Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Bones of the foot provide balance to the whole weight of the body. The combination of the bones along with the soft tissues muscles of the foot help a human body to stand and move accordingly. During birth, the baby's body consists of a total of 300 bones which get fused into 206 bones with its growth and time. The bones of the body help in building the structure of the human body and give external and internal protection to all the organs.
| Table of Content |
KeyTakeaways: Foot, Phalanges, Metatarsals, Tarsals, Human body, Bones, Tibia.
Division of Foot
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot are the three major divisions of the foot. In the foot of the leg, we have three bones tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges which are placed in the above mentioned three layers of the foot.

Division of Foot
- Hindfoot- It consists of the Proximal group of the Tarsals i.e. the Talus and the Calcaneus.
- Midfoot- It consists of the Distal group of the Tarsals i.e. the Cuneiform bone, as well as Cuboid bone and the Navicular bone.
- Forefoot- It consists of the Metatarsals and the Phalanges.
Also Read:
Tarsals
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The human Body foot has seven tarsal bones and they appear before metatarsals and phalanges in the foot.
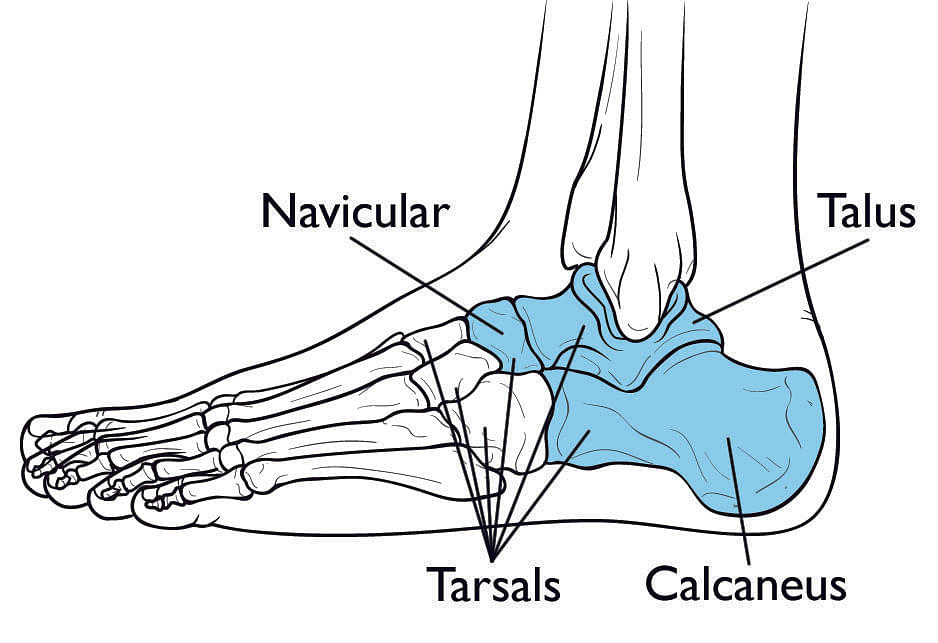
Tarsals
The tarsals can be grouped into two parts:
- Proximal group (Hindfoot part)
- Distal group (Midfoot part).
Proximal Group
The proximal group again has two bones. One of them articulates with the tibia bone and the fibula bone and is called Talus. The second bone is called Calcaneus. This part of the foot is within the Hindfoot part of the Foot.
Talus: The superior bone of the hindfoot is the Talus. Almost the entire body weight is held by the Talus. Talus sends the body forces from the tibia bone to the calcaneus bone. Since it articulates with the next largest bone of the foot, it helps the ankle to maintain the stability or balance of the entire body.
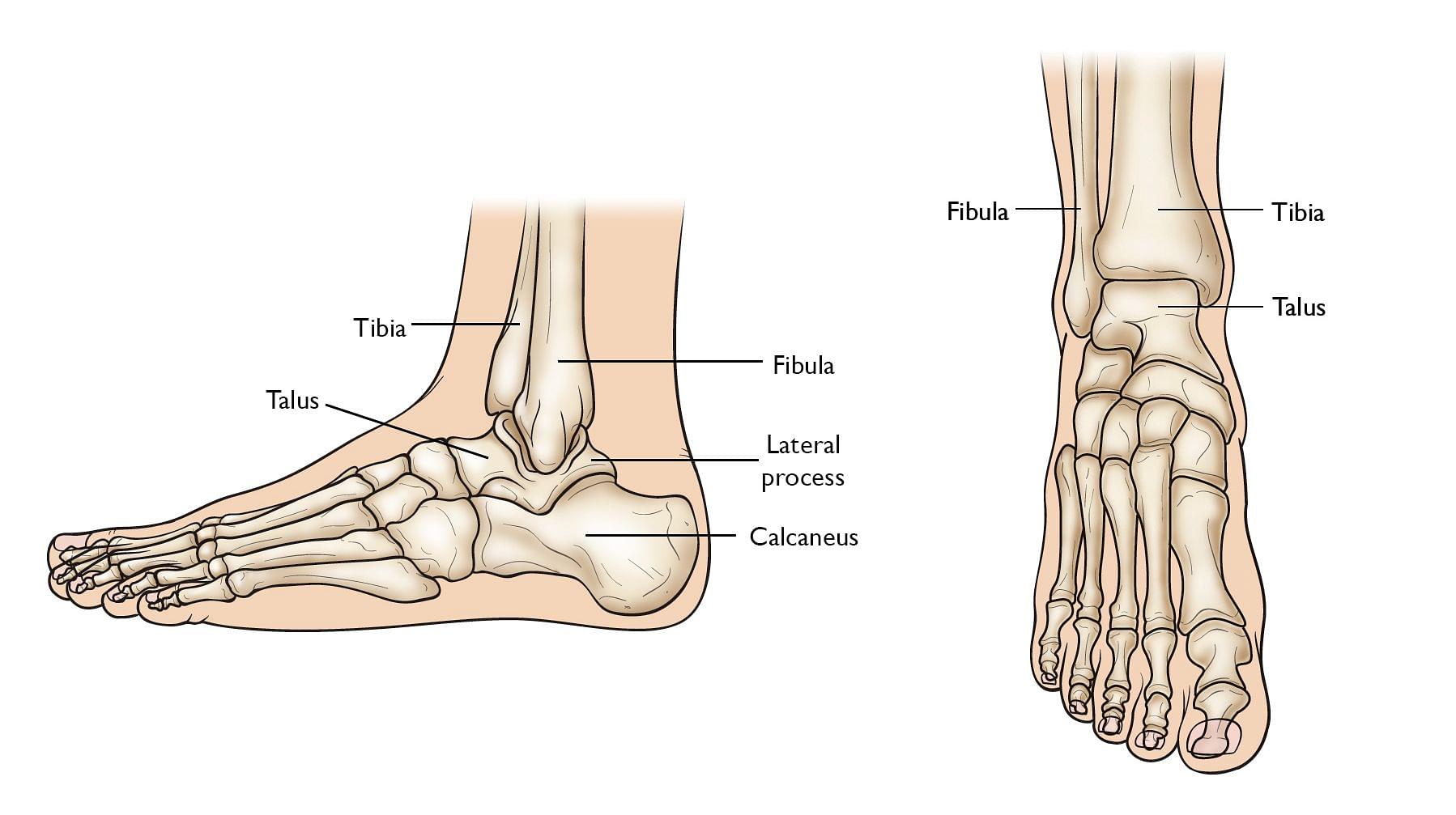
Talus
The top of the talus connects to the tibia and to the fibula which is the two long bones of the lower leg and is called superior articulations. The connection between the talus and the calcaneus and the talus and the navicular joint are known as Inferiorly and Anteriorly articulations. And the subtalar joint articulation between the talus and the calcaneus is called the Inferiorly Articulations.
Calcaneus: The calcaneus bone is the heel bone which is the largest bone of the foot. The calcaneus has a cushy layer of fat underneath it. It softens the impact of the footsteps. It handles the weight of the whole body towards the posterior side.

Calcaneus
The calcaneus bone connects to the talus at the subtalar joint which is also called the talocalcaneal joint and is known as the superior articulations. Again, the connection created between the calcaneus and the cuboid is known as the Anteriorly articulations. The posterior part of the calcaneus is called the Calcaneal Tuberosity and Achilles Tendon is attached to it to make a balance of the posterior weight of the body.
Distal Group (Mid Foot)
Mid-foot is divided into 5 tarsal bones which are irregularly shaped tarsal bones. These include the five uniform bones-
- Medial cuneiform bone
- Intermediate cuneiform bone
- Lateral Cuneiform bone
- Cuboid bone and
- Navicular bone.
The arch of the foot is the resultant of the midfoot bones. The midfoot bones also act as a shock absorber.

Mid Foot
In the Distal group, there are four bones. The bones in the distal row of the foot articulate with the metatarsals. The four types of bones in the distal group are Cuneiform bones.
- The medial bone and the lateral bone articulate with the first two-thirds metatarsals.
- The Cuboid bones are placed laterally on the foot and it articulates with the lateral to metatarsals. The intermediate bone sits between the proximal and the distal rows. This bone is called Navicular.
- If you are looking at the lateral view then it can get a bit confusing because the Cuboid bone lies in line with the Navicular bone, yet the cuboid bone is in the distal group. Hence, the distal group of Tarsal bones is just those bones that articulate with the metatarsals. So, the intermediate bones, the Navicular bone, sit between the proximal row and the distal row of tarsal bones.

Tarsal Bones
Collectively the mid and the hindfoot bones- the talus, calcaneus, and the three cuneiform cuboids and the navicular bones are called the tarsals. Overall the foot and the ankle consist of 26 bones, 14 phalanges, 5 metatarsals, and 7 tarsals. Between the two feet of the quarter of the bones in the body, these bones are connected by 33 joints and are moved by more than 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons connect muscles to the bones and the ligaments connect bones to the bones.
Also Read:
Metatarsals (Forefoot)
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The forefoot bears half of the weight of the body and is composed of the phalanges, five toes, and metatarsals. The three metatarsal bones are articulated with the Cuneiform bones of the foot. A human foot has five metatarsals and each metatarsal has a base shaft and a head.
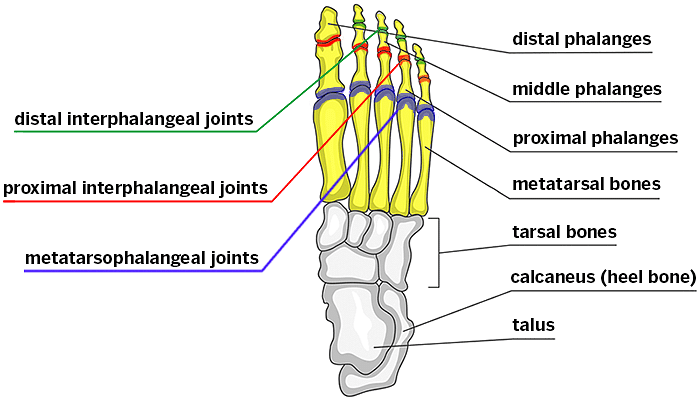
Forefoot
Metatarsals are the longest bines of the foot that maintains the balance of the whole body. The big toe is attached to the first metatarsal bone of the foot. The attachment is called the metatarsal phalangeal joint. Under the distal area of the metatarsal, you will get two small round-shaped bones called the sesamoid bones. Below these sesamoid bones, the ball of the foot lies that maintain the strength of the whole foot.
Phalanges (Forefoot)
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Phalanges consist of three bones-
- Proximal
- Intermediate and
- Distal except for the phalanx
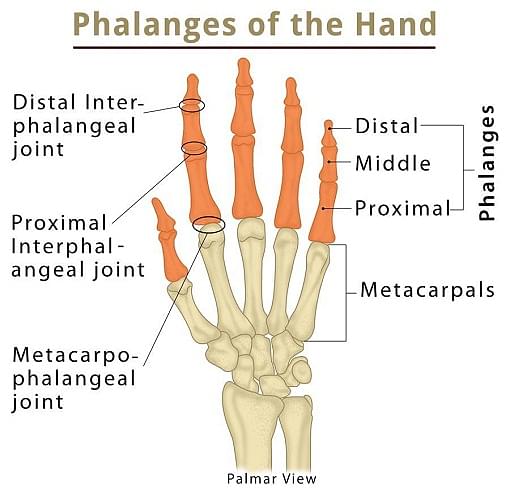
Phalanges
Things to Remember
- Metatarsals mainly have three Articulations- Proximal articulation, Lateral articulation, and distal articulation.
- The foot bones and the structure are almost similar to the hand - the only difference being the weight-bearing capacity of the foot and fewer movements.
- The foot starts with the tibia and the fibula and ends with the ankle articulations.
- Cuneiforms are positioned close to the five metatarsal bones of the foot.
- The toes of the body are mainly built by the phalanges bones which look just like the thumb of the hand.
- The phalanges consist of the distal phalanges, middle phalanges, and the proximal phalanges.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. Describe the function of tarsal bones. (2 marks)
- The tarsal bone forms the rear portion of the foot and has a total of 7 bones. The anklebone is called the talus bone that connects the tibia and the fibula bones of the foot.
- Calcaneus is the heel bone of the foot. It is the largest bone of the foot that stabilizes the overall weight of the human body.
- The third is the tarsal bones which are again divided into five parts and lie mainly in the midfoot of the leg. It helps in getting the support of the posterior part of the human body.
Ques. Describe the role of the phalanges bones. (2 marks)
Ans. Phalanges are present in the foot of the human body. Phalanges mainly form the whole of the foot as it is in the midfoot division of the leg. It is divided into three parts that are the proximal, middle, and distal Phalanges. They are attached to the different joints of the toe. The Phalanges joint the metatarsals and the proximal of the foot and it helps in balancing the weight of the body. The first metatarsal phalangeal joint is the area where majorly the foot pains or other related problems take place.
Ques. What do you know about bunions? (2 marks)
Ans. Bullion is a kind of bump that appears on the foot near the big toe. When the first metatarsal starts separating from the base to the second metatarsal, then this kind of bump generally takes place. The more drift takes place between the metatarsals, the bump increases more. When such kind of bump is seen at the big toe, then a person should start resting otherwise it can worsen the situation of the foot. Rest can only bring the two metatarsals to the same position otherwise standing or walking can separate both the metatarsals. It can increase the pain in the big toe and can extend towards the midfoot and the ankle.
Ques. Describe the Cuboid bone. (2 marks)
Ans. The cuboid bone is a part of the tarsal bones that are located on the outer area of the foot. The main function of the cuboid bone is to connect the foot and the ankle and to help in maintaining the balance of the foot as well as the whole body. It is located between the 4th and the 5th metatarsals which are located between the toes and the calcaneus. The lateral surface of the cuboid bone is called the peroneal sulcus and the posterior surface gets articulated with the calcaneus front surface. The inner portion of the cuboid bone is a four-sided area and it articulates between the third cuneiform and the navicular bone. The weight of the body and the flexibility of the foot also depend on the cuboid bone to some extent.
Ques. Explain Flexor Digitorum Brevis. (2 marks)
Ans. Flexor Digitorum Brevis is located on the sole that helps in maintaining the arch of the foot. It is located deep inside the connective tissue of the foot and it divides the lateral plantar vessels from those connective tissues. The Flexor Digitorum Brevis receives the nerve supply which is called the medial plantar nerve. When there is movement in this Brevis, the tendons of the foot get separated and get divided into four lateral tendons.
Ques. Describe the three articulations of the Talus. (2 marks)
Ans. Talus is the superior bone of the Tarsal bone. It helps in maintaining the strength of the whole body. The three articulations of the Talus are
- Ankle joint- It is the superior articulation that happens between the tibia and fibula bones of the foot.
- Subtalar joint- It is the inferior articulation that takes place between the Talus and Calcaneus
- Talonavicular joint- It is the anterior articulation that takes place between the Talus and the Navicular bones of the foot.
Ques. Explain the articulations of Metatarsals. (2 marks)
Ans. In metatarsals generally, three kinds of articulations take place that helps in the movement of the foot and also hold the posterior weight of the body.
- Tarsometatarsal joints- It is the proximal articulation that takes place between the metatarsal and the tarsal bones.
- Intermetatarsal joints- It is the inter-metatarsal joint that takes place between the different metatarsals of the foot.
- Metatarsophalangeal joint- It is the distal articulation that takes place between the metatarsal head and the proximal phalanx.
Ques. What are the names of the seven parts of tarsals? (2 marks)
Ans. Three Cuneiform bones in the foot
- One Talus bone
- One Calcaneus bone
- One Navicular bone
- One Cuboid bone
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:



Comments