Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
There are lots of changes occurring around us. Some of the changes are noticeable while some are not. In fact, everything that exists on the earth undergoes certain changes. These changes are natural as well as man-made. There are many changes happening in our environment like turning of the day into night and vice versa, change of weather, change of season, change of climate, leaves fall from the trees, rusting of an iron etc.
Related Links
- Appearing for NEET, Download NEET PYQ for all subjects
- Appearing for CUET, Download CUET PYQ for all subjects
| Table of Contents |
Key Takeaways: Biology Changes, Changes, Contraction, Expansion, Evaporation, Melting, Reversible, Irreversible Chnage.
Changes Around Us
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
When any substance or object alters one state to another state then it is called a change. During this process, a substance or an object can transform into many kinds. All these changes sometimes occur instantly or take a long time. Some changes are periodic while others are not. The changes are taking place in the environment due to man-made activities as well as nature. The most common example of change is the growth of humans from a baby to an elder person.

Stages of Human Being
There are many real-life examples of changes which are mentioned below:
- Rising of sun
- Rusting of iron
- Melting of ice
- Elongation of a spring
- Cooking of food
- Germination of seeds
- Folding of a paper
- Growing of plants and
- Frying an egg and many more.
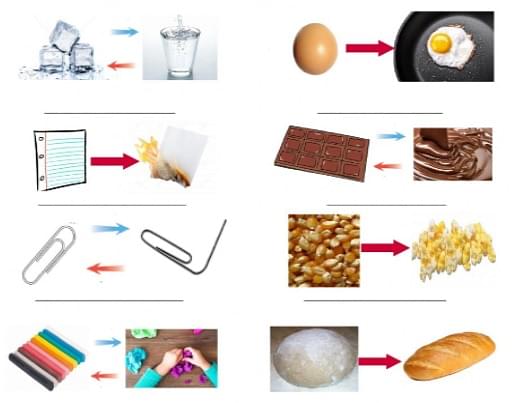
Change Examples Diagram
Classification of Change
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
On the basis of various factors such as size,shape,periodicity etc. changes are classified into many types which are mentioned below:
- Reversible Changes
- Irreversible Changes
- Physical Changes
- Chemical Changes
- Slow Changes
- Fast Changes
- Desirable Changes
- Undesirable Changes
- Periodic Changes
- Non-periodic Changes
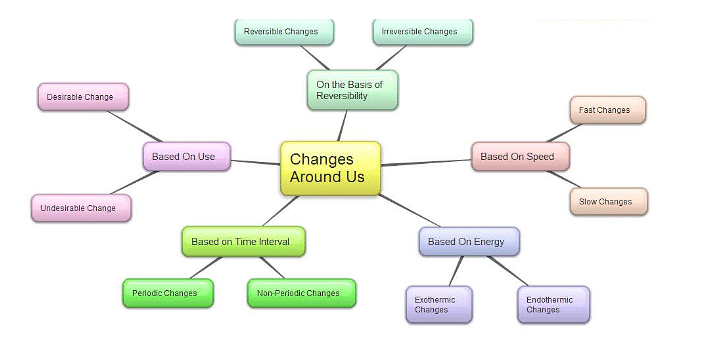
Classification of Changes Diagram
Reversible Changes
When a substance or an object regains its original shape after a change then it is called a reversible change. In reversible change, any body which undergoes a certain change comes into its original state. There is no formation of new substances that takes place in reversible changes. These changes are temporary in nature.

Spring Example(three stages of spring)
To understand more about the reversible change let us consider an example of a spring.
Case 1: In this case, where we can compress the spring. The size of the spring decreases. But, when we stop pushing the spring then it gets back into its original state.
Case 2: Take a spring, stretch it. We all know that we can stretch a spring at a certain limit by pulling it. When we stop pulling the spring then you can see spring immediately get back to its original shape. The size and shape of spring do not change.
Apart from this, there are some more examples of reversible changes which are shown below:
- Melting of ice
- Inflation of balloon
- Boiling of water
- Folding of a paper
- Stretching of a rubber band
- Knitting a sweater
- Melting of chocolate etc.
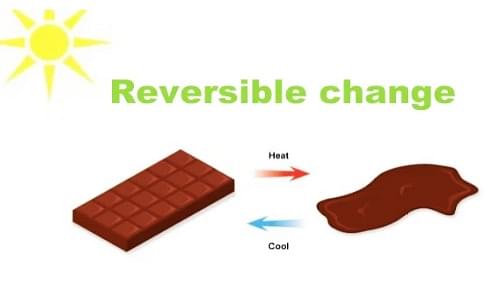
Reversible Change Example
Irreversible Changes
When a substance or an object which cannot regain its original shape after a change is known as irreversible change. In irreversible change, the shape and size of the substance are changed completely. It is impossible to come into its original shape after a change. These changes are permanent in nature. There are some other substances formed after the change takes place in irreversible changes.

Candle Example(Irreversible Change)
To understand more about the reversible change let us consider an example of a Candle.
Take a candle that has a specific shape and size. When we burn the candle, after some time the candle starts losing its shape. When the candle is fully burned, it is impossible to turn into its original state. So, this change cannot be reversed.
Apart from this, there are some more examples of irreversible changes which are shown below:
- Burning of a paper
- Baking a cake
- Rusting of an iron
- Falling oa a leaf from tree
- Bursting of a balloon
- Mixing of cement into water
- Dissolving a salt into water
- Burning of woods etc.

Irreversible Changes Examples
Physical Changes
Physical Change is defined as a change in which physical appearance such as shape, size, state, texture etc. of a substance or an object is changed. There is no chemical reaction that takes place during the physical change. The physical properties of the substance change while chemical properties remain the same. There is no formation of a new substance, only the physical appearance of the substance changes. In physical changes, most of the changes are reversible in nature i.e. temporary.

Physical States of Water
There are some real life examples of physical changes which are mentioned below:
- Melting of an ice cube
- Boiling of water
- Carbon changing from graphite into a diamond
- Shredding of paper
- Breaking a glass etc.

Physical Changes Examples
Chemical Changes
Chemical change is defined as a change in the chemical properties of the substance. During the chemical change, physical properties of the substance do not change. Only the chemical composition of the substance changes which forms the new substance. There is a formation new substance takes place after a chemical change. Most of the chemical changes are irreversible i.e. permanent.

Chemical Changes Examples
There are some real-life examples of chemical changes which are mentioned below:
- Baking a cake
- Frying an egg
- Rusting of an iron
- Burning of wood
- Digestion a food
- Mixing acid and base etc.
Slow Changes
Slow change is defined as the change which takes a long time to complete. These changes do not happen immediately, it takes a lot of time to complete its process.

Autumnal Leaves Shedding
There are some most common examples of slow changes which are shown below:
- Rusting of iron
- Photosynthesis process
- Digestion of food
- Weathering
- Erosion
- Deposition
- Growth of living organisms etc.
Fast Changes
Fast change is defined as the change which happens very quickly i.e. takes less time to occur. There are some most common examples of fast changes which are shown below:
- Melting of ice
- Bursting of crackers
- Volcanic eruptions
- Earthquakes
- Landsliding
- Burning of paper etc.

Fast Changes Examples
Periodic Changes
Periodic change is defined as the change which happens after a regular period of time. Periodic changes repeat themselves after a particular period of time.
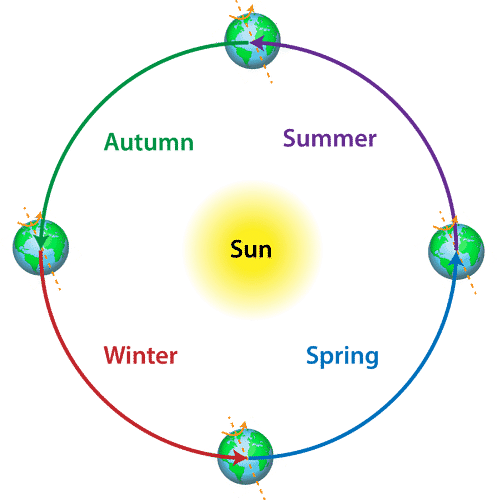
Periodic Changes Examples
Examples:
- Swinging of a pendulum
- Change of season
- Change in the phases of the moon
- Beating of heart
- Day and night cycle.
Non-Periodic Changes
Non-Periodic changes are defined as the changes which do not occur at regular intervals of time. Non-periodic changes do not repeat after a particular time period.
Examples:
- Eruptions of volcanoes
- Forest fires
- Earthquakes
- Rusting of an iron
- Accidents etc.

Non-periodic Changes Examples
Desirable Changes
Desirable changes are defined as the changes which are required for us. Desirable changes are useful for all living beings. Desirable changes are caused by humans as well as nature.

Desirable Changes Examples
Example:
- Change of season
- Germination of seeds
- Ripening of fruits
- Preservation of fruits and vegetables through adding chemicals
- Growth of humans etc.
Undesirable Changes
Undesirable changes are defined as the changes which are not required or useful for living organisms. Undesirable changes are harmful to humans as well as to the environment. These changes are a threat to living organisms.

Souring of Milk
Example:
- Flooding of rivers
- Spoilage of items
- Forest fire
- Volcanic eruption
- Souring of milk
- Global warming etc.
Reason behind Changes
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Nature and human activities are responsible for the changes happening in our surroundings. Also, there are some major causes which makes changes such as:
Changes Caused by Heating and Cooling
When we heat or cool, some substances change their state. Moreover, sometimes a new substance is formed as a result.
- Due to heating, some things become hot.
- Due to cooling, some things become cold.
- The substance start expanding after heating.
- The substance start contracting after cooling.
- There are certain things which burn due to heating
- There are certain things which change their state after heating or cooling like solid to liquid or liquid to solid.

Expansion due to Heat
Read More: Metals and Non Metals
Changes Caused by Pressure
When we apply pressure on certain things, the shape and size of the things changes. Also, some things break due to high pressure. These changes are reversible and irreversible in nature. Example:
- Dough changes its shape after applying pressure.
- Brittle substances like biscuits, glass and coal break into pieces after applying pressure

Change due to Pressure
Changes Caused by Mixing
Due to the mixing of substances, many changes occur. Moreover, both reversible and irreversible changes occur due to the mixing of substances.
Example:
- Dissolving salt into water(salt solution) [reversible change]
- Dissolving quicklime into water(slaked lime) [irreversible change]

Dissolving of Sugar Solution
Things to Remember
- In reversible changes, a substance or an object can regain its original shape after a change.
- In irreversible changes, a substance or an object cannot regain its original shape after a change.
- In reversible changes, there is no formation of new substances.
- There are other substances formed after a change in an irreversible process.
- Physical properties of the substance do not change in a chemical change.
- The chemical composition of the substance changes during chemical change while it remains the same in physical change.
- It is considered that most of the physical changes are reversible changes. While all the chemical changes are irreversible changes.
- The expansion and contraction takes place when we apply heating or cooling.
- Solid state converts into liquid state and vice versa after applying heating or cooling.
Sample Questions
Ques. Mention some of the ways of bringing changes in the materials around us. [2 marks]
Ans. There are many ways which bring changes in the materials around us. List of the some important ways is mentioned below:
- Expansion
- Contraction
- Evaporation
- Condensation
- Mixing of the two or more substances
- Pressure
- Separation
- Burning
Ques. What is the purpose of separation? [2 marks]
Ans. Separation of the two or more substance are done for the following purposes:
- Due to separation, the harmful and useless components are removed.
- To getting the useful component
- To remove impurities for obtaining the pure sample or substance.
Ques. Why are desirable changes necessary for the living organisms? [3 marks]
Ans. Desirable changes are those changes which are necessary for the survival of humans as well as animals. Desirable changes are the need of living organisms.
For Example:The change of season is necessary for the growth of crops because there are some certain kinds of crops which are grown in a particular season. If the season does not change then it is not possible for us to grow different types of crops. Apart from this, desirable changes are required to maintain the balance between the environment.
Ques. Define Expansion and contraction? [3 marks]
Ans. When any substance or material expands when a required amount of heat is applied to it then it is referred to as an expansion. In expansion, the particles of the substance start expanding and become loose when temperature increases. For example: railway tracks, cracks in road, sags in electrical power lines etc.
When any substance or material contracts or shrinks after cooling is called a contraction. In contraction, the particles of the substance start shrinking and become tight when temperature decreases. For Example: formation of ice, shrinking of balloon due to cold air etc.
Ques.How a metal rim is fixed around the wooden wheel of the cart. Explain. [3 marks]
Ans. A metal rim is foxed around the wooden wheel of the cart due to the expansion and contraction process. The iron rims of the wooden bullock carts or horse carts are of a thin kind (i.e. Thin iron rims around them). The iron rim needs to be smaller in size than the wheel so that it can easily fit in it. The iron rim is heated uniformly with the fire so that it expands and the size of the rim increases. Due to the bigger size of the iron rim, the hot iron rim is easily put around the wooden wheel. After that, the cold water is poured over the hot iron rim to cool it down. With the help of cooling, the iron rim contracts and becomes smaller in size which can help to tightly fit the iron rim in the wooden wheel.

Fixing of the iron rim into the wooden wheel
Ques. What do you mean by Change? Give some examples of changes happening arounds us. [3 marks]
Ans. Those substances which undergo certain alterations or changes are known as changes. Most of the things which are present on the earth undergo certain changes. These changes can happen in a minute or a long time to complete. There are many examples of changes which are mentioned below:
- Rising of sun
- Turning of day into night
- Change of weather
- Change of season
- Swinging of pendulum
- Volcanic eruptions
- Growth of humans
- Frying of an egg
- Elongation of a spring etc.
Ques. What are the differences between reversible and irreversible changes? [5 marks]
Ans. The main differences between reversible and irreversible changes are mentioned below:
| S.No. | Reversible Change | Irreversible Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Any substance or an object which can regain its original state after change is called a reversible change. | Any substance or an object which cannot regain its original state after change is called an irreversible change. |
| 2. | In reversible change, initial and final state is same | In irreversible change, the initial and final state is not the same. |
| 3. | Reversible changes are temporary in nature | Irreversible changes are permanent in nature |
| 4. | Chemical properties of the substance do not change in reversible changes. | Chemical properties of the substance changes in irreversible changes |
| 5. | Common Examples are: ice melts into water, freeze water turns into ice, stretching of a rubber band, folding of a paper etc. | Common examples are: cement mixed into water, frying of an egg, baking a cake, rusting of an iron etc. |
Ques. What are Chemical changes? Explain it with the help of an example. [5 marks]
Ans. Chemical changes are those changes in which the chemical composition of the substance changes. The initial and final state of a substance is different from each other. The formation of new substances takes place. However, the physical properties of the substance remain the same. Moreover, all the chemical changes are irreversible in nature. In chemical changes, the rearrangement of atoms takes place which forms new molecules as a product.
To understand chemical changes in more depth let us consider a common example of rusting of iron.
How rusting takes place: initially the colour of nail or iron metal is silver.when we place the iron metal or nail in the air or outside. After some time, the colour of the nail or iron metal is changed and turns it into reddish brown which is called rust. This is happening due to the chemical reaction that takes place in between the iron metal or nail and air.
Mathematically, Nail + Air → Rusting of an iron

Chemical Change Reaction Diagram
Check-Out:




Comments