Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
Unit of Acceleration in Physics is Meters per Second Squared (m/s2). Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time in terms of both speed and direction.
- Acceleration is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity.
- It is equal to the difference between the initial and final velocities divided by the time.
- The SI Unit of Acceleration is Meters per Second (m/s2).
- It can also be written as ms−2.
- Acceleration can also be expressed in some other units like Gal, Standard Gravity (g), Planck Acceleration (ap), and ft/s2.
Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Units and Measurements
Key Terms: Unit of Acceleration, Acceleration, Acceleration Formula, Velocity, Planck Acceleration, Standard Gravity, Retardation
What is Acceleration?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. An object is said to be accelerated if there is a change in its velocity. The change in the velocity can either be an increase or decrease in the speed of the object or a change in the direction of its motion.
- Acceleration is a vector quantity with both direction and magnitude.
- It is denoted by the symbol ‘a’.
- The SI Unit of Acceleration is m/s2.
- The dimensional formula of Acceleration is given as M0 L1T -2.
- If the object’s velocity increases with time, it is referred to as Positive Acceleration.
- If the object’s velocity decreases with time, it is referred to as Negative Acceleration or Retardation.
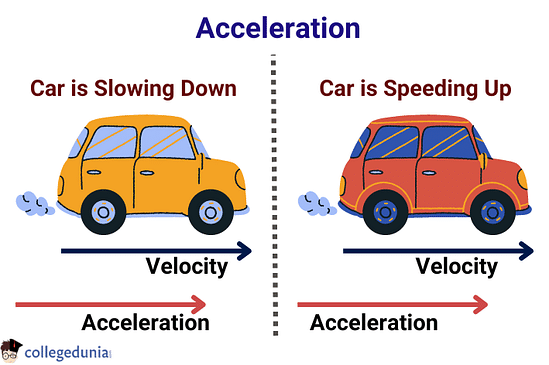
Acceleration
Read More:
SI Unit of Acceleration
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
SI units are the standard measurement units laid out by the International System of Units that are accepted and used uniformly throughout the world to avoid confusion in different units of a physical quantity.
| The SI Unit of Acceleration is m/s2. |
- An object whose change in velocity is 1 m/s in 1 second is said to have an acceleration of 1 m/s2.
- Acceleration is equal to the difference between the initial and final velocities of an object divided by time.
- The unit of length is meter (m) and the unit of time is second (s). Thus, the SI Unit of acceleration is m/s2.
Units and Measurements Detailed Video Explanation
Other Units of Acceleration
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Acceleration can also be measured in various other units apart from its standard unit m/s2. Other units of acceleration include foot per second squared, Galileo or gal, standard gravity, orders of magnitude, and plank acceleration. Here is a detailed explanation of other units of acceleration:
Feet Per Second Squared
- Feet Per Second Squared is a unit of the FPS (foot-pound-second) system.
- An object whose change in velocity is 1 ft/s in 1s is said to have an acceleration of 1 ft/s2.
| 1 ft/s2 = 0.3048 m/s2 |
Gal
- Gal is another unit of measurement for acceleration that is named after Galileo Galilei.
- He was the first to study acceleration due to gravity.
- It is used for the precise measurement of acceleration due to gravity on Earth or other celestial bodies.
- Gal is a unit of measurement for acceleration in the CGS or Gaussian System of Units.
- 1 gal = 1 cm/s2
| 1 gal = 0.01 m/s2 |
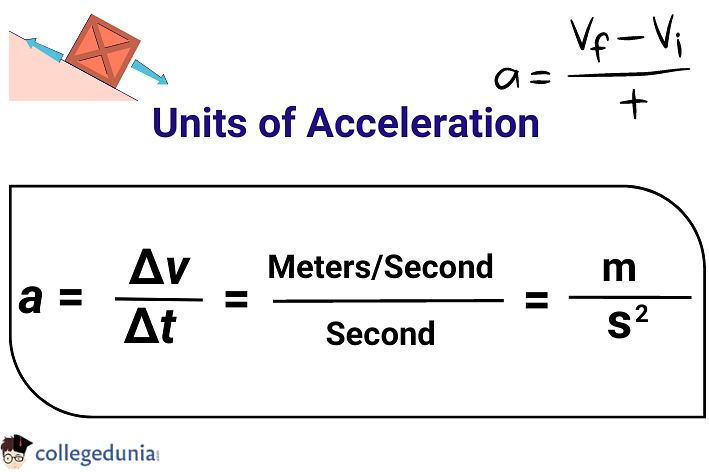
Unit of Acceleration
Read More: Units and Measurements Important Questions
Standard Gravity
- The standard acceleration due to Earth’s gravity is 9.8 m/s2.
- It is a convenient standard to compare the accelerations of different objects.
- For an object, 1 g is the normal state, at 2 g everything is twice as heavy and at 0 g, the object is weightless.
- It is also referred to as g force, but should not be confused with force.
- Standard acceleration due to gravity (denoted by roman g) with the natural phenomenon called acceleration due to gravity (denoted by italicized g).
- The standard acceleration due to gravity is predefined, i.e. 9.8 m/s2.
- On the other hand, the natural phenomenon called acceleration due to gravity has to be measured.
| Standard Gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2 |
Planck Acceleration
- The change in velocity from zero to the speed of light in one Planck time is called Planck acceleration.
- It is a unit for acceleration in the Planck system of units.
- It is named after Max Planck.
- Planck acceleration is denoted by ap.
| ap = 5.56 x 1051 m/s2 |
Check More:
Things to Remember
- Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
- If the change in the value of acceleration is positive, it is called Positive Acceleration.
- If the change in the value of acceleration is negative, it is called Deceleration or Retardation.
- The SI Unit of Acceleration is m/s2.
- If the change in velocity of an object is 1 m/s in 1 second, then the acceleration of the object will be 1 m/s2.
- Other commonly used units of acceleration are Foot per Second Squared, Gal, Standard Gravity, and Plank Acceleration.
- The value of standard acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.8 m/s2.
- The CGS unit of acceleration cm/s2 is also called Gal. Thus, 1 cm/s2 = 1 Gal.
- The unit for acceleration in the Planck System of Units is denoted by ap. ap = 5.56 x 1051 m/s2.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Previous Years’ Questions
- A screw gauge has the least count of 0.01 mm… (NEET – 2020)
- Dimensions of stress are… (NEET – 2020)
- Lumen is the unit of… (UPSEE – 2019)
- Displacement x versus t2 graph is shown for a particle. The acceleration... (UPSEE – 2017)
- Planck’s constant (h), speed of light in vacuum (c) and... (NEET – 2016)
- A quantity z, to be estimated has a dependency n the variables… (TS EAMCET – 2019)
- A student measured the diameter of a small steel ball… [NEET – 2018]
- The nearest star to our solar system is 4.3 light years away. The… (AMUEEE – 2018)
- A physical quantity of the dimensions of length that can be formed… (NEET – 2017)
- Einstein was awarded the Nobel prize for his work in… (COMEDK UGET – 2014)
- A juggler keeps on moving four balls in the air throwing the balls after... (BITSAT – 2018)
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the SI Unit of acceleration?
(a) cm/s2
(b) Gal
(c) m/s2
(d) ft/s2 (1 Mark)
Ans. (c) m/s2
Explanation: The SI unit of acceleration is m/s2. Acceleration is calculated by dividing the difference between the initial and final velocities by time. The unit of length or distance is meter (m) while the unit of time is second (s). Therefore, the SI Unit of acceleration is m/s2.
Ques. What is Gravitational Acceleration? (3 Marks)
Ans. Gravitational Acceleration is the rate at which the velocity of a body falling freely toward the earth increases. It is independent of the form, size, and mass of the object. Gravitational Acceleration is represented by the letter g.
Gravitational Acceleration Formula is given as
g = GM/R2
Where
- G represents the gravitational constant.
- M refers to the Earth's mass.
- R refers to the radius of the Earth.
Ques. 1 m/s2 = ___ Gal
(a) 0.01
(b) 100
(c) 1000
(d) 0.001 (1 Mark)
Ans. (b) 100
Explanation: We know that, 1 Gal = 0.01 m/s2.
Thus, 1 m/s2 = 100 Gals.
Ques. A scooter traveling at 10 m/s speeds up to 20 m/s in 4 sec. Find the acceleration of the scooter. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- Initial Velocity, u = 10 m/s
- Final Velocity, v = 20 m/s
- Time, t = 4 sec
Using the Acceleration Formula,
Acceleration a = (v – u) / t
a = (20−10)/4 = 10/4 = 2.5
a = 2.5 m/s2
Thus, the acceleration of the scooter is 2.5 m/s2.
Ques. What is the difference between acceleration and retardation? (2 Marks)
Ans. Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time in terms of both speed and direction.
- When the velocity of the object increases with time, it is referred to as Positive Acceleration or simply Acceleration.
- When the velocity of the object decreases with time, it is referred to as Negative Acceleration or Retardation.
Ques. Differentiate between Acceleration and Velocity. (3 Marks)
Ans. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement whereas Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. The difference between Acceleration and Velocity is as follows:
| Velocity | Acceleration |
|---|---|
| Velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement. | Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. |
| It is a vector quantity as it has both magnitude and direction. | It is also a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction. |
| Velocity can be positive or negative or zero. | Acceleration can be either positive or negative but cannot be zero. |
| The SI Unit of Velocity is m/s. | The SI Unit of Acceleration is m/s2. |
| Velocity Formula = Displacement/Time | Acceleration Formula = Velocity/Time |
Ques. A bus accelerates from 25 km/h to 40 km/h in 10 sec. Find:
(i) Acceleration
(ii) The distance traveled by bus. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- Initial Velocity, u = 25 km/h
- Final Velocity, v = 40 km/h
- Time, t = 10 sec
(a) Using the Acceleration Formula,
Acceleration, a = (v – u) / t
a = (40 − 25) / 10 = 15/10
a = 3/2 = 1.5 km/h = 0.42 m/s2
(b) Using the second equation of motion, we get
s = ut + 1/2at2
Given that, u = 25 km/hr = 6.94m/s
s = 6.94 × 10 + ½ × 0.42 ×102 = 69.4 + 21
s = 90.4 m
Thus, the acceleration is 0.42 m/s2 and the distance traveled is 90.4 m.
Ques. A bike traveling at 25 m/s speeds up to 35 m/s in 4 sec. Find the acceleration of the bike. (3 Marks)
Ans. According to the question,
- Initial Velocity, u = 25 m/s
- Final Velocity, v = 35 m/s
- Time, t = 4 sec
Using the Acceleration Formula,
Acceleration a = (v – u) / t
a = (35-25)/4 =10/4 = 2.5 m/s2
Thus, the acceleration of the bike is 2.5 m/s2.
Ques. An object dropped from a cliff falls with a constant acceleration of 10 m/s2. Find its speed 5 s after it was dropped. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- a = 10 m/s2
- t = 5 sec
- u = 0 (Dropped from Rest)
- v =?
Using the first equation of motion,
v = u + at
v = 0 + 10 × 5 = 50 m/s
Thus, the speed of the object 5 seconds after dropping is 50 m/s.
Ques. A bus starts from rest and acquires a velocity of 44 km/h in 2 sec. Find:
(a) Acceleration of Bus
(b) Distance traveled by Bus (Assume Motion of the Car is Uniform) (3 Marks)
Ans. Given parameters are:
- Initial Velocity = u = 0 m/s
- Final Velocity = v = 44 km/hr = 12.2 m/s
- Time = t = 2 sec
(a) Using the first equation of motion,
v = u + at
a = (v-u)/t = 12.2/2 = 6.1 m/s2
(b) Using the second equation of motion, we get
s = ut + 1/2at2
s = = 0 + 1/2 × 6.1 × 22 = 12.2 m
Check-Out:




Comments