:
Valence e- in Free State = 6
Number of non-bonding e- in Lewis structure = 4
No of bonding pairs in Lewis structure = 4
Formal charge = 6-4-4/2
6 -6 = 0
Oxygen (O) -2:
Valence e- in Free State = 6
Number of non-bonding e- in Lewis structure = 6
No of bonding pairs in Lewis structure = 2
Formal charge = 6- 6 – 2/2
= 6-7 = -1
Oxygen (O)-3:
Valence e- in Free State = 6
Number of non-bonding e- in Lewis structure = 4
No of bonding pairs in Lewis structure = 4
Formal charge = 6- 4 – 4/2
= 6-6 = 0
Oxygen (O) -4:
Valence e- in Free State = 6
Number of non-bonding e- in Lewis structure = 6
No of bonding pairs in Lewis structure = 2
Formal charge = 6- 6 – 2/2
= 6-7 = -1
Ques. Which atom will carry a formal charge in HCN? (2 Marks)
Ans: due to triple bonding, the carbon atom has 3 electrons and a single pair of electron that it owns. All together it has 7 electrons with the addition of 2 inner core electrons. Thus the carbon atom is formally negatively charged as its atomic number is 6.
Ques. What is the process in which the formal charges can be reduced? (2 Marks)
Ans: if formal charges 1+ and 1- are situated side by side, the formal charges can be reduced by having a single pair of electrons. The 1- charge shares atoms with the 1+ charge and becomes a bonding pair of electrons.
Ques. What does the formal charge of 0 represent? (2 Marks)
Ans: the formal charge is supposed to be zero if the number of electrons that are assigned is similar to the group number. The total charge of the molecule or ion consists of the addition of all the formal charges of each atom.
Ques. What is Lewis's structure? (2 Marks)
Ans: the representation of the valence shell electrons in a molecule in a simple way is known as the lewis structure. The arrangement of the electrons around each atom in a molecule is explained by the lewis structure.
Ques. What is the method to calculate the formal charge of O3? (3 Marks)
Ans: first the formal charge of each molecule has to be calculated after which the formal charge of all the individual atoms needs to be added up.
The formal charge of an atom = valence electron – ½ bonding electrons – nonbonding electrons
An ozone molecule consists of 3 oxygen atoms where the formal charge of each oxygen atom is 1.
The formal charge of oxygen atom 1 = 6 – 4/2 – 4 = 0
The formal charge on oxygen atom 2 = 6 – 6/2 – 2 = 1
The formal charge on oxygen atom 3 = 6 – 2/2 – 6 = -1
Therefore, the total formal charge of the ozone = 0 + 1 -1 = 0
Ques. What is the formal charge of NO2- (2 Marks)
Ans: FC = V-N – B/2
The formal charge in the nitrogen atom :
5 – 2 – 6/2
= 5-2-3
= 0
The formal charge in the double-bonded oxygen atom :
6- 4- 4/2
= 6 – 4 -2
= 0
The formal charge in the single-bonded oxygen atom:
6-6- 2/2
= 6 -6 -1
= -1
Ques. What is the formal charge of the sulfur atom in bisulphate ion? (2 Marks)
Ans: formal charge = valence electrons – (non bonding valence electrons) - bonding electrons2
Valence electrons = 6
Non bonding valence electrons = 0
Bonding valence electrons = 8
Therefore, formal charge = 6 – (0) – 8/2 = +2
Check-Out:



Comments