Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert | Updated On - Jul 25, 2025
Uniform Motion is a type of Motion in which an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. The velocity of the object remains constant in a uniform motion.
- Motion is defined as the change in the position of an object with respect to time.
- Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion are the two major types of Motion.
- If the speed of an object that moves along a straight line keeps on changing, it is known as Non-Uniform Motion.
- If the object keeps moving along a straight line with constant speed, then it is called Uniform Motion.

In Uniform Motion, the velocity of the object remains constant as it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. The distance-time graph of uniform motion shows a straight line.
Related Links
- Appearing for JEE Main, Download JEE Mains PYQ for all sabjects
- Appearing for NEET, Download NEET PYQ for all subjects
Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Motion in a Straight Line
Key Terms: Uniform Motion, Motion, Non-Uniform Motion, Displacement, Velocity, Straight Line, Accelerated Motion, Linear Motion
What is Motion?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Motion is the change in the position of an object with respect to its surroundings in a given time interval. Motion can be defined as the movement of an object with respect to some stationary object.
- Everything in the universe, including atoms, is in a state of continuous motion.
- It depends on the type of force acting on the object.
- On the basis of movement, motion is classified into three types namely Linear Motion, Rotatory Motion, and Oscillatory Motion.

Motion
Motion of an object is described by four major parameters as follows:
- Distance
- Displacement
- Speed
- Time
Motion in a Straight Line Detailed Video Lecture
Read More: Motion in a Straight Line
What is Uniform Motion?
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Uniform Motion is a type of motion in which an object travels at a uniform speed.
- It is defined as the motion of an object traveling in a straight line.
- The velocity of the object remains constant along the straight line as it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
- The magnitude of displacement is equal to the actual distance covered by the body in uniform motion.
- The slope of the distance-time graph of uniform motion gives the velocity of the body.
- Examples of Uniform Motion include the movement of hands of a clock, rotation of the earth, movement of the blades of a fan, etc.
Example: If a vehicle has uniform motion and covers 1 m in 1 minute in a given direction, then it indicates that it will cover 2 m in every 2 min, 3 m in 3min, 4 m in 4 min… and so on.
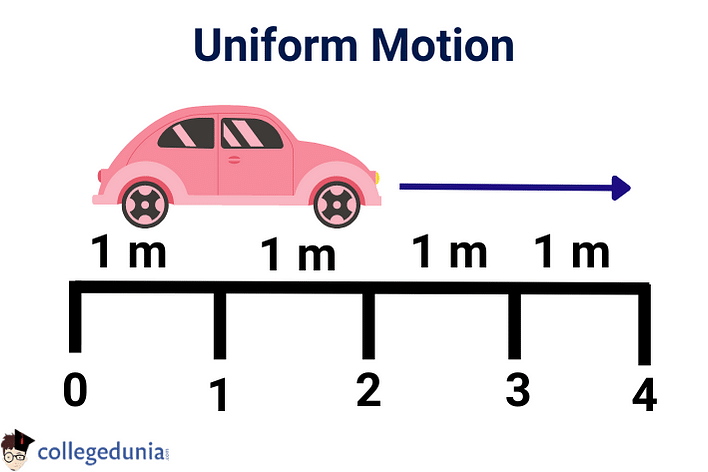
Uniform Motion
Frequently Asked QuestionsQues. Is Acceleration zero in Uniform Motion? Ans. Yes, acceleration is zero in Uniform Motion. The velocity of an object is constant in uniform motion, thus, the acceleration is zero. Ques. What are Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion? Ans. If an object travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, then the motion of the object is uniform motion. If an object travels unequal distances in equal time intervals, then the motion of the object is non-uniform. |
Uniform Motion Examples
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Here are some common examples of Uniform Motion that can be seen in daily life:
- Hand of a Clock moves with constant speed, completing the movement of a specific distance in 60 minutes.
- Movement of Blades of a Fan.
- Suspended Pendulum
- An airplane taking off at a height at a steady speed.
- A bicycle moving on a straight level road at a steady speed.
- A successive vibrating spring of a sewing machine.
- A ship steaming on a straight course at a constant speed.
- A train going along the tracks at a constant speed.
- Earth moves around the sun in a consistent motion.
- A cooling fan running at the same speed.
Read More:
Uniform Motion Graph
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Uniform Motion is described as a type of Motion in which the object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
- The graph of Uniform Motion is a straight line.
- It is a straight line as the object is covering equal distances in equal intervals.
- The slope of the uniform motion graph gives the velocity of the object.
Here is the Graph for Uniform Motion:
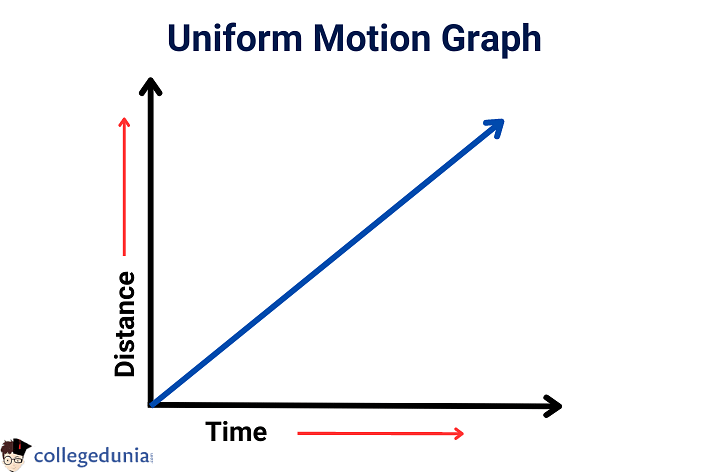
Uniform Motion Graph
Read More: Motion in a Straight Line Important Questions
Non-Uniform Motion
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Non-Uniform Motion is defined as a motion of an object that travels inconsistent distances in the same interval of time. Non-Uniform Motion is also referred to as Discontinuous Motion or Accelerated Motion.
- It is a type of motion in which an object doesn’t cover an equal distance at equal intervals.
- When the speed of the object changes by different proportions in the same time interval, then, the motion of an object is non-uniform motion.
- The graph for non-uniform motion will be a curved line.

Non-Uniform Motion Graph
Example: If an object is dropped from the roof of a tall building, it can be noticed that it will cover 2 meters in the 1st second, 6 meters in the 2nd second, 10 meters in the 3rd second, and so on and so forth. Thus, a freely falling object covers an unequal distance in an equal interval of time.
Non-Uniform Motion Examples
The common examples of Non-Uniform Motion are as follows:
- A horse running.
- A man running in a 1000 m race.
- A bouncy ball.
- A car colliding with another car.
- A plane crossing through the clouds and then landing.
- Dragging a box from a path.
- A truck on its way to the market.
- A car coming to a halt.
- A train coming to its end spot.
- Movement of an asteroid.
Difference Between Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Uniform Motion and Non-Uniform Motion are the two types of Motion.
- Uniform Motion is the one in which an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
- Non-Uniform Motion is the one in which an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
The difference between Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion is as follows:
| Parameters | Uniform Motion | Non-Uniform Motion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a type of motion in which an object moves in a linear path with uniform speed covering equal distances in equal intervals of time. | It is a type of motion in which an object moves in a non-linear path with varying speeds covering unequal distances in equal intervals of time. |
| Distance Covered | Equal distance is covered in uniform motion. | Unequal distance is covered in non-uniform motion. |
| Average Speed | It is equal to the actual speed of an object | It varies with the actual speed of an object |
| Acceleration | The acceleration in uniform motion is Zero. | The acceleration in non-uniform motion is Non-Zero. |
| Distance-Time Graph | Uniform Motion Graph shows a straight line. | Non-Uniform Motion Graph shows a curved line. |
| Example | The movement of the hands of a clock is an example of uniform motion. | A speedy vehicle on a busy highway is an example of non-uniform motion. |
Uniform Circular Motion
- Uniform Circular Motion is a motion in objects that travel at a constant speed around a fixed axis.
- In uniform circular motion, the object given moves around a curved path.
- It maintains a constant radial distance from the center point at any given time and it moves in a tangent to the curved path.
Non-Uniform Circular Motion
- Non-uniform circular motion is an inconsistent motion in which the object travels at a variable angular speed around a fixed axis.
- The object covers a curved path and will have some variable radial acceleration due to which its velocity would change every second.
Read More:
Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 Handwritten Notes
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Given below are the handwritten notes on Motion in a Straight Line and related concepts:




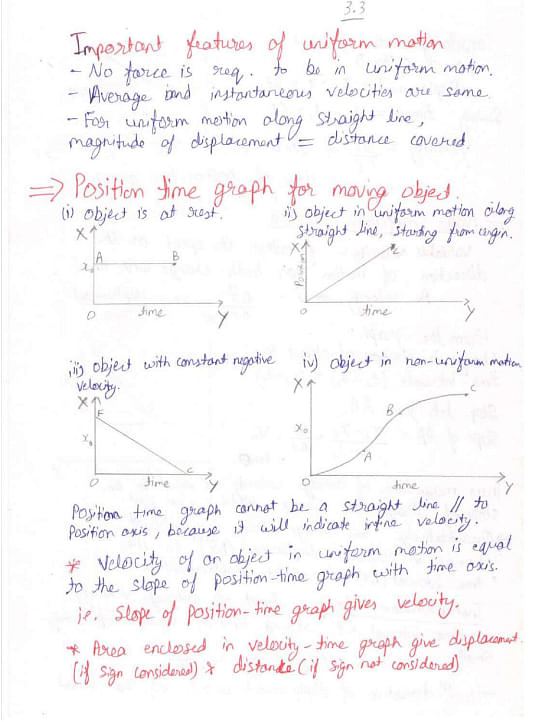



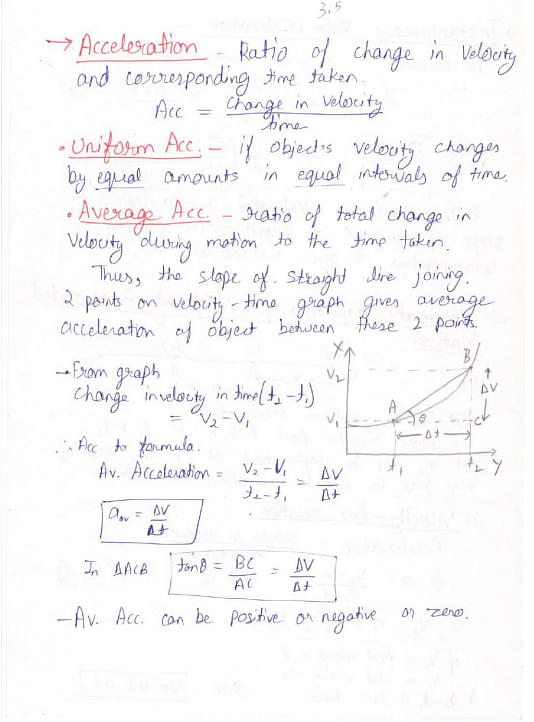







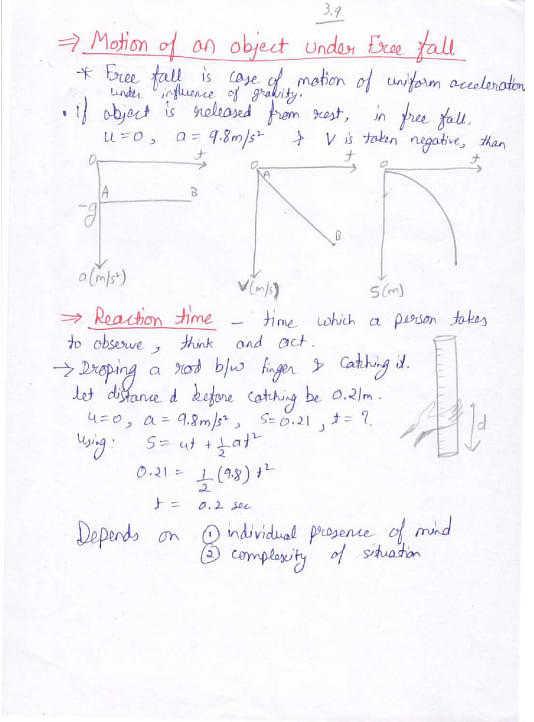
Things to Remember
- Uniform Motion is a type of motion in which an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
- The object travels in a straight path in uniform motion.
- The displacement of the object is equal to the actual distance covered by the object in uniform motion.
- The graph of uniform motion is a straight line depicting constant velocity.
- Movement of the blades of a fan, hands of a clock, suspended pendulum, etc are all examples of Uniform Motion.
- Non-Uniform Motion is another type of Motion in which the object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
- Some examples of non-uniform motion are bouncy balls, cars colliding with one another, a man running in a race, and more.
Previous Years’ Questions
- At a metro station, a girl walks up a stationary escalator in… (KCET – 2020)
- A body is projected with a speed u at an angle... (AP EAPCET – 2018)
- A ball is thrown vertically downward with a velocity of 20m/s... (NEET – 2020)
- In a car race on a straight road, car A takes a time t less than car... (JEE Main – 2019)
- A particle moves along a circle of radius r with constant tangential... (MHT CET – 2016)
- A person standing on an open ground hears the sound of a jet... (JEE Main – 2019)
- A particle shows distance-time curve as shown in the figure. The maximum... (KCET – 2018)
- A juggler keeps on moving four balls in the air throwing the balls after... (BITSAT – 2018)
- A passenger train of length 60 m travels at a speed of 80 km/hr. Another... (JEE Main – 2019)
- A particle starts from origin O from rest and moves with a uniform acceleration... (JEE Main – 2019)
- A man in a car at location Q on a straight highway is moving with speed... (JEE Main – 2018)
- Displacement x versus t2 graph is shown for a particle. The acceleration... (UPSEE – 2017)
Sample Questions
Ques. What is Motion? (3 Marks)
Ans. Motion is the change in the position of an object with respect to time. A person walking on the road, an object from the table, a running dog, etc. are all examples of motion.
Motion is affected by four major parameters as follows:
- Distance (d)
- Displacement (s)
- Speed (v)
- Time (t)
Ques. What are Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion? (2 Marks)
Ans. Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion are the two major types of motion.
- Uniform Motion: If an object travels in a straight line and covers an equal amount of distance in an equal interval of time, it is said to have uniform motion.
- Non-Uniform Motion: If unequal distance is covered in equal intervals of time by an object, it is said to be in non-uniform motion.
Ques. What are other types of motion apart from Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion? (3 Marks)
Ans. The other types of motions apart from Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion are as follows:
- Rotational Motion: The object moves along a circular path about a fixed axis in this motion.
- Translational Motion: The object moves along a path in any of the three dimensions in translational motion.
- Periodic Motion: It is defined as a motion that repeats itself after certain intervals of time.
- Simple Harmonic Motion: In this motion, the restoring force acts in the direction opposite to the direction of motion of the object.
Ques. What is the difference between Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion? (3 Marks)
Ans. The difference between Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion is as follows:
| Uniform Motion | Non-Uniform Motion |
|---|---|
| The object travels in a straight line or linear path. | The object travels in a non-linear pattern or path. |
| It covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. | It covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time. |
| The distance-time graph of a uniform motion is a straight line. | The distance-time graph of a non-uniform motion is a curved path. |
Ques. What are the Equations of Motion? (3 Marks)
Ans. Equations of Motion are three fundamental equations used to find the related quantities in motion in a straight line. They are known as kinematic equations and the quantities associated with these kinematic equations are Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration, and Time. The three equations of motion are as follows:
- v = u + at
- v2 = u2 + 2as
- s = ut + (1/2)at2
Ques. What is Uniform Motion? (2 Marks)
Ans. Uniform Motion is a motion in which a body travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, irrespective of the duration of the time intervals. The distance-time graph for uniform motion is a straight line.
Example: A car running at a constant speed say 20 meters per second, will cover equal distances of 20 meters, every second, thus, its motion will be uniform.
Ques. List some examples of Uniform Motion. (3 Marks)
Ans. Some examples of Uniform Motion are as follows:
- An airplane taking off at a height with a steady speed.
- A train moving along the straight tracks at a steady speed.
- A car moving along a straight road at a steady speed.
- A ship moving on a straight path at a steady speed.
Ques. What is Uniform Circular Motion? (3 Marks)
Ans. Uniform Circular Motion is defined as the movement of an object in a circle at a constant speed. It is the periodic motion of a particle moving along the circumference of a circle with constant speed.
Examples of Uniform Circular Motion are:
- The motion of an artificial satellite orbiting Earth.
- Stone tied to a rope and swung in circles.
- Motion of hands of a clock.
- Motion of wheels of a bicycle.
Ques. State a few examples of Motion. (3 Marks)
Ans. Here are some examples of motion:
- Motion is seen in day-to-day activities such as walking, running, playing, etc.
- A car or a vehicle moving from one place to another is an example of motion.
- The revolution of planets around the sun or moons around a planet is another instance of motion.
Ques. State the three Laws of Motion. (3 Marks)
Ans. The three laws of motion are as follows:
- According to the first law of motion, a body at rest or uniform motion will continue to be at rest or uniform motion until and unless a net external force acts on it.
- According to the second law of motion, the force acting on the body is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration.
- According to the third law of motion, there is an equal and opposite reaction for every action.
Check-Out:







Comments