Anjali Mishra Content Writer-SME
Content Writer-SME
A living thing is anything that has life, while a non-living thing is anything that does not have life. Cell division allows living things to grow. Amoeba and other unicellular creatures grow by increasing the size of the organism's solitary cell. The incorporation of outside material allows non-living creatures to grow. There are numerous characteristics that distinguish living from nonliving things.
This distinguishing element is not limited to actions such as walking, jogging, or eating, but includes much more. Many organisms on Earth, as we all know, do not move, run, or eat, yet they are still alive. Plants, for example, do not have the ability to move. Although plants do not eat, they do have a life of their own. Bacteria that are invisible to the naked sight are thought to be the first form of life on Earth.
Our Earth
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Earth is the only planet that comprises living creatures in the entire universe. There are both living as well as non-living things present on Earth. There are two categories of things/items in our surroundings which are living things and non living things.
All living things have senses, breathe, eat, grow, move, and reproduce. Non-living things don't consume, grow, breathe, move, or reproduce in the same way as live things do. They do not have senses.

Living Things and Non Living Things
Let's take a closer look at the distinguishing features of living and non-living entities, as well as the differences between the two.
Difference between Living and Non-Living Things
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The following are some of the most significant differences between living and non-living things:
| Comparison | Living Things | Non-Living Things |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Those things present on earth which have life are called living things. | Those things present on earth which do not have life are called non-living things. |
| Reproduction | Living things have the ability to give birth to their offspring. | Non-living things do not reproduce. |
| Requirement | Living things need water, air, and nourishment to survive. | Non-living things have no such requirements |
| Sensation | Living things are sensitive and responsive to stimuli. | Non-living things are not responsive to stimuli and do not react to them. |
| Metabolic Reactions | Metabolic reactions constantly occur in all living things. | Non-living things do not have metabolic reactions. |
| Growth and Development | Living organisms undergo growth and development. | Non-living things do not develop or grow. |
| Lifespan | They have a lifespan and are not immortal. | They don't have a lifespan and are immortal. |
| Movement | Living things move from one place to another. | Non-living things cannot move by themselves. |
| Biological Processes | They respire and the exchange of gases takes place in their cells. | Non-living things do not respire. |
| Examples | Example: Humans, animals, plants, insects. | Example: Rock, pen, buildings, gadgets. |
What are Living Things?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Living things are made up of small structures called cells and are alive. They mature and begin to move or locomote. They go through anabolic and catabolic responses as part of their metabolic processes.
Living entities are capable of producing new life that is of their own species through the process of reproduction. Living things have a finite lifespan and are not impervious to death. Cellular respiration is the process through which living creatures obtain energy, which is then used by cells to carry out their duties. They use food to get energy and expel waste from their bodies.
Examples: Animals, birds, insects, and humans.

Living Things
Characteristics of Living Things
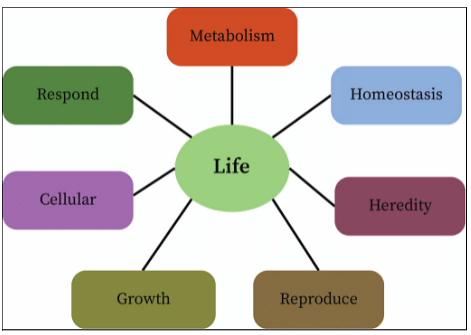
The following are some of the most important features of living things:
- Cellular organization: As previously said, all living organisms must have a cellular structure. Living entities can be unicellular or multicellular, but they cannot exist without the existence of cells. Moreover, numerous activities within the cell serve as operating systems for specific functions. Cellular respiration, for example, is the primary source of energy creation. It's the process of taking in nutrients from meals and converting them to energy.
- Respiration: It is the second basic process that ensures life's continuation. Exchanging gases is the process of respiration. The purpose of breathing is to produce energy. This process also produces waste products in living creatures that must be removed from the body.
- Nutrition: Proteins, carbs, and lipids are the building blocks of our bodies. These nutrients are obtained from food by living creatures. The absorption of nutrients from raw materials or food is hence the process of nutrition.
- Growth: In the life cycle of living beings, there are various stages of development. This is referred to as development. All living things continue to develop. As a result, growth is a crucial property of living creatures.
- Locomotion: Most living creatures have the ability to move. Animals are capable of moving on their own. Leopards, cats, and dogs, for example, can run. Plants, for example, migrate towards the sun since it is necessary for their growth.
- Response to stimulus: All living creatures react to stimuli in their environment. They have a high sensitivity to touch and react to their surroundings.
- Excretion: Various chemical processes occurring in the bodies of living beings produce an unusable bi-product. This is garbage, which must be expelled from the body. Excretion is the process of eliminating the waste produced by the body. Excretion is another feature that only living organisms have.
- Reproduction: Only living entities have the potential to generate offspring that carry their generation forward. They have a sliver of genetic material from their parents, as well as genetic variety owing to gene mixing. Reproduction is also another crucial property of living beings.
Characteristics of Living Things
What are Non-Living Things?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Non-living things are not alive. They are lifeless. They have no cells, don't grow, and don't move. Anabolic and catabolic processes are not present in their metabolism. They don't have any offspring.
There is no life span for non-living things. They don't breathe and don't excrete because they don't require food for energy. They are not born, grow, or die in a predictable pattern. External forces help to create and destroy them.
Examples: Stone, pen, book, cycle, bottle, and others.

Non-Living Things
Characteristics of Non-living Things
The following are some of the most important qualities of non-living things:
- Non-living things are devoid of life. They are lack cells and protoplasm, which are both required for life to exist.
- The absence of protoplasm leads to a lack of metabolic activity.
- They lack a distinct and defined size of their own. They take on the shape of the substance in which they are confined, such as a liquid taking on the shape of its container. The changing environment and landscape shape stones, rocks, and boulders. An external impact causes a change in the status of non-living things.
- Non-living things "grow" through the process of accretion. It happens when materials are brought in from the outside. A snowball, for example, may grow in size due to the accumulation of smaller units on its outer surface.
- Non-living creatures do not perish since they lack cells with a fixed lifespan. Immortality is a defining characteristic.
- Non-living things lack basic life functions such as reproduction, feeding, and excretion.
Criteria for Comparison between Living & Non-Living Things
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
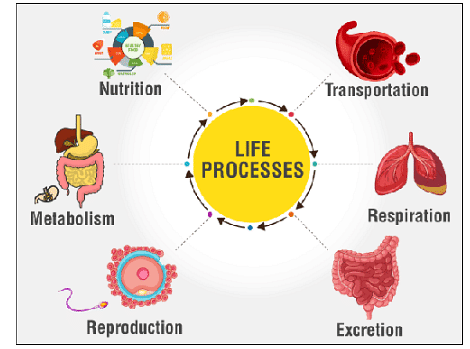
Scientists have come up with attributes or properties that are unique to living creatures in order to distinguish them from non-life objects. To avoid incorrect grouping, a classification criterion is required. As a result, science established a classification system. Living beings are defined as everything that has life. Humans, trees, dogs, and other animals are examples. Non-living things are those that have no life in them. For instance, a stone, a mountain, a watch, and so on.
Scientists have established a few criteria for distinguishing between living and non-living organisms. Here are a few:
- Living things have the ability to grow and develop.
- Energy is obtained and used by living things.
- Living beings adjust to their surroundings.
- Every living being is made up of one or more cells.
- Living things react to stimuli in their environment.
- All living creatures expel waste from their bodies.
- Living beings have the ability to reproduce and give birth to their offspring.
- All living beings require energy to carry out various metabolic operations, which they obtain from food/nutrition.
- All living beings, with the exception of plants, travel from one location to another.
- Locomotion is the term used to describe this type of movement.
- To breathe and make energy, all living things, including humans, animals, plants, birds, and insects, require oxygen gas.
Life Processes in Living Beings
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- A living thing is anything that has life, while a non-living thing is anything that does not have life.
- All living things have senses, breathe, eat, grow, move, and reproduce.
- Non-living things don't consume, grow, breathe, move, or reproduce in the same way as live things do.
- Living things are made up of small structures called cells & are alive.
- They go through metabolic processes that include anabolic & catabolic responses.
- Cellular respiration is the process through which living creatures obtain energy.
- They use food to get energy and expel waste from their bodies.
- Non-living things are not alive. They are lifeless. They have no cells, don't grow, and don't move.
- Anabolic and catabolic processes are not present in their metabolism. They don't have any offspring.
Sample Questions
Ques. What are living things? Give some examples. (3 Marks)
Ans. A living thing is anything that has life. Living things are alive and are made up of little structures called cells. They reach adulthood and begin to move about or locomote. They go through anabolic and catabolic responses as part of their metabolic processes.
For example- birds, animals, humans, and insects.
Ques. What are non-living things? Give some examples. (3 Marks)
Ans. A non-living thing is anything that does not have life. They are lifeless. They have no cells, don't grow, and don't move. Anabolic and catabolic processes are not present in their metabolism. They don't have any offspring.
For example- Stone, pen, book, cycle, bottle, and others.
Ques. Plants are not living entities because they are unable to move. Why? (3 Marks)
Ans. Cells are the primary units of life in all living beings. They exist in plants as well. The presence of cells indicates that metabolic activity and numerous life processes are occurring. Food is required by the plant, and waste is eliminated in the form of gases and water. Other biological activities, such as reproduction and growth, are also demonstrated by plants. Plants do not migrate from one place to another directly; instead, they bend towards a source of light in order to survive. Plants are classified as living entities as a result.
Ques. Why can’t non-living things respire? (3 Marks)
Ans. Non-living things do not have metabolic activities that go on inside them. They do not produce energy and use it to carry out any process. Non-living things don't consume, grow, breathe, move, or reproduce in the same way as live things do. They do not have senses. Hence, non-living things do not need to breathe & do not respire.
Ques. What is the difference between living & non-living things? (5 Marks)
Ans. The difference between living & non-living things are:
- Living Things: They possess life. Living things are capable of giving birth to their young ones. Living beings need water, air, and nourishment to survive. They do not live forever and have a lifespan. Living things move from one place to another. They respire and the exchange of gases takes place in their cells. Example: Humans, animals, plants, insects.
- Non-living Things: They do not possess life. Non-living things do not reproduce. For survival, non-living things don't depend on water, air, and food. They have no lifespan and are immortal. Non-living things cannot move by themselves. Non-living things do not respire. Example: Rock, pen, buildings, gadgets.
Ques. What is cellular respiration? (3 Marks)
Ans. Cellular respiration is the process through which living creatures obtain energy, which is then used by cells to carry out their duties. They use food to get energy and expel waste from their bodies. Cellular respiration is carried out to provide energy to the living organisms to perform their day to day tasks. The following is a summary of their life cycle: birth, growth, reproduction, and death.
Ques. What are the characteristics of living things? (3 Marks)
Ans. There are several characteristics of living things: cellular organization, locomotion, breathing or respiration, excretion, growth, sensitivity, response to stimulus, and reproduction. Non-living things may exhibit one or two of these characteristics, but live things exhibit all of them. Living things have certain life processes that they perform owing to their bodily functions and structure.



Comments