
Content Curator
Atoms and molecules make up the matter around us. Matter is anything that occupies space and possesses mass. The matter is made up of a unit substance known as atoms. More than one atom makes a molecule. Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles namely neutrons, protons, and electrons. Thus, atoms and molecules are the structural units of any substance.
| Table of Content |
Key Takeaways: Atoms, Molecules, Ions, Neutrons, Electrons, Protons, Atomic Mass, Molecular Mass, Elements, Compounds
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest entity that makes up any compound. It is the fundamental, structural and functional unit of all the compounds, which can take part in any chemical reaction. However, while taking part in any chemical reaction, atoms can only be transformed, they are neither synthesized nor broken down during the process.
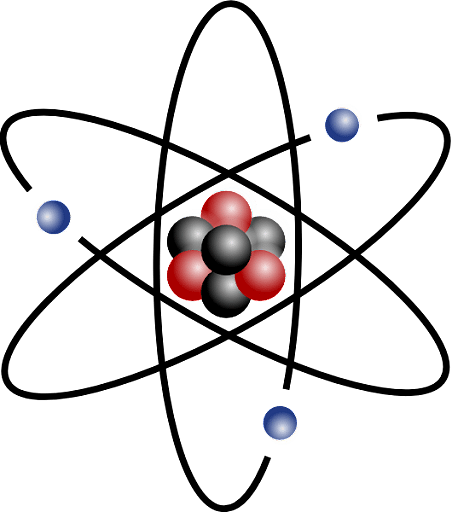
Atom
Atoms are extremely small and cannot be seen by naked eyes. They are spherical entities and their size is measured in terms of their diameter. The diameter of an atom is measured in nanometres (1 nanometre = 10-9 meters).
Read More:
Components of an Atom
An atom contains three basic components, neutrons, protons, and electrons. These three principal components are present in two regions of the atom. An atom can be divided broadly into two parts:
- Nucleus - the centre of the atom
- Outermost region
Nucleus of the Atom
The nucleus of the atom is present in the center of the atom and possesses the entire mass of the atom. The nucleus contains two of the three principal subatomic components, they are:
Neutrons
- All the atoms, except hydrogen, have neutrons in their nucleus.
- Neutrons are neutral in terms of charge, unlike protons and electrons.
- Neutrons are subatomic particles that possess a mass of 1 a.m.u (atomic mass units) or 1.67 X 10-27 kg.
- Neutron is also a spherical subatomic particle and has a diameter of 1.7 X 10-15 meters.

Structure of Atom
Read More: Energy Level Diagram
Protons
- All the atoms, including hydrogen, have protons in their nucleus.
- Protons, unlike neutrons, are positively charged (+1).
- Protons are subatomic particles that also possess a mass of 1 a.m.u (atomic mass units) or 1.67 X 10-27 kg.
- Proton is also a spherical subatomic particle and has a diameter of 1.7 X 10-15 meters.
- Protons and neutrons together make up the atomic mass of the atoms.
Outermost Region of the Atom
The outermost region of the atom is composed of electrons.
Electrons
- The electrons are small subatomic particles that are present outside the nucleus.
- They are present in circular imaginary circles, like the orbits of the planets. These imaginary circular paths are called shells.
- Each shell has a specified number of electrons, the shells are termed as- k,l,m,n… or 1,2,3… etc.
- Electrons, unlike neutrons and protons, possess negligible mass, which is equal to 1/2000 parts of the mass of neutrons or protons, that is 1/2000 of 1 a.m.u.
- Electrons are negatively charged, -1.
- The atom has an equal number of protons and electrons in them.
Read More:
Atomic mass
The mass of an atom is termed atomic mass. Every atom has a specific mass. The protons and the neutrons of an atom make up the mass of an atom. The S.I Unit of atomic mass is a.m.u or u (atomic mass unit). The atomic mass can also be expressed in units of Dalton, Da. 1 Da is defined as 1/12th the mass of Carbon-12 isotope. The mass of an atom is also expressed in terms of average atomic mass.

Atomic Mass Unit
Atomic Symbol and Atomic Number
The symbol of an atom is expressed concerning their Latin names. The symbol of an atom comprises of three parts:
- The symbol of the element (X), Example: C for Carbon, O for Oxygen, etc.
- The atomic number (Z), which is the representation of the position of the element in the periodic table. Example: 6 is for carbon, 8 is for oxygen, 7 is for nitrogen, etc.
- The mass number (A), which is the mass of the element, is equal to the total number of protons and neutrons. Example: 12 is of Carbon, 16 is of Oxygen, etc.

Atomic Number and Mass Number
Read More: Orbitals
What is a Molecule?
Two or more atoms when combined result in the formation of a molecule. These atoms are bonded by chemical bonds. A molecule is defined as the smallest constituent of a compound that has the ability to exist individually and independently. Molecules can be produced by chemical bonds between the same atoms or different atoms too.

Water Molecule
For example, O2 is an oxygen molecule, formed by a chemical bond between two oxygen O atoms. Similarly, CO is a molecule of carbon mono-oxide, formed by a chemical interaction between two different atoms, carbon and Oxygen.
Read More:
Molecules of Elements and Compounds
As we know molecules can be composed of the same atoms or different atoms. A molecule composed of the same elements is called an element, and a molecule of different atoms is called a molecule of the compound.
Molecules of the same element are made up of one type of atom only. The number of atoms present in a molecule is called its atomicity. There can be different types of atomicity depending on the number of atoms present in the molecule.
| Atomicity | Number of atoms | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Monoatomic | 1 | Argon (Ar), Helium (He) |
| Diatomic | 2 | Oxygen (O2), Hydrogen (H2) |
| Triatomic | 3 | Oxone (O3) |
| Tetratomic | 4 | Phosphorus (P4) |
| Polyatomic | multiple | Graphite, Diamond, (Cn) |
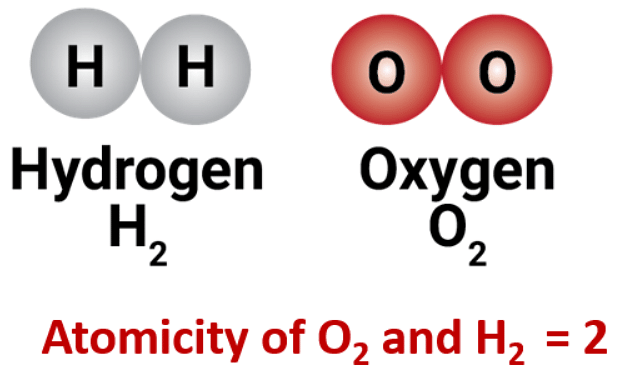
Atomicity
Read More: Clemmensen Reduction Reaction
Molecules of a compound are made up of different types of atoms together. They can also possess a different number of atoms.
| Atomicity | Number of atoms | Example | Elements present |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diatomic | 2 | Carbon mono-oxide (CO) | Carbon, Oxygen |
| Triatomic | 3 | Water (H2O) | Hydrogen, Oxygen |
| Tetratomic | 4 | Ammonia (NH3) | Nitrogen, Hydrogen |
| Polyatomic | multiple | Glass (n SiO2) | Silicon, Oxygen |
Molecular mass
Molecular mass is the mass of a molecule. It is determined by the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms present in the molecule. For example, the molecular mass of one molecule of water, H2O, is calculated as follows.
Number of atoms of hydrogen = 2
Number of atoms of Oxygen = 1
The atomic mass of hydrogen = 1 a.m.u
The atomic mass of Oxygen = 16 a.m.u
Molecular mass = (2 x 1) + (1 x 16) = 2 + 16 = 18 a.m.u
Read More: Tollen’s Test
Differences Between Atoms and Molecules
The difference between atoms and molecules is mentioned below in the table:
| Parameters | Atom | Molecule |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An atom is the smallest entity that makes up any compound. It is the fundamental, structural and functional unit of all the compounds, which can take part in any chemical reaction. | A molecule is defined as the smallest component of an element or a compound that is capable of existing individually. |
| Type of occurrence | They may or may not exist freely. Example: Helium (He), exists freely Oxygen (O) cannot exist freely | They can exist freely. Example: Carbon mono-oxide (CO) exists freely |
| Components | It contains a nucleus (proton, and neutron) and an outermost region composed of electrons. | It contains two or more different or same atoms that are bonded together by chemical bonds. |
| Shape | They have a spherical shape. | They have a triangular (water), linear (carbon dioxide), or angular (Ozone). |
| Ability to undergo reactions | They are highly reactive. | They are comparatively less reactive. |
| Nature of bond | It is composed of a nuclear bond. | It is composed of a covalent bond. |
Read More: Williamson Ether Synthesis
Things to Remember
- An atom is the smallest entity that makes up any compound.
- Atoms are the fundamental, structural and functional unit of all the compounds, which can take part in any chemical reaction.
- A molecule can exist independently and stably without undergoing any chemical reaction unless put under reactive conditions.
- A molecule is defined as the smallest constituent of any element or a compound that is having the ability to exist individually and independently.
- The number of atoms present in a molecule is called its atomicity. Atomicity can vary from one to multiple.
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques. What is an atom, and a molecule? Explain with an example. (2 marks)
Ans. An atom is the smallest entity that makes up any compound. It is the fundamental, structural and functional unit of all the compounds, which can take part in any chemical reaction. For example, C is an atom of Carbon element, O is an atom of Oxygen element.
A molecule is defined as the smallest component of an element or a compound that is capable of existing individually. A molecule can exist independently and stably without undergoing any chemical reaction unless put under reactive conditions. For example, Oxone (O3), Water (H2O), etc.
Ques. What is Dalton’s Atomic Theory? (3 marks)
Ans. Dalton’s atomic theory is a theory stated by Dalton to explain the concept of atoms. It is composed of five statements to explain the same,
- All the matter around us is made up of invisible components, that is atoms.
- All the atoms of any given element are the same, including their mass. Atoms of different elements have differences in their nature.
- Atoms of different elements are combined in fixed ratios to form a compound.
- Atoms can neither be created nor be destroyed.
- The relative number of atoms and the kind of atoms present in a compound are fixed in nature.
Ques. What is a Mole? (2 marks)
Ans. A mole is a fixed number of atoms or molecules present in a given quantity. A mole of atoms or molecules is equal to 6.022 X 1023 atoms or molecules. For example, one mole of ammonia is equal to 6.022 X 1023 molecules of ammonia.
Ques. What are the components of an atom? (2 marks)
Ans. An atom contains three basic components, neutrons, protons, and electrons. These three principal components are present in two regions of the atom. An atom can be divided broadly into two parts:
- Nucleus, the center of the atom: It contains the neutrons and protons, and
- Outermost region: It contains the electrons arranged in shells.
Read More:
Ques. What is the mass of 0.5 moles of water? (3 marks)
Ans. The molecular formula of water is H2O
Number of atoms of hydrogen = 2
Number of atoms of Oxygen = 1
The atomic mass of hydrogen = 1 a.m.u
The atomic mass of Oxygen = 16 a.m.u
Molecular mass = (2 X 1) + (1 X 16) = 2 + 16 = 18 a.m.u
Mass of one mole of water molecules is 18 gm
Mass of 0.5 moles of water molecules is = 18 X 0.5 = 9 gm
Ques. What is the atomicity in Sulphur, Ozone, Chlorine, Benzene, and Graphite? (3 marks)
Ans. The number of atoms present in a molecule is called its atomicity.
- Sulfur: S8, has 8 atoms, hence the atomicity is Octatomic.
- Ozone: O3, has 3 atoms, hence the atomicity is triatomic.
- Chlorine: Cl2, has 2 atoms, hence the atomicity is Diatomic.
- Benzene: C6H6, has 12 atoms, hence the atomicity is polyatomic.
- Graphite: Cn, is a polymer of Carbon, has n, multiple atoms, hence the atomicity is polyatomic.
Ques. What are the different laws governing a chemical reaction? (2 marks)
Ans. There are two laws governing a chemical reaction, they are:
Law of conservation of mass: Mass can neither be destroyed nor synthesized in a chemical reaction.
Law of constant proportion: In a chemical substance the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
Read More:
Ques. Is benzene a molecule or atom? Find its mass too. (2 marks)
Ans. Benzene: C6H6, has 12 atoms, of different elements. Hence, benzene is a molecule of a compound.
Number of C atoms: 6
Number of H atoms: 6
Mass of C atom: 12
Mass of H atom: 1
Mass of Benzene: (6 x 12) + (6 x 1) = 78 u
Ques. Define ionization energy. How would the ionization energy change when an electron in a hydrogen atom is replaced by a particle of mass 200 times that of the electron but having the same charge? (CBSE 2016) (2 marks)
Ans. “The minimum energy, required to free the electron from the ground state of the hydrogen atom, is known as Ionization Energy.”
The ionization energy is given by :

Ionization Energy will become 200 times the mass of the given particle is 200 times.
Ques. Write two important limitations of the Rutherford nuclear model of the atom. (CBSE 2016) (2 marks)
Ans. Important limitations of Rutherford Model :
- According to the Rutherford model, electrons orbiting around the nucleus continuously radiate energy due to the acceleration; hence the atom will not remain stable.
- As the electron spirals inwards; its angular velocity and frequency change continuously; therefore it. will emit a continuous spectrum.
Read More:





Comments