Rhiti Mohanta Content Curator
Content Curator
Chemical bond is a group of atoms held together in a chemical compound. Chemical bonding is very important for living beings as all the compounds and enzymes required by our body are held by a chemical bond.Ionic Bond or Electrovalent Bond is a kind of linkage that is formed from the electrostatic connections between two of the oppositely charged ions of those particular chemical compounds. Whereas, the mutual sharing of one or more pairs of electrons can be described as the Covalent Bond. On the other hand, the forceful bond that holds the atoms together in a metallic substance, is known as the Metallic Bonds.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms- Ionic Bonds, Covalent Bonds, Metallic Bonds, Differences, chemical Bondings
What are Ionic Bonds?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are certain atoms that tend to become more stable when losing or gaining one electron.
An ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between two ions having an opposite charge.
- Metallic elements form compounds with non-metallic elements through ionic bonds due to huge differences in their electronegativity.
- Solid compounds which are bonded with these bonds are crystalline in nature and have low electrical conductivity, which is due to the absence of free electrons.
- Examples of ionically bonded compounds are - LiF, NaCl, CaF2, BeO.
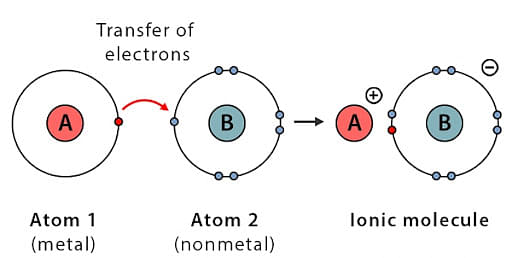
Ionic Bonds
Covalent Bonds
[Click Here for Previous Year's Questions]
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share their valence electrons with each other. Covalent bonds are formed between atoms having small differences in electronegativity.
- Two same atoms can also have a covalent bond.
- Example- fluorine needs one electron to complete its octet , similarly, two fluorine atoms share their valence electrons with each other to form a covalent bond and become stable.
- Covalently bonded molecules are found in all three states - solid, liquid, and gas. Some examples of covalent molecules are hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, diamond, silica, etc.
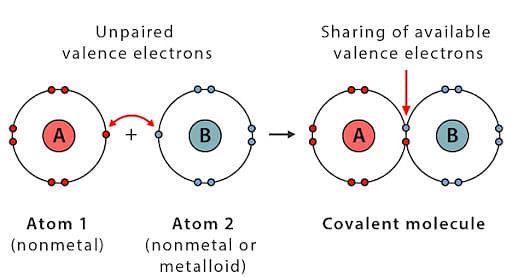
Covalent Bond
Metallic Bonds
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In a metal lattice, valence electrons are loosely attached by the nuclei of other atoms. Thus the valence electrons require very low energy to release themselves from nuclei. When these electrons come out of the atom, the atom becomes positively charged. All these atoms of the metal are surrounded by free negatively charged electrons which are also called the electron cloud. Electrostatic forces are developed between these ions and electrons. These are called metallic bonds.
- Almost every metal atom releases a free electron.
- These electrons are indistinguishable from each other therefore these are called delocalized electrons.
- Because of these free electrons, metals are good conductors of electricity. Example - iron, copper, silver, nickel, etc.
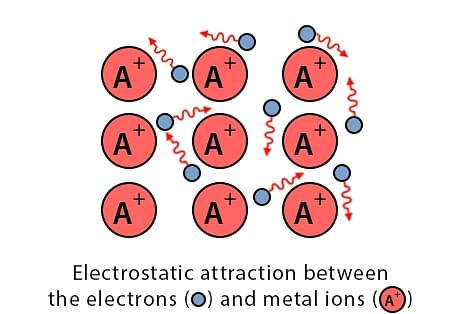
Metallic Bonds
Also Read:
| Related Links | ||
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Lewis Dot Structure | Octet Rule |
| Formal Charge | Lattice Enthalpy | Bond Parameters |
| Resonance Structures | Polarity | Dipole Moment |
Difference between covalent, ionic bonds ,and metallic bonds:
[Click Here for Previous Year's Questions]
The difference between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds is as given below:
| Ionic bonds | Covalent bonds | Metallic bond |
|---|---|---|
| Occurs during transfers of electron | Occurs when two atoms share their valence electron | The attraction of metal cations/atoms and delocalized electrons |
| Binding energy is higher than the metallic bond | Binding energy is higher than the metallic bond | Binding energy is less than the covalent and ionic bond |
| Low conductivity | Very low conductivity | Has very high electrical conductivity |
| Non-directional bond | Directional bond | Non-directional bond |
| Present only in one state-solid state | Present only in three states: solid,liquid and gas. | Present only in one state - solid state |
| Non-malleable | Non-malleable | malleable |
| Higher melting point | Lower boiling point | High boiling point |
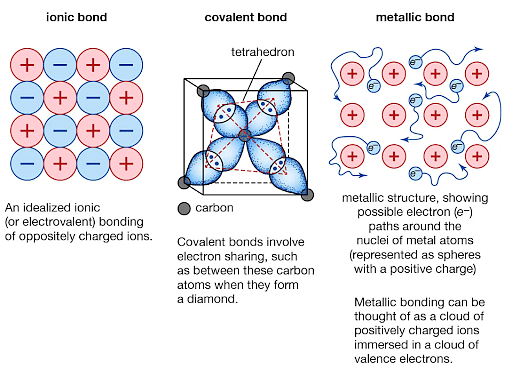
Differences Between Ionic, Covalent and Metallic Bonds
Things to remember
- An ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between two ions having an opposite charge.
- Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share their valence electrons with each other.
- Only metallic bonds are electrically conducting.
- Only covalent bonds are directional bonds.
- Ionic bonds have a higher melting point.
- Covalent bonds are found in all the three states of matter - solid, liquid and gas
- Metallic bonded elements are malleable in nature.
- In metallic bonds, almost every metal atom releases a free electron. These electrons are indistinguishable from each other therefore these are called delocalized electrons.
Previous Year Questions
- Which of the following has a regular geometry?
- Which of the following has the strongest H-bond ?
- The paramagnetic property of the oxygen molecule is due to the presence of unpaired electrons present in...[KEAM]
- Among the following molecules: SO2,SF4,ClF3,BrF5SO2,SF4,ClF3,BrF5 and XeF4XeF4, which of the following shapes does not describe any of the molecules mentioned?[KEAM]
- The covalent bond length is the shortest in which one of the following bonds?[KEAM]
- Consider the following species 1 . [O2]2−[O2]2− 2. [CO]+[CO]+ 3. [O2]+[O2]+ Among these sigma bond alone is present in[KEAM]
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding exists in[KEAM]
- In which one of the following compounds does the central atom obeys the octet rule?[KEAM]
- Covalent compounds have low melting points because[KEAM]
- Sodium chloride is an ionic compound whereas hydrogen chloride is mainly covalent because[KEAM]
- Chemical bond implies[KEAM]
- A lone pair of electrons in an atom implies[KEAM]
- The lattice energy of NaClNaCl is 788kJmol−1788kJmol−1. This means that 788kJ788kJ of energy is required[KEAM]
- The hybridization of oxygen atom in H2O2H2O2 is[KEAM]
- The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below .This variation in bond angle is a result of (i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases (ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule (iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron pair[KEAM]
- Which one of the following pairs consists of only paramagnetic species?[KEAM]
- Arrange the following ions in the order of decreasing X-0 bond length, where X is the central atom in SiO4−4,ClO−4,PO3−4,SO2−4
- Allyl cyanide molecule contains[KEAM]
- The carbon atoms in calcium carbide are held by[KEAM]
- NO+NO+ has bond order[KEAM]
Sample Questions
Ques. What are ionic bonds? Give some examples. (3 marks)
Ans. An ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between two ions having an opposite charge. There are some atoms that require one more electron or lose one electron to get into a more stable configuration.
- The bond in sodium chloride is an example of an ionic bond.
- The valence electron of sodium is transferred to chlorine’s outer shell.
- This makes both the atoms stable. Ionic compounds are made up of ionic molecules having ionic bonding.
Ques. What are covalent bonds? What are the three types of covalent bonds? (3 marks)
Ans. Covalent bonding only takes place in non-metals. It occurs when two or more atoms share a pair of electrons with each other.
- For example, Chlorine has 7 electrons in its outer shell.
- They have one unpaired electron.
- Therefore two chlorine atoms share their electrons with each other which completes their octet.
- The two atoms are combined and form a bond that is very strong that holds them together.
- This is called covalent bonding.
There are three types of covalent bonding - single bond, double bond, triple bond.
Ques. What are metallic bonds? How are they formed? (3 marks)
Ans. In a metal lattice, valence electrons are loosely attached by the nuclei of other atoms. Thus the valence electrons require very low energy to release themselves from nuclei. When these electrons come out of the atom, the atom becomes positively charged. All these atoms of the metal are surrounded by free negatively charged electrons which are also called the electron cloud. The electrostatic attraction between these ions and electrons are called metallic bonds.
Ques. Give some examples of metallic bonds and mention their properties. (3 marks)
Ans. Magnesium, Aluminium, Sodium, etc are examples of metallic bonds. Gold, silver, iron, copper, nickel also have metallic bonds. Metallic bonds provide malleability and ductility to the compounds. Malleability is the tendency of metals to be beaten into thin sheets. Ductility means the ability to draw the metal into a thin wire. They have high electrical conductivity, opacity, and luster.
Ques. What determines whether a bond is covalent, ionic, or metallic? (3 marks)
Ans. Based on the following points, we can determines whether a bond is ionic, covalent, or metallic-
- An ionic bond is always formed between a metal and a non-metal due to their difference in electronegativity.
- A covalent bond is formed between two nonmetals where atoms differ slightly in electronegativity.
- Metallic bond is only found in metals.
Ques. Which bond is stronger - metallic or covalent? (3 marks)
Ans. Metallic bonds are found to be stronger than covalent bonds. Metallic bonds are strong bonds. The ionic bonds are strong due to the crystalline structure.
However, there are exceptions such as carbon, silicon, and diamond which are extremely stable in nature and hence are much stronger than metallic bonds.
Ques. Give three examples for ionic bonds and three examples for covalent bonds. (3 marks)
Ans. Examples of covalent bonds:
- Carbon dioxide
- Nitrogen
- Water
Examples of covalent bonds:
- NaF - sodium fluoride
- KF - potassium fluoride
- BeO - Beryllium oxide
Ques. Write any five differences between covalent bonds and ionic bonds. (5 marks)
Ans.
| Covalent bonds | Ionic bonds |
|---|---|
| Occurs during transfers of electron | Occurs when two atoms share their valence electron |
| Binding energy is higher than the metallic bond | Binding energy is higher than the metallic bond |
| Low conductivity | Very low conductivity |
| Non-directional bond | Directional bond |
| Present only in one state-solid state | Present only in three states: solid,liquid and gas. |
Also Read:



Comments