Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Omnivores are the group of animals having a wide range of food preferences that include both plants and animals. From the evolutionary perspective, all animal species tend to take on a particular type of diet, however, omnivores deviate as they survive on both plant and animal diets. This feature gives them an evolutionary advantage as they can feed on a wide range of food materials and can survive in some of the most difficult times. The physical traits of these animals are often combinations of that of the herbivores and carnivores with some exceptional characteristics of their denture, teeth and digestive systems. Apart from humans, animals such as dogs, cats, pigs, civets, chimps, orangutans and bears are some well-known examples of omnivorous animals.
| Table of Content |
Key Takeaways - Omnivorous animals, Dentures, Evolutionary Advantage, Nutrition and diet.
Omnivores
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Food is an essential basic need to sustain life. Depending on the food preferences there are three types of animals-
- Herbivores
- Carnivores
- Omnivores.
The herbivores are the group of animals that feed on the plants and the carnivores are the group of animals that depend on other animals for their food. The group omnivores are characterized by their wide range of food preferences which include both plants and animals. Thus, an omnivorous animal has both characteristics of being a herbivore and a carnivore as it depends on both plant and animal diet for their nutrition.
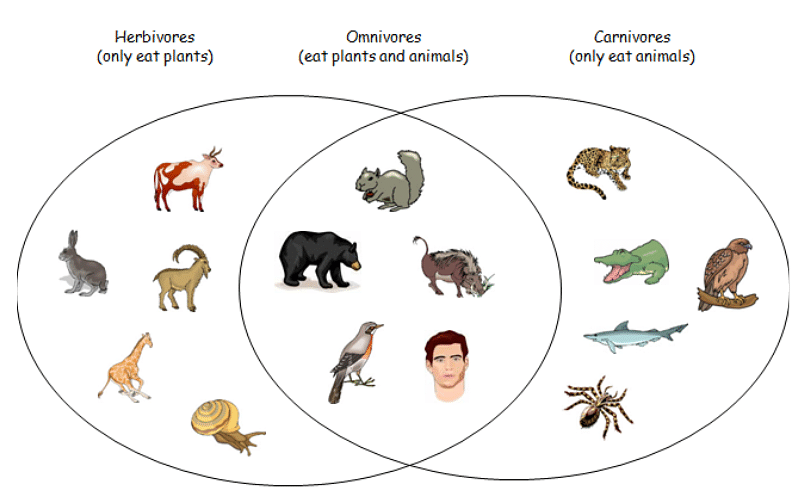
Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores
In evolutionary terms all the animal species tend to take on a particular type of diet, however, they deviate as the circumstances and the niches demand. Many small animals and birds are omnivores. For instance, the deer mice and the mocking birds may have a predominance of insects and berries at different points in time. Again, many animals are generally considered as carnivores are typically omnivores. For example, the red fox feeds on berries and other plant supplies and the snapping turtle gets almost one-third of its diet from the plant materials.
Read More:
Characteristic Features of Omnivores
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The physical traits of omnivorous animals are a combination of herbivores and carnivores. However, some characteristics are specific to the omnivores and common to all.
Teeth
The denture of omnivorous animals stands out for having incisor teeth or fangs or some other flattened teeth. The incisor teeth are often used to tear meat and the flat teeth to break plants and seeds. The dentures are not as big as those of carnivores but the incisor fangs are sharp enough. In the case of omnivorous birds, a specialized digestive system is observed in which they can grind food to small particles. This specialized digestive sac is known as gizzard. The gizzard is more like a muscular structure, filled with stones, collected by the same animal to facilitate proper grinding of the food.

Teeth Structure of Omnivores
Read More:
Digestive System
In general, the digestive system of omnivores consists of a single stomach and intestines of intermediate length in between herbivores and carnivores. Usually, the digestive system of an omnivore is simpler than that of a herbivore while being more complex than the digestive system of carnivorous animals. Such a digestive system can take advantage of the nutrients of both meat and vegetable food.

Omnivore and Herbivore digestive systems
The diet of omnivorous animals including humans varies widely depending on the season or short-term climatic factors and the availability of food in the habitat they reside. There are omnivorous animals found in the most inhospitable areas where very less resources are available throughout the year. The conditions make them adaptable to the situations in which they have to survive on vegetables and animals whatever is available.
Read More: Catabolism and Anabolism
Evolutionary Advantage of the Omnivorous Animals
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The natural ecosystems are governed by various environmental factors such as availability of resources and their distribution, availability of water, climatic conditions, abiotic factors etc. Thus different animals have to develop evolutionary characteristics to adapt to the new conditions. Omnivorous animals have a great evolutionary advantage over other animals with a narrow range of food preferences. This is because when it comes to the food supply, the omnivores can supply themselves more quickly with a diverse range of food. This feature also helps them to expand their range as well as habitat.

Food Chain
Read More: Difference between Warm blooded and Cold blooded animals
Examples of Omnivores
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Following are some examples of omnivorous organisms-
- Human beings are omnivorous as we depend on both the plant and animal diet for our survival. Apart from humans, many other mammals live on an omnivorous diet. For instance, racoons which are opportunistic feeders are not very picky and eat anything from fish to mice to fruits and vegetables to even human wastes such as leftover food.
- Other organisms such as pigs, rats, skunks and most of the bear species are opportunistic feeders. The jerboa is a kind of desert rodent that eats plant seeds and insects.
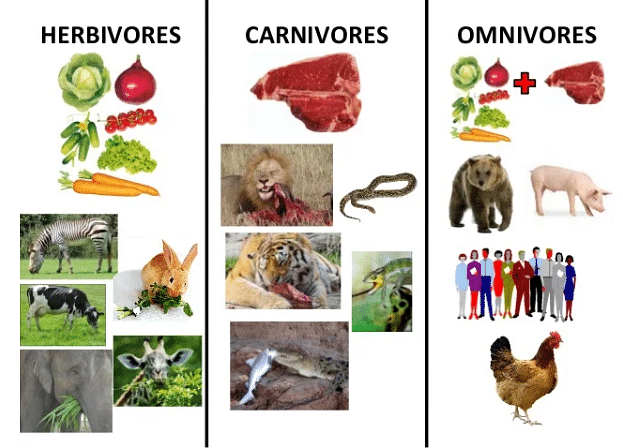
Omnivores animals
- For the bird roadrunner, the diet is composed of fruits and seeds mainly although a significant percentage of animal material such as rodents, small snakes and insects is consumed by them.
- Parrotfish and Damselfish are omnivores that feed on planktons and other smaller fish. There are several omnivorous birds as well that include kea, chicken, duck, crows and robbins. Some members of the reptile family such as turtles and lizards are also omnivorous.
Read More:
List of Omnivorous Organisms
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
More than 8.7 million species of animals have been identified. There are some lesser-known examples of omnivorous animals with fascinating features and characteristics. Following is a list of such omnivores that are opportunistic feeders.
- Bear
- Orangutan
- Chimpanzees
- Catfish
- Chipmunks
- Dogs
- Pigs
- Civets
- Piranhas
- Hedgehogs
- Earthworms
- Earwigs
- Bonnethead sharks
- Badgers
- Skunks
Read More: Respiration and Combustion
Things To Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Depending on the food preferences there are three types of animals- herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
- Omnivores are those animals that have a wide range of food preferences including both plants and animals.
- Generally, the physical traits of omnivorous organisms are a combination of that of herbivores and carnivores.
- The denture of omnivorous animals usually has incisor teeth or fangs or some other flattened teeth. The incisor teeth are used to tear meat and the flat teeth break plant materials and seeds.
- The digestive system of omnivores is of intermediate length that falls in between that of herbivores and carnivores.
- Generally, the digestive system of an omnivore is simpler than that of a herbivore while being more complex than the digestive system of carnivorous animals.
- The omnivorous animals have a great evolutionary advantage over animals with a narrow range of food preferences. This is because when it comes to the food supply, the omnivores can supply themselves more quickly with a diverse range of food.
- Humans are the most common example of omnivores. However, there are some lesser-known examples of omnivorous animals present in nature such as Chimpanzees, Catfish, Chipmunks, Dogs, Pigs, Civets, Piranhas, Hedgehogs, Earthworms etc.
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques: What are omnivores? (2 marks)
Ans: Omnivores are animals characterized by their wide range of food preferences as they feed on both animal food resources. Some of the most common examples of omnivores are humans and dogs.
Ques: State some characteristics of the omnivores. (2 marks)
Ans: Some of the characteristics of the omnivores are as follows-
- The denture of omnivorous animals stands out for having incisor teeth or fangs or some other flattened teeth. The incisor teeth are often used to tear meat and the flat teeth to break plants and seeds.
- In some omnivorous birds a specialized type of digestive system is found in which they can grind food to small particles. It’s called the gizzard.
- The digestive system of an omnivore is simpler than that of a herbivore while being more complex than the digestive system of carnivorous animals.
Ques: Give some examples of omnivores. (2 marks)
Ans: Some of the examples of the omnivores are:
- Bear
- Orangutan
- Chimpanzees
- Catfish
- Chipmunks
- Dogs
- Pigs
- Civets
- Piranhas
- Hedgehogs
- Earthworms
Ques: Are humans omnivores? (2 marks)
Ans: Yes. Humans are omnivores as they depend on both plants and animals for their diet and survival.
Ques:How are herbivores and carnivores different from omnivores? (2 marks)
Ans: The herbivores are the animals that feed on the plants and the carnivores are those animals that feed on the animals. On the other hand, carnivorous animals are those who feed on both plants and animals, thus, having a broader range of food preferences.
Ques: Do the omnivores get any evolutionary advantage for their food preference? (2 marks)
Ans: Yes, Omnivorous animals have a great evolutionary advantage over other animals with a narrow range of food preferences. This is because when it comes to the food supply, the omnivores can supply themselves more quickly with a diverse range of food.
Ques: Where do omnivores live? (2 marks)
Ans: Omnivores live everywhere. They are found in every part of the world including the most inhospitable places on the planet.
Ques: State some domestic animals that are omnivores. (2 marks)
Ans: Interestingly some of the common domestic animals such as cats and dogs are some good examples of omnivorous animals as they feed on both plants and animals.
Ques: Why do omnivores possess a contradiction for the classification of animals? (2 marks)
Ans: Omnivores are those animals that drive energy and nutrition from the plants and the animal matters. However, some animals, which are classified as herbivores, are ones to consume plant materials while the carnivores such as tigers and lions consume plant materials. Thus, they can be categorized into two separate categories but the omnivorous species create certain contradictions among the scientific community as their food preferences are much wider than the other groups.
Read More:




Comments