Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Force is responsible for everything we do. Force can be defined as an interaction between two or more bodies that causes a change in the state of motion of the objects when unopposed. An object is pushed or pulled by a force. To move an object, we employ force. When we brush our hair, we are pulling the brush through our hair with force. When we dunk a basketball, we use force to propel ourselves off the ground and into the air. Some forces are observable, while others are not. Force can be either modest or powerful. To understand the Interaction of forces, we can think of it as a push or a pull that results in the change in the state of motion that corresponds to either a change in the speed of the body and or a change in the direction of motion of the body. Here we will discuss the interaction of forces, as well as the elements that influence it and the changes that a force can produce.
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Force, Weak Force, Strong Force, Change in Motion, Change in Shape, Direction Of Force, Magnitude of Force, Push, Pull, Acceleration, Interaction of Forces
Introduction to Interaction of Forces
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Something that creates a change in the condition of motion is called a force. A push or a pull can be conceived of as the interaction of forces. A change in the state of motion refers to either a change in the speed or the direction of motion of the body. The speed shift could signify either acceleration or slow down (deceleration).
A ball, like a chair or a table, is incapable of moving by itself. Unless a force is operating on them, all non-living objects are stationary. When forces work in opposite directions, they cancel each other out, but when they act in the same direction, they add up. A force can cause a stationary body to move, a moving object to stop, and it can increase or reduce the speed of a moving body.

Force
Also Read: Force and Motion
Factors Influencing Interaction of Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The main factors influencing the interaction among forces are as follows:
Forces Acting in the Same Direction
When two forces act in the same direction on a body, the net force equals the total of the two forces acting on it. In this scenario, the combined force is always far stronger than either of the individual forces applied separately.
Two persons pulling a heavy car or any other heavy object in the same direction, for example. When moving a heavy load from one location to another, a large number of workers apply forces in the same direction to move the item.
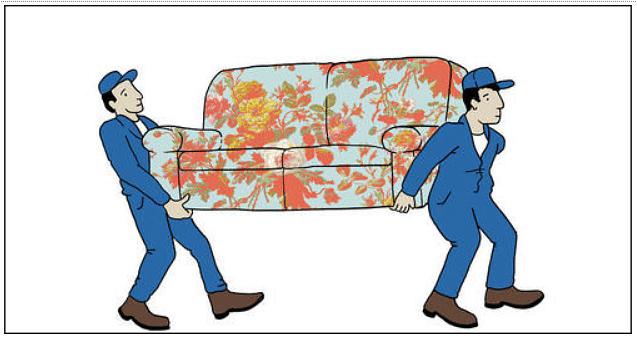
Forces Acting in the Same Direction
Forces Acting in Opposite Directions
When two forces interact and act on a body in different directions, the net force exerted on it is the difference between the two forces.
Examples: Consider two labourers attempting to push a heavy cargo in different directions. If the two forces exerted on it in opposite directions are equal in magnitude, the net force on the object is zero, and if any uneven forces are applied, the box moves in the direction where the higher force is applied.

Forces Acting in Opposite Directions
Magnitude and Direction of Force
The magnitude and direction of a force interaction can be more or lesser than one another. To fully define the action of force interaction on the body, we must also explain the direction in which it acts. When the direction or amount of a force changes, the effect changes as well.
For example, consider two girls who are circling each other while holding hands. They would not have been able to move around if there had been no interaction between them. In this situation, the direction and amplitude of forces should be equal and opposed so that they can all travel at the same pace.
Check More:
<
Effect of Interaction of Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
With changes in movement, velocity, and direction, force and its fundamental interactions in nature produce a variety of outcomes. However, other aspects influence its gestures, one of which is the shape and material of the object.
- The state of motion of an object can be changed through the interaction of force between objects: A change in the speed or direction of motion of an item, or both, is referred to as a change in its state of motion. A fielder, for example, catches a fast-moving cricket ball and brings it to a halt. Ram strikes the ball and causes it to change direction.

Striking a Ball can Change its Direction
- The shape of a body can be changed by force interaction: Force can be used to affect the shape of a body. In some circumstances, we employ it to get the desired shape of the body or object. Exercising two hands-on any inflated balloon compresses or affects the shape of the balloon. We adjust the shape of the dough as needed while creating it.

Force can Change the Shape of an Object
Also Read: Effects of Force
Weak Interaction Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The weak interaction, commonly known as the weak nuclear force, is a fundamental interaction that occurs in nature between subatomic particles and is responsible for radioactive erosion in atoms. The two most commonly utilised theories for understanding weak interaction force are quantum flavour dynamics (QFD) and electroweak theory (EWT). Charged-current interaction and neutral-current interaction are two other interactions. The commencement of the nuclear reaction that powers the sun and the disintegration of unstable subatomic particles like mesons are two instances of weak nuclear force.
Strong Interaction Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The strong interaction force governs quarks in clusters of subatomic particles such as neutrons and protons, and it is based on a feature called colour, which is not to be confused with the generic term colour. Particles with the property function with a strong force, whereas subatomic particles without the property, like leptons and electrons, do not experience any strong forces. Similar to plastic, the force between two quarks increases in speed as the distance between them decreases.
Things to Remember
- The push or pull is considered to be called Force. Force is the interaction between two or more bodies that causes a change in the state of motion of the objects when unopposed.
- When two forces act in the same direction on an item, the forces combine to produce a huge force.
- When forces act in opposite directions to each other, they cancel out each other.
- The state of motion of an object can be changed through the interaction of force between objects.
- The shape of a body can be changed by the interaction of forces.
Sample Questions
Ques. What do you understand by force? Explain its effects. (3 Marks)
Ans. The mechanical interaction between bodies is referred to as force. A force can alter both the motion and deformation of the body on which it acts. Forces can be generated by direct contact between bodies or delivered at a distance. Forces operating at a distance are spread over the volume of the body, whereas contact forces are distributed over the surface area of the body. Forces and motion concepts are used to explain and predict the movement and shape of objects, both when they change and when they remain the same.
Ques. What are the different types of force interaction? (3 Marks)
Ans. According to current understanding, there are four basic interactions or forces: gravitation, electromagnetism, weak interaction, and strong interaction. A body force is a force that operates across the volume of a body and has a wide range of frequency and actions. Gravitational forces, electric currents, and magnetic fields are examples of body forces. The forces of the body are in contrast to the forces of touch or surface forces imparted to the surface of an object.
Ques. Give two examples of interactions between bodies that resulted in force. (3 Marks)
Ans. We can claim that interaction between the bodies generates force in two ways:
- When we attempt to push a block without touching it, we are unable to do it. When we push a block with our hands and exert force, the block moves.
- A book cannot be moved or lifted without coming into contact with it. So, when we touch and lift the book, we exert force on it, which causes it to be lifted by our hands.
Ques. Define interaction force pairs. (3 Marks)
Ans. Two forces are acting on the two interacting objects in every interaction which are as follows:
- The force applied to the first object is applied in the opposite direction to the force applied to the second object.
- These forces are always found in pairs, with equal and opposing action-reaction forces.
Ques. Give examples of how force might cause a moving item to change its direction. (3 Marks)
Ans. Force may change the direction of a moving item in a variety of ways.
- When a batsman hits the ball with a bat in cricket, the ball's direction changes.
- Your car's steering wheel functions in a similar way. You can change the direction of your car's travel by applying force to the steering wheel.
Ques. What is the net force on an object when two forces act in opposite directions? (1 Mark)
Ans. The net force on an object is zero if two forces of equal size but opposite diversity act on it (null vector)
Ques. When two forces act in the same direction, what happens? (3 Marks)
Ans. When two forces act in the same direction on an item, the forces combine to produce a huge force. The resultant force is calculated by adding the magnitudes of two forces acting in the same direction. If two forces acting on an object are f1 and f2, the resultant force is f= f1 + f2.
For example, it is easier to push a vehicle or car with the help of 2-3 people instead of one because force adds up as when all people are pushing in the same direction, all the forces are combined and act together on the same leading to pushing the car easily.
Ques. Why does the bicycle slow down when one stops pedalling? (1 Mark)
Ans. When the rider halts/stops the pedalling, there is a motion in the opposite direction with friction in motion causing the bicycle to slow down and finally halt.
Ques. What happens when forces act in opposite directions? (3 Marks)
Ans. When forces act in opposite directions to each other, they cancel out each other.
For example, In a tug-of-war game, two teams apply forces acting in opposite directions. Both the teams are pulling the rope towards them, that is, one is pulling the rope towards the right and another is trying to pull the rope to the left. Thus both the teams are cancelling the force.
Check More:



Comments