Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Sleeping Sickness is a tropical, parasitic disease caused by the Trypanasoma brucei parasite carried by the Tsetse fly. This disease is native to the African Continent. Sleeping sickness is also known as African Trypanosomiasis and affects rural areas more.
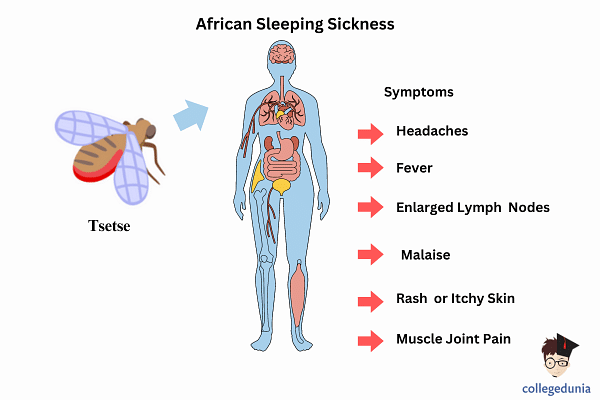
The Tsetse fly bite presents in the form of a red sore, and increases to fevers, muscle and joint aches, lymph gland swelling, irritation and headaches.
What is Sleeping Sickness?
Sleeping Sickness is a parasitic or tropical disease. This disease should be treated properly otherwise it can be very dangerous. This disease spreads through the bite of Tsetse fly. These species are found in the African continent by which the African people living in rural areas are mostly affected by this disease. The bite of a Tsetse fly develops into a red sore. This would make the person experience fever, swelling in the lymph glands, irritation, headache, muscle and joint ache.
African Sleeping Sickness
This disease attacks the central nervous system in advanced stages. At this stage, people would start feeling personality changes, biological clock alteration, and seizures. They would experience difficulty walking, talking and speaking. If not treated immediately, an infected person can also die.
Biological Classification: Quick Revision Notes
Causes of Sleeping Sickness
Following are the causes of Sleeping Sickness:
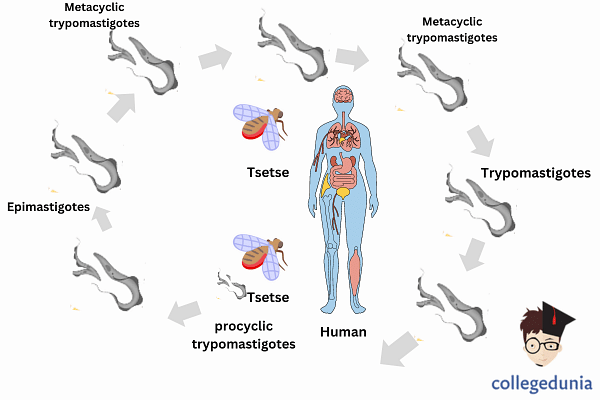
- The main cause of this disease are the 2 parasites namely Trypanosoma brucie gambiense and Trypanosoma brucie rhodesiense.
- Species of Tsetse Fly found in the African continent have these parasites which transmit this disease.
- The infection spreads throughout the body through the blood when Tsetse Fly bites.
- The parasites can be transmitted from mother to child as it can transfer through placenta.
- It can be infected through contaminated needles.
- It only spreads by the bite of an infected Tsetse fly as this disease is not contagious.
Symptoms of Sleeping Sickness
Following are the symptoms of Sleeping Sickness:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle Pain
- Feeling of sleeplessness
- Severe sweating
- Red Sores formation on the place of fly bite
- Changes in Mood
- Rashes on skin
- Personality changes
- Feel difficulty in walking and talking
- Joint Pain
- Seizures
- Irritation
- Swelling on the brain
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Weakness in the body
Sleeping Sickness: Prevention
Following are the preventions and treatment measures of Sleeping Sickness:
- Treatment of the infected person should be started on time even if there are no symptoms.
- For the bite of Tsetse fly, people should use insecticides to protect themselves.
- Villages and residential areas should be maintained and cleaned.
- People should use repellents or fly traps.
- Correct guidance of medicine should be taken.
Things to Remember
- Sleeping sickness is a disease caused by the Tsetse fly. It is a tropical illness, native to the African Continent.
- The disease is caused by two parasites named Trypanosoma brucie gambiense and Trypanosoma brucie rhodesiense. They are present in the Tsetse fly.
- The major symptoms of Sleeping Sickness are: sores, fever, body aches, swelling etc. In advanced stages, the symptoms start affecting the central nervous system and victims can experience seizures, changes in personality, restricted bodily movement, etc.
- Sleeping Sickness should be treated immediately even when no symptoms are apparent. Maintaining general hygiene and cleanliness are recommended methods of prevention.
Sample Questions
Ques: How is the treatment of Sleeping Sickness disease?
Ans: The treatment of Sleeping Sickness disease makes the use of 4 drugs which includes Pentamidine, Suramin, Melarsoprol, and Eflornithine. For special authorization, a drug namely Nifurtimox is used.
Ques: Is the disease of Sleeping Sickness caused in Humans only?
Ans: This disease also occurs in animals and the incubation period is 4 days to 8 weeks in them. Weight loss, anemia, fever, edema, adenitis, and nervous disorder are the major symptoms in animals.
Ques: Is Sleeping Sickness Disease Contagious?
Ans: Sleeping sickness spreads through biting of Tsetse Fly and this fly is native to the African continent that is why this disease of sleeping sickness is not contagious.
Ques: What are the types of Sleeping Sickness?
Ans: There are two types of Sleeping Sickness which includes East African sleeping sickness and West African sleeping sickness.
Ques: What is the Reservoir of Infection?
Ans: The living organism or any substance where the parasite lives or multiplies them through the process of reproduction without harming that organism or substance is known as the reservoir of infection.




Comments