Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Separation of substances is a common practice that can be observed all around us. Removing stones from rice and filtering tea are two common examples. Separation techniques are methods in which mass transfer takes place and mixtures of substances can be converted into two or more substances. Sometimes, the substances separated are equally important, otherwise only some of them are important.
Read More:- Classification of Matter
| Table of Contents |
Keyterms: Separation, substances, melting point, compound, elements, pure substance
Mixtures and Pure Substances
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In chemistry, “pure” doesn’t convey the same meaning as in the literary sense. A pure substance is a substance that consists only of one element or one compound. Pure substances have a sharp melting point.

Mixtures and Pure Substances
Mixtures consist of two or more elements or compounds not chemically joined together. They melt over a range of different temperatures.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Isotopes of Hydrogen | Sublimation | |
| Celsius Scale | Azeotropic Distillation | |
Separating Mixtures
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Separating mixtures means separating one or more elements or compounds from a mixture. Sometimes only one substance in the mixture is important but otherwise more of them could be important. Also, separating substances in a mixture is often done to separate harmful substances from useful ones. Examples of processes for separating mixtures include threshing, winnowing, sedimentation, etc
Handpicking
Handpicking is usually applied when the impurities that need to be separated are very large and can be picked out easily by hand. Also, the shape and color of the impurities are considerably different than that of the useful substance. Pebbles, broken grains, and insects being separated from wheat and rice is an example of handpicking.

Handpicking
Read More:- Vapour Pressure
Threshing
Threshing is the loosening of the edible part of the grain from the stalk to which it is attached by loosening the stalk. It is the next step in the grain preparation after reaping. Threshing is either done by farmers manually or using a threshing machine. The common ways of manual threshing are hand-beating against an object or holding the crop against a rotating drum with spikes or rasp bars.

Threshing
Winnowing
The process in which chaff is separated from the grain by throwing the mixture into the air is called winnowing. It is the next step in grain preparation following threshing. During the process of winnowing, lighter chaff is blown away and the heavier grain falls back down. Winnowing is necessary to separate the chaff from clean grains so that they can be used for eating.

Winnowing
Sedimentation and Decantation
Sedimentation and decantation are the processes used for the separation of insoluble substances heavier than the liquid.

Sedimentation and Decantation
Sedimentation refers to the settling down of heavier impurities after a time due to gravity. The lighter impurities, on the other hand, will float. Decantation follows sedimentation. A natural and easy example of sedimentation is the dirt and mud in muddy water settling down.
Decantation is the process of pouring out the liquid and the lighter impurities after the heavier impurities have settled down.
Sieving
Sieving is used when the substances to be separated are of different sizes. The mixture is passed through a sieve allowing the smaller substances to pass through while the larger substances stay in the sieve.
An example of sieving would be separating impurities from wheat flour. When the flour is passed through a sieve, the fine wheat powder passes through while the larger impurities remain in the sieve.

Sieving
Read More:- Difference Between Transpiration and Evaporation
Evaporation and Condensation
The conversion of a liquid to a gas by heating it to the boiling point of the liquid is called evaporation. Using this method, the liquid component of a mixture can be separated from the solid component. Usually, the mixture is heated till no more liquid remains.

Evaporation and Condensation
The conversion of a gas to a liquid by cooling is called condensation. For example, the water vapor formed by evaporation from the water sources on earth is returned to earth in the form of rain.
Evaporation and condensation can be used individually to separate mixtures and also in combination. Salt and water can be separated from a solution by the combination of evaporation and condensation.
Distillation
A liquid can be separated from the solution of a soluble solid by the process of distillation. The solution is heated in a flask and the vapor produced is passed through a condenser. The vapor is condensed into a liquid. The pure liquid is then collected into a beaker. Pure water is separated from saltwater by the process of distillation.
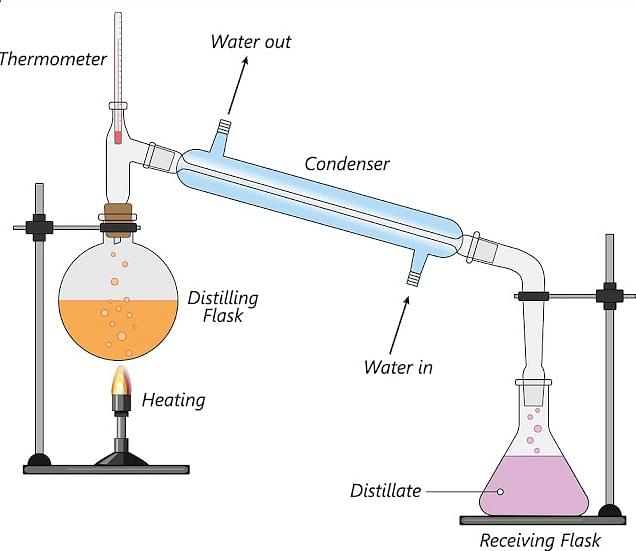
Distillation
Read More:- Difference between Element and Compound
Points to Remember
- A pure substance contains only one element or compound. A mixture contains multiple elements or compounds. There are many ways to separate the elements or compounds that make up a mixture
- Handpicking is used when the impurities are very large and are different in color and shape from the useful substance.
- Threshing means separating the edible part of the grain from the stalk. Threshing can be done manually or using a machine.
- Winnowing is separating the chaff from the grain by throwing the mixture in the air. The lighter chaff will be blown away while the heavier grain falls back to the ground.
- The settling of insoluble impurities in a mixture due to gravity is called sedimentation. The lighter impurities float to the surface. The liquid and the lighter impurities are then poured away. The process is called decantation.
- Impurities that vary in size can be separated from a mixture by the process of sieving. The mixture is passed through a sieve. The smaller substances pass through the sieve while the larger substances remain in the sieve.
- Evaporation is the conversion of a liquid to gas after it is heated to its boiling point. Condensation is the conversion of gas to liquid by cooling. Individually and together they can be used for the separation of mixtures.
- Distillation is the process of separating a liquid from the solution of a soluble solid. The solution is heated in a flask and passed through a condenser. The pure liquid is collected in a beaker.
Read More About Aldol condensation
Sample Questions
Ques 1. What is handpicking? When is the process used? (2 marks)
Ans. Handpicking is simply picking out the impurities in the mixture by hand. Handpicking is used when the impurities in the mixture are very large and differ greatly in color and shape from the useful substance. Pebbles and insects being picked out of rice and wheat is an example.
Ques 2. Explain what is meant by a pure substance. Do pure substances have a sharp melting point? How does that differ from a mixture? (2 marks)
Ans. Pure substances mean that the substance contains only one element or compound. Because they only consist of one element or compound, they have a sharp melting point. Mixtures on the other hand melt at different temperatures because they consist of different elements or compounds.
Ques 3. What is threshing? (1 mark)
Ans. Threshing is the process of separating the edible part of the grain from the stalk. It is done either manually by farmers or with machines. The common way of manual threshing is hand beating against an object.
Ques 4. What is sedimentation? Give an example of sedimentation. (2 marks)
Ans. Sedimentation is used for separating insoluble impurities that are heavier than a liquid from the liquid. After some time, due to gravity, the impurities will settle down at the bottom while the lighter impurities will float.
An example of sedimentation would be the dirt and mud in muddy water settling down at the bottom.
Ques 5. Explain the process of winnowing. (1 mark)
Ans. Winnowing is the process of separating grain from the chaff. The mixture is thrown into the air. The lighter chaff will be blown away while the heavy grain falls back down. It is the next step after threshing.
Ques 6. When is the process of sieving used? (1 mark)
Ans. Sieving is used when the impurities in a mixture are different in size than the useful substance. The mixture is passed through a sieve. The smaller particles pass through the sieve while the larger ones remain in the sieve.
Ques 7. What are evaporation and condensation? (2 marks)
Ans. Evaporation is the transformation of a liquid to gas as it is heated to its boiling point. Condensation is the transformation of gas to liquid as it is cooled down. The processes of evaporation and condensation can be individually and together used for the separation of mixtures.
Ques 8. What is distillation? Give an example. (2 marks)
Ans. Distillation is the process of separating a liquid from a solution of a soluble substance. The solution is heated in a flask and the vapor is passed through a condenser. As the vapor condenses into a liquid, the pure liquid is condensed into a beaker.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:



Comments