
Content Strategy Manager
Cuboidal epithelium is a type of tissue found in the lining of various organs and structures throughout the body. Its distinctive cuboidal form, in which the cells are roughly as tall as they are wide and have a cube-like appearance when viewed under a microscope, gave rise to its name.
- These epithelial cells are closely packed and form a continuous layer, forming a barrier of defence and lining numerous bodily cavities, ducts, and tubules.
- Due to its unique structural and functional properties, the cuboidal epithelium is essential to many biological processes.
- It is present in many organs, including the kidney tubules, which are essential for the reabsorption and secretion of chemicals during urine production.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Simple Cuboidal Epithelium, Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium, Microvilli, Cilia, Tissues, Organs
Cuboidal epithelium
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Cuboidal epithelium is well-suited to its functions due to the presence of specialized cellular structures and features.
- Cuboidal cells contain a centrally located nucleus, surrounded by organelles like mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum
- Which are involved in the movement of secretions.
- Cuboidal epithelium can also be found in parts of the respiratory system, the thyroid gland, and the ducts of certain exocrine glands.
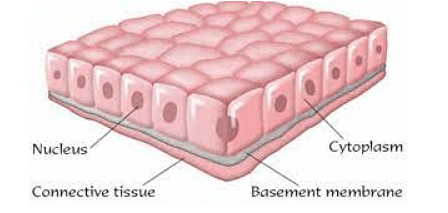
Cuboidal Epithelium
Types of Cuboidal Epithelium
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are two main types of cuboidal epithelium based on their structural arrangement:
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Each cuboidal cell in this type is shaped like a cube or a sphere and grouped in a single layer in a regular pattern.
- The lining of kidney tubules, which plays a critical role in the reabsorption
- The release of substances throughout the process of urine generation, is one area in the body where simple cuboidal epithelium can be found.
- Additionally, it is found in some glands, including the thyroid gland, where it plays a role in hormone release.
- Some of the smaller exocrine gland ducts are lined with straightforward cuboidal epithelium.
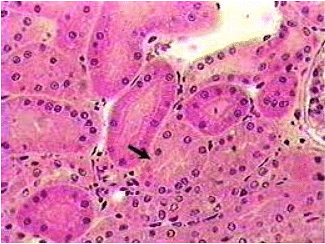
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
This kind has cuboidal cells stacked in numerous layers on top of one another. Stratified cuboidal epithelium is a relatively uncommon and localized condition in the body. It is seen in the larger ducts of some exocrine glands, including the sweat, breast, and salivary glands. The layered architecture further supports and shields the underlying tissues in these ducts.
- The cells of both varieties of cuboidal epithelium have a distinctive cube-like form, but they differ in how they are arranged and distributed throughout the body.
- Depending on their precise location and organizational structure, these epithelial tissues provide a variety of activities, including absorption, secretion, and protection.
- The cuboidal epithelium is crucial for preserving the structural integrity of organs and tissues and promoting particular bodily processes.
- These cells' cube-like structure makes it possible to efficiently cover surfaces and line interior cavities of various structures
- Promoting the general well-being and functionality of numerous body systems.

Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Read More: What is Adaptation
Physical Characteristics
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Physical Characteristics of Cuboidal Epithelium:
- Form: Cuboidal epithelial cells have a cube-like appearance under a microscope, as suggested by their name. They appear boxy because their height, width, and depth are equal.
- Single or Stratified: Cuboidal epithelium can comprise just one layer of cells (simple cuboidal epithelium) or several layers stacked on top of one another.
- Nucleus: Each cuboidal cell usually has a single circular nucleus positioned in the middle of the cell. The genetic material and controls for the cell's operations are found in the nucleus.
- Surface Specializations: Microvilli, which are small, finger-like projections that increase the surface area for absorbing chemicals and secreting compounds.
Read More: Female Hormones
Functions of Cuboidal Epithelium
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The functions of Cuboidal Epithelium are mentioned below:
- Absorption and Secretion: In numerous organs and glands, cuboidal epithelium is essential for absorption and secretion.
- For instance, simple cuboidal epithelium in the kidney tubules plays a role in reabsorbing water & essential nutrients
- From the filtrate while also secreting waste materials to generate urine.
- Cuboidal epithelial cells line the ducts in glands and let secretions pass more quickly.
- Defence: The cuboidal epithelium acts as a barrier against diseases and physical harm.
- For instance, the cuboidal epithelium that lines some exocrine glands' more giant ducts is a barrier
- It acts as a defence against mechanical forces.
- Support and Structure: Stratified cuboidal epithelium gives the underlying tissues more support
- It gives structural integrity thanks to its numerous layers.
- It can be found in larger ducts where there may be more mechanical stress.
- Control: The cuboidal epithelium can control how substances are transported across the cell layer. On the cell surface, ion channels and transporters can occasionally permit the controlled transit of ions and molecules.
- Sensation: Specific cuboidal epithelial cells with specialized roles may have sensory properties that aid in detecting particular stimuli in different organs and tissues.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hormones in Animals | Androgen Hormone | Blood Coagulation |
| ADH Hormone | Melatonin Hormone | Human body |
Things to Remember
- A form of tissue called cuboidal epithelium can be discovered in the lining of numerous organs and body parts.
- It is distinguished by having a cube-like form, with cells that are roughly as tall as they are wide.
- Simple cuboidal and stratified cuboidal are the two primary varieties of cuboidal epithelium.
- Simple cuboidal epithelium, present in exocrine gland ducts, thyroid glands, and kidney tubules, is composed of a single layer of cube-shaped cells.
- Stratified cuboidal epithelium is seen in the more giant ducts of exocrine glands and is composed of numerous layers of cube-shaped cells.
- Cuboidal epithelial cells may have cilia or microvilli on their surface in addition to having a centrally placed nucleus.
- Cuboidal epithelium plays vital roles in absorption, secretion, defence, support, control, and sensation in various organs and tissues.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is cuboidal epithelium? (1 mark)
Ans: The lining of different organs and structures throughout the body is covered in a kind of tissue known as cuboidal epithelium, distinguished by its cube-like form.
Ques. Where can simple cuboidal epithelium be found in the body? (1 mark)
Ans: The lining of kidney tubules, various glands, including the thyroid gland, and specific exocrine gland ducts, all include simple cuboidal epithelium.
Ques. What is the main difference between simple cuboidal epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium? (2 marks)
Ans: The key distinction is that stratified cuboidal epithelium consists of numerous layers of cube-shaped cells layered on top of one another, as opposed to the plain cuboidal epithelium, which has a single layer of cube-shaped cells.
Ques. What are the surface specializations of cuboidal epithelial cells? (2 marks)
Ans: Cuboidal epithelial cells may feature cilia, which are hair-like structures that help move materials along the cell's surface, as well as microvilli, finger-like projections that increase surface area.
Ques. What are some functions of cuboidal epithelium? (2 marks)
Ans: Cuboidal epithelium functions include absorption and secretion in organs and glands, defence against diseases and physical harm, providing structural support, and sensory functions in specific cells.
Ques. How does the structure of cuboidal epithelium contribute to its functions in the body? (3 marks)
Ans: Cuboidal epithelial cells' cube-like form enables them to cover surfaces and line inner cavities effectively, supporting the overall health and functionality of many body systems. These cells' absorption, secretion, and defence functions are determined by their single or stratified arrangements. Microvilli and cilia, two surface specializations that increase surface area for absorption and support substance movement, improve their roles. Movement of secretions and other cellular functions are facilitated by the nucleus, which is positioned at the centre of the cell, and the organelles.
Ques. Can you explain the significance of simple cuboidal epithelium in the kidney tubules? (2 marks)
Ans: In the kidney tubules, simple cuboidal epithelium is essential for the reabsorption and secretion of chemicals during the formation of urine. Reabsorbing vital nutrients and water from the filtrate and bringing them back into the bloodstream is made possible. Waste products are also secreted simultaneously into the tubules to be removed as urine.
Ques. What are some examples of body structures where stratified cuboidal epithelium is found, and how does it provide support and protection? (2 marks)
Ans: Localized across the body, stratified cuboidal epithelium is relatively uncommon. Larger ducts of various exocrine glands, including sweat, breast, and salivary glands, contain it. The underlying tissues are given more support and structural integrity by the several layers of cuboidal cells, which increases their resistance to mechanical loads and pressures that may be present in these ducts.
Ques. How does cuboidal epithelium contribute to the body's defence mechanisms? (2 marks)
Ans: Cuboidal epithelium acts as a barrier against diseases and physical harm. For example, the cuboidal epithelium that lines some exocrine glands' bigger ducts is a protective barrier against mechanical forces. Additionally, specific cuboidal epithelial cells in various organs and tissues may have specialized roles in detecting specific stimuli, aiding in the body's sensory response to external and internal changes.
Ques. Why is cuboidal epithelium considered essential for the integrity of organs and tissues in the body? (2 marks)
Ans: In many organs and structures, the cuboidal epithelium performs vital tasks such as absorption, secretion, defence, and structural support. It is ideal for these activities due to its distinctive structural qualities, which include the cube-like shape, single or layered organization, and specialized surface properties. Cuboidal epithelium is a crucial component of the body's intricate structure since it contributes significantly to general health and well-being by preserving the integrity and efficiency of organs and tissues.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also Check:





Comments