Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Goiter is a disease caused due to deficiency of certain vital macronutrients in the human body such as vitamins, minerals, etc. Goiter disease means an enlarged thyroid in humans which leads to either too much or too little generation of hormones. In this article, we will be looking into the various types of Goiter disease and learn about its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
| Table of Content 4.Symptoms |
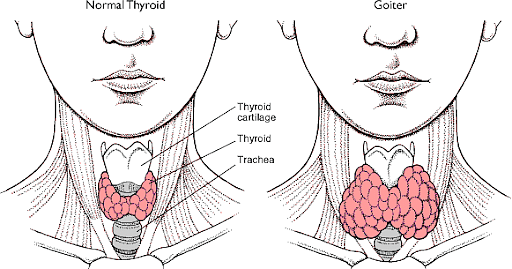
Goiter causes two conditions which are Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
- In Hyperthyroidism, the hormones are overly secreted.
- In Hypothyroidism the hormones are under secreted.
Check out Chemical Coordination and Integration. (Goiter.pdf)
Types of Goiter
There are a few different types of goiter that can happen to a person. These may also depend upon the cause of the disease. Therefore, the various types of goiter are:
- Colloid Goiter (Endemic): This condition occurs when there is a deficiency of iodine in the body.
- Non-Toxic Goiter (Sporadic): The cause of this condition is still unknown but studies indicate it may be due to intake of Lithium.
- Toxic Goiter (Nodular or Multinodular): The condition causes hyperthyroidism by forming one or more nodes that produce their own hormones.
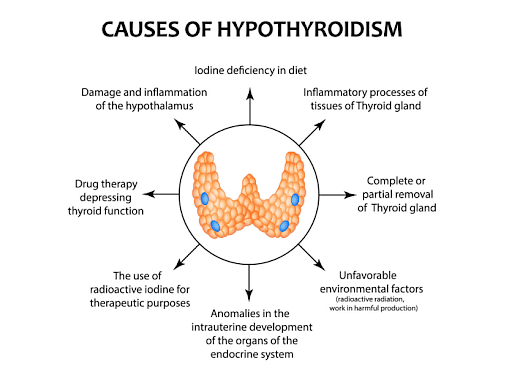
Causes of Goiter
Goiter is caused by the deficiency of macronutrients and minerals in the body. The most common deficiency which causes thyroid is iodine deficiency. The thyroid gland requires iodine to function normally and when this is not available, the gland enlarges and tries to produce the hormones required.
The other causes are:
- Inflammation: When the gland suffers an inflammation, a condition known as thyroiditis is caused. This causes Goiter.
- Graves’ Disease: This is due to the overproduction of hormones also known as hyperthyroidism.
- Hashimoto’s Disease: This is due to the overproduction of hormones also known as hypothyroidism.
- Nodules: These are cysts that grow on the thyroid gland causing it to enlarge. Nodules are non-cancerous.
- Thyroid Cancer: Cancerous cells on the thyroid can also cause Goiter
- Pregnancy: In some cases, pregnancy leads to enlargement of the thyroid gland and causes Goiter.
Symptoms of Goiter
The symptoms of Goiter are listed below:
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland just below Adam’s apple in the neck area is the most common symptom.
- Tightness in the neck area
- Scratchy and Hoarse voice
- Dizziness
Other less common symptoms include difficulty in breathing, coughing, wheezing, pain in swallowing, tiredness, dry skin, constipation, menstrual irregularities, and weight gain.

Diagnosis of Goiter
Doctors are able to diagnose thyroid goiters by examining the neck of a patient by observing whether it is enlarged or not. To confirm the diagnosis, however, the doctor may prescribe some tests which will include ultrasound, blood tests ( thyroid hormones), and a radioactive scan
Treatment of Thyroid Goiter
The treatment of Thyroid mainly depends on the type of goiter. For instance, if it is caused by Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, patients are required to take a daily medication meant for thyroid hormone replacement. One should intake radioactive iodine or medication viz. a treatment that helps in decreasing the size of the goiter, in the case of Graves disease.
Things to Remember
- Goiter is a disease caused in the human body which causes the thyroid gland to enlarge in the front and side areas of the neck.
- Goiter causes two conditions which are Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism
- There are a few different types of goiter that can happen to a person such as Colloid Goiter, Non-Toxic Goiter, and Toxic Goiter.
- Goiter is caused by the deficiency of macronutrients and minerals in the body.
- The most common deficiency which causes thyroid is iodine deficiency.
- Doctors are able to diagnose thyroid goiters by examining the neck of a patient and through some tests.
- The treatment of Thyroid mainly depends on the type of goiter.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is a goiter? 2 marks
Ans. Goiter is a disease caused in the human body which causes the thyroid gland to enlarge in the front and side areas of the neck. It is caused due to a deficiency of certain vital macronutrients in the human body such as vitamins, minerals, etc.
Ques. What are the symptoms of goiter? 3 marks
Ans. The symptoms of Goiter are listed below:
- Tightness in the neck area
- Scratchy and Hoarse voice
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Dizziness
Ques. What are the types of goiter? 3 marks
Ans. The various types of goiter are:
- Colloid Goiter (Endemic): Due to deficiency of iodine in the body.
- Non-Toxic Goiter (Sporadic): This might be due to the intake of Lithium.
- Toxic Goiter (Nodular or Multinodular): Causes hyperthyroidism by forming more nodes.
Ques. How is Goiter diagnosed? 5 marks
Ans: Several tests may help in the diagnosis. A standard procedure for the diagnosis of the Goiter includes:
- Physical Examination of the neck. Observing the area for signs of tenderness or nodules.
- Blood test to measure the levels of hormones by thyroid.
- Blood Test that identifies specific antibodies that are generally produced by various goiter types.
- Ultrasound
- Injecting radioactive materials in a vein for scanning or imaging thyroid.
- MRI or CT Scan to measure the spread and the size of goiters.
Ques. What are some of the treatments available? 5 marks
Ans. Treatment depends upon the growth, causes, and symptoms. Conventional treatments available for goiter include the following:
- Observing if the goiter is small, won’t bother you.
- Medications for treating hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, as per the cause
- Treatment through the administration of radioactive iodine orally. It kills the thyroid cells, thereby shrinking the gland.
- Biopsy for the removal of the cells or tissue for a study if large nodules are present in the thyroid gland.
- Surgery, if the size of the goiter is causing swallowing issues or breathing difficulties.






Comments