Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Bond order refers to the number of chemical bonds that are formed between two atoms in a molecule. The stability of a molecule is also dependent on these bonds, an increase in bond order also increases the stability. An increase in bond order also leads to an increase in bond enthalpy and decreases bond length. In order to calculate the bond order, the bond order formula is used. This article talks and discusses bond order and various important related concepts under the topic of bond order and bond order formulas.
| Table of Contents |
Keyterms: Bond Order, Atom, Molecule, Bond Enthalpy, Bond Length, Covalent bond, Chemical bonding
What is Chemical bonding?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Chemical bond refers to the attractive force which holds the constituents such as atoms together in a chemical species, it is this bond that keeps the atoms of a component held together. Chemical Bonding can take place in various ways, some of them are: covalent bond- a covalent bond refers to the chemical bond in which two atoms share one pair of electrons. Another way of chemical bonding is electrovalent bonding in which there is a complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another.
Also read: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
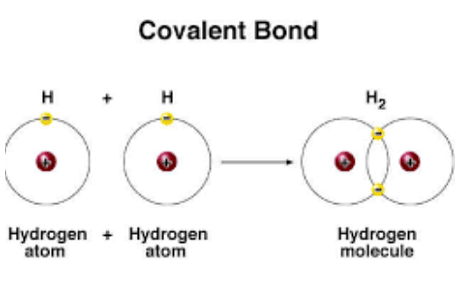
Covalent Bond
What is a Bond order?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bond order, hence, refers to the number of chemical bonds between two atoms in a molecule. Bond order plays an important role in the molecular orbital theory and it is also of significance in the valence bond theory. The concept of bond order was introduced by Linus Pauling. Bond order is also defined as the difference between the number of anti-bonds and bonds.
Bond order formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bond order formula is used to calculate the number of bonds. It is defined as the difference between the electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals divided by half.
Bond Order (BO) = ½ (Nb- Na)
Here Nb refers to the number of bonding electrons,
Na refers to the number of antibonding electrons
And here, the molecule will be stable if Na < Nb, and if Na > Nb, the molecule shall be unstable.
Importance of Bond order formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bond order formula is an important formula in chemistry. Bond order is important not only for helping us learn and understand important facts about chemical bonding such as bond length, bond angle, bond strength but it also helps us understand and learn about about atoms, the bonds that are made between atoms.
Also read: Bond Enthalpy
Solved Examples
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Ques. Using the bond order formula, find the bond order of hydrogen (H2) gas. (5 Marks)
Solution: (1) Before finding the bond order, we need to find the electronic configuration of H2.
Electronic Configuration of (Hydrogen gas) H2:
H2 has a total of 2 molecules in its molecule. Hence, its electronic configuration will be 1s1.
(2) After determining the electronic configuration one can find the bond order using the bond order formula.
Bond Order (b.o.) formula = ½ (Nb - Na) (Here, Na = antibonding electrons, Nb = bonding electrons)
Now applying this formula,
b.o. = ½ (2-0) = 1
(3) And hence, we get;
BOND ORDER OF H2 = 1
Ques. Find the bond order of C2 using the bond order formula. (5 Marks)
Solution: (1) Before finding the bond order we need to determine the electronic configuration of C2. The electronic configuration of C2 is as follows:
C2 has a total of 12 electrons, therefore its electronic configuration will be = (σ2s)2 (σ*2s) n(2px)2 n(2py)2
(2) Now we can calculate the bond order from the electronic configuration thus obtained will be
BOND ORDER (B. O.)= ½ (Na - Nb)
This gives us,
BOND ORDER (B. O.) = 2
Ques. Using the bond order formula to calculate the bond order of Bromine (Br2). (5 Marks)
Solution: (1) First step will be finding the electronic configuration of Bromine (Br2), its electronic configuration [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p5
(2) The next step will be to calculate the bond order of Bromine (Br2), using the bond order formula
B.O. = ½ (Na - Nb)
This gives us,
B.O. = 1
Ques. Find the bond order of Boron Nitride (BN) using the bond order formula. (5 Marks)
Solution: (1) First step in determining the bond order will be finding the electronic configuration of BN. The number of electrons in BN are 12 (5+7). Therefore, the electronic configuration of BN will be (σ1s2 σ*1s2) (σ2s σ*2s2) ( 2px2 = 2py2)
(2) Once we have determined the electronic configuration we can determine the bond order using the bond order formula, that is,
BOND ORDER (B.O.) = ½ (Na - Nb)
(3) Therefore, (B.O.) = 2
Ques. Using the bond order formula determine the bond order of O2. (5 Marks)
Solution: (1) Firstly, find the electronic configuration of O2.
Electronic configuration of O2 = (σ1s2 σ* 1s2 σ2s2 σ2p2z σ2p2x Π2p2y Π * 2p1x Π 2p1y)
(2) The next step will be to find the bond order using the formula
Bond order = ½ (Na - Nb)
This gives us the bond order as,
BOND ORDER = 2
Ques. Explain (i) bond strength (ii) bond length (iii) bond angle. (3 Marks)
Solution: (i) Bond strength refers to quite literally the strength or how strongly the atoms present are bonded. When the number of electrons connected increases the strength of the bond between the atoms also increases.
(ii) Bond Length refers to the distance in average between the atoms that are bonded.
(iii) Bond Angle refers to the average angle between the two bonded electrons around the atom.
Ques. Explain briefly what is a bond order. (3 Marks)
Solution: Bond order refers to the number of chemical bonds that exist between the two atoms present. An increase in bond order means there is a higher level of attraction among the atoms. It also means that there is a higher level of stability in the atoms.
Ques. Why is bond order considered important in relation to bond strength and bond length? (3 Marks)
Solution: Bond order has an important relation with bond strength because bond order impacts the bond strength of the component as well. Both are directly proportional, that is, with an increase in bond order, there is an increase in bond strength as well. In terms of bond length, the relation is rather inverse because with an increase in bond order the bond length decreases. Bond order also impacts the stability of the chemical bond as well.
Ques. Determine the bond order of carbon monoxide (co). (5 Marks)
Solution: (1) First step here will be to determine the electronic configuration of carbon monoxide(co). Carbon Monoxide has 14 electrons and its electronic configuration is:
(σ1s) 2(σ*1s)2(σ2s)2(σ*2s)2(Π)4(2pz)2
(2) Once the electronic configuration is obtained, the bond order can be calculated using the formula:
BOND ORDER = ½ (Na - Nb)
This gives us the answer as,
Bond order of Carbon Monoxide (CO) = 3
Ques. Use the bond order formula to determine the bond order of Nitrogen gas(N2). (5 Marks)
Solution: (1) The first step will be to find out the electronic configuration. The electronic configuration of N2 is: ( σ1s σ* 2 σ2s2 σ* 2s2 Π2px2 Π2py2 Π2p2z)
(2) The next step will be to determine the bond order using the formula, that is,
BOND ORDER = ½ (Na - Nb)
Therefore, the bond order of N2 is,
BOND ORDER of N2 = 3
Read Also:



Comments