Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Insectivorous plants are a special type of plant, commonly known as carnivorous plants. These plants are known for their specific characteristics of trapping and eating insects via chemical processes that make these plants different from others.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Insectivorous Plants, insectivorous plants examples, insectivorous plants names
What are Insectivorous Plants?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Biology defines the Insectivorous plants as the insect–eating plants. These plants tend to survive by the nature of deriving most of their nutrition from the insects around them. The salient feature of these insectivorous plants is that they have the ability to trap the insects flying around them and consuming them as their food.
Insectivorous plants
Another important feature of the insectivorous plants is that these plants grow in humid areas, that is, under the availability of ample amount of sunlight and moisture. Insectivorous plants are grown easily in the nitrogen deficient soil and this type of soil serves as an important habitat for these plants. This nitrogen deficiency is also one of the reasons due to which these plants trap and digest the insects in order to absorb the nutrients. The insectivorous plants are also known as the Carnivorous plants, similar to that of carnivorous animals.
Read more : difference between radicle and plumule
Insectivorous Plants: Characteristics
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
There are certain important characteristics of insectivorous plants that eventually make them unique.
Nitrogen Deficiency
Insectivorous plants are grown in the nitrogen deficient soil which ultimately makes them lack the enough amount of nitrogen. Therefore, as a result, they tend to entrap the insects and digest them, considering it their food, to satisfy their nitrogen requirement.
Read more : Seed Dispersal
Attractants
Another important characteristic of the insectivorous plants is their colourful and the shiny texture. These plants are immensely beautiful in appearance which works as a bait to attract the insects. They often have nectars and a pleasant odour as well which also contribute a lot in attracting the insects.

Insectivorous Plant
Wet and Damp Habitats
Insectivorous plants are found only in wet, damp and humid environments. The presence of acidic soil that is deficient in nutrients, such as swamps, bogs, wetlands, coastal plains, etc. is another important characteristic of insectivorous plants. For instance, they are found in the wet regions of North America, Australia, and tropical regions.
Read more : Androecium
Digestive Enzymes and Organisms
These insectivorous plants have the phenomenon of secreting a type of digestive enzyme that ultimately dissolves insects for better absorption. Some insectivorous plants also have some kind of bacteria or mites in their digestive tract that mimic the functions of the human digestive tract. They digest the prey for the absorption of the nutrients by the plants.
Read more : Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
Inescapable Traps
The defining characteristic of insectivorous plants is their inescapable traps. Many insectivorous plants have the special or modified parts of the plant for trapping the insects. The hair - lined edges are present on the mouth of insectivorous plants that consist of the characteristic of shutting the mouth as soon as the insect touches the hair, thereby, trapping the insects. The presence of the sticky mucus - like substances on the plants’ stalks allow the insects to get trapped there, thus, preventing any kind of movement.
| Important Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tap Root System | Fibrous Root System | Inflorescence |
| Vegetative Characters of Solanaceae | Vegetative Characters of Liliaceae | tendril |
Insectivorous Plants: Types of Traps
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Insectivorous plants exhibit diverse varieties of physical features, such as leaves, roots, etc. The leaves of these plants are usually modified into the traps for the insects. The trapping mechanisms are designated as active or passive depending upon whether they move to capture the prey or not. So, let us see the different types of traps that are found in insectivorous plants.
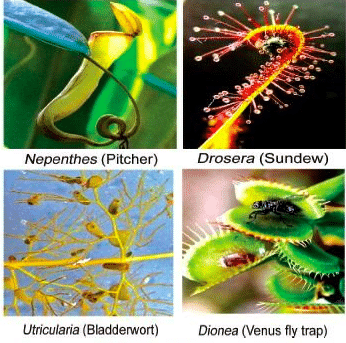
Pitfall Traps: These traps contain a hollow leaf along with a lid that is filled with liquid to digest the prey. These traps are found in the insectivorous plant known as pitcher plant.
Snap Traps: These are the traps which are found in the Venus flytrap. They act by shutting their leaves rapidly as soon as the prey touches the trigger hair.

Types of Carnivorous Plant Traps
Flypaper Traps: Flypaper traps are the kind of traps which are again sticky in nature. The leaves in this case are covered in the stalked glands that secrete the sticky mucilage.
Lobster - pot Traps: These traps are found in the corkscrew plants. They possess downward - pointing hair that pushes the prey deep inside the trap.
Bladderwort Traps: These traps are commonly found in the insectivorous plant called Utricularia. The bladderwort trap simply uses a partial vacuum like structure that allows it to trap the small organisms.
Insectivorous plants digest their prey with the help of the enzymes and bacteria that are secreted by them. It facilitates the chemical digestion and absorption of the insects. The end products of this chemical breakdown are absorbed by the plants in the form of the nutrients which help them to survive under unfavourable conditions. The examples of these insectivorous plants are tabulated below for better and comprehensible understanding of the same.
Related Articles:
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
- Insectivorous plants are carnivorous plants that trap and eat insects via chemical processes to gain nutrition.
- Examples of Insectivorous plants include Venus Flytrap, Bladderwort, Pitcher Plant, Round leaved Sundew, etc.
- Characteristics of Insectivorous Plants include: Nitrogen Deficiency, Attractactive features, Wet and Damp Habitats, Presence of Digestive Enzymes, Inescapable Traps, etc.
- Mostly, the leaves of insectivorous plants are modified to create traps. Some of the different types of traps are: Pitfall traps, Flypaper traps, Snap Traps, etc.
Read more : Plumule
Previous Years Questions
- Which one of the following plants belongs to the Family Apocynaceae?….[COMEDK UGET 2009]
- Madhunashini is the popular name for…..[COMEDK UGET 2006]
- The roots that originate from the base of the stem are… [ NEET 2020]
- Bicarpellary gynoecium and oblique ovary occurs in...[ NEET 2001]
- Tetradynamous conditions occur in….[ NEET 2001]
- In which of the following plant sunken stomata are found...[ NEET 2001]
- What is the eye of potato?…[ NEET 2001]
- Edible part of banana...[ NEET 2001]
- Which is correct pair for edible part?….[ NEET 2001]
- Coconut fruit is a….[ NEET 2017]
- Commercial cork is obtained from… [NEET 1991]
- Botanical name of cauliflower is…. [NEET 1991]
- Banana is...[JKCET 2007]
- Tricarpellary syncarpous superior ovary is….[JKCET 2007]
- The edible part in hesperidium fruit is...[JKCET 2007]
- The bladders of Utricularia and pitchers of….[JKCET 2004]
- Phylloclades are...[JKCET 2004]
Sample Questions
Ques. What are insectivorous plants? (2 marks)
Ans. Insectivorous plants are the plants that derive most of their nutrition by trapping the insects and consuming them with the help of the enzymes. For example, Venus flytrap, Bladderwort, etc. Insectivorous plants are also called carnivorous plants because instead of making food through photosynthesis these plants eat animals and insects.
Ques. How are insectivorous plants different from other plants? (2 marks)
Ans. All the plants except that of insectivorous plants, make their food through the process of photosynthesis, while insectivorous plants get nutrients by consuming the insects, therefore, known as carnivorous plants.
Ques. How do Nepenthes catch insects? (3 marks)
Ans. Nepenthes are a kind of insectivorous plant and these plants have the feature of capturing their prey or the insects with the help of the specialised patterns of the leaves. These specialised leaves are known as pitfall traps. Such traps have a slippery and colourful surface which attracts the insects into it and the slippery surface makes them slip down for easy and quick digestion and absorption of the nutrients.
Ques. Why are insects attracted towards insectivorous plants? (2 marks)
Ans. The insects are usually attracted towards insectivorous plants because of the beautiful, colourful and the shiny appearances held by these plants and their pleasant odour also play an important role in attracting the insects.
Ques. What is another name for insectivorous plants? Explain. (3 marks)
Ans. Insectivorous plants are also called carnivorous plants. These plants are characterised by a significant feature of absorbing the nutrients from the insects or the small organisms. Therefore, they are called carnivorous plants.
Likely, the carnivorous animals which have the other smaller creatures as their prey, insectivorous plants also act similarly. The source of energy for insectivorous plants, like that of Venus flytraps, etc., is insects which is why they are called the carnivorous plants.
Ques. Define the Lobster - pot Traps and the Bladderwort Traps. (4 marks)
Ans. Insectivorous plants perform their main function of acquiring the nutrients from the insects by trapping them with the help of the specialised traps which are associated with different types of insectivorous plants. Lobster - pot Traps are usually found in insectivorous plants which are known as corkscrew plants. These traps tend to possess downward - pointing hair that plays a great role in pushing the prey deep inside the trap.
While on the other hand, the Bladderwort traps are the ones which are commonly found in insectivorous plants called as Utricularia. The bladderwort trap simply uses a partial vacuum like structure that allows it to trap the small organisms.
Ques. Illustrate the habitat of insectivorous plants. (4 marks)
Ans. Wet and Damp Habitats are the most preferential conditions for the growth of insectivorous plants. Insectivorous plants are found only in the wet, damp and humid environment. The presence of acidic soil that is deficient in nutrients, such as swamps, bogs, wetlands, coastal plains, etc. is another important characteristic of insectivorous plants.
Insectivorous plants are grown in nitrogen deficient soil which ultimately makes them lack sufficient nitrogen. Therefore, as a result, they tend to entrap the insects and digest them, considering it their food, to satisfy their nitrogen requirement. For instance, these plants are usually found in the wet regions of North America, Australia, and tropical regions.
Do Check Out:




Comments