
Exams Prep Master
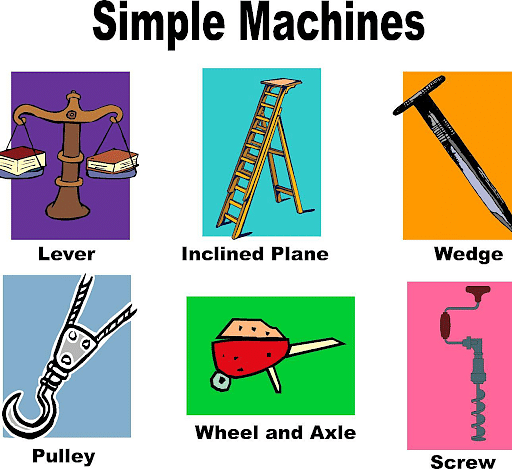
Simple Machine is any device that has very few or almost no parts. Simple machines modify the direction of motion and applied force to perform work. The term machine is attributed to the Greek playwright Aeschylus (523–426 BCE) in reference to theatrical machines such as the "deus ex machina" or "god from a machine." Work is done by exerting a force over a long distance. Machines generate a greater output force than input force. There are six types of machines and when these machines are combined, they can create an even greater mechanical advantage like that of a bicycle.
Also Read: Potential Energy
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Simple Machine, Force, Pulley, Mechanical, Lever, Screw, Wheel, Axle, Inclined Plane, Wedge, Friction
What is a Simple Machine?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Simple machines are devices that are simple in construction and make our work easier and faster by changing the direction of force (s).
Also Check:
| Important Topics Related to Simple Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kinetic Energy | Thermal Energy | Potential Energy |
| Work Energy Theorem | Law of Conservation of Energy | Mechanical Energy |
| Kinetic Vs Potential Energy | Gravitational Potential Energy | Potential Energy of Spring |
Types of Simple Machines
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Lever
A lever is a rigid rod that can rotate about a fixed point known as the fulcrum. Load, Load arm, Effort, Effort arm, and Fulcrum are the components of a lever.
Levers are classified into three types based on the position of the load, the fulcrum, and the effort.
- Lever of First Class (Fulcrum in between)
- Second-Class Lever (Load in between)
- Lever of Third Class (Effort in between)
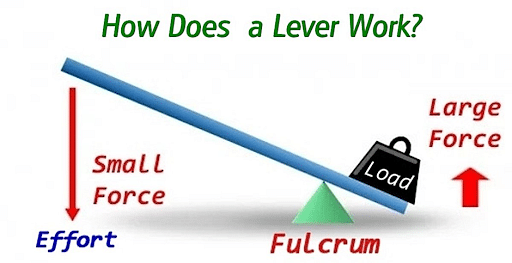
Working of a Lever
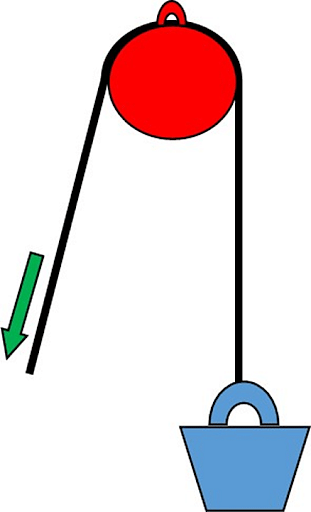
Pulley
A pulley is a circular disc with a groove around its circumference that allows a rope to pass through. It assists us by changing the direction of force applied as well as multiplying our force.
Based on the number of pulleys in a system, there are three types of pulleys.
- Single fixed pulley: The pulley in this type of pulley is fixed and does not move up and down with the load. A single fixed pulley's MA and VR are always. Despite the fact that it does not multiply our force, it is widely used because it uses our own body weight to overcome load and makes our work easier by changing the direction of force applied.
- Single movable pulley: The pulley in this type of pulley moves up and down with the load. A single movable pulley's MA and VR are always equal. It is used to overcome heavier loads because it doubles our applied effort.
- Block and tackle system: Two or more pulleys are combined in this type of pulley. The number of pulleys used determines the MA and VR of this type of pulley.
Also read: Average Velocity Formula & Solved Examples
Wheel and Axle
A wheel and axle is a system of two co-axial cylinders, the larger of which is called a wheel, and the smaller is called an axle. A continuous lever is a wheel and axle with load, effort, and a fulcrum, similar to a lever. In addition, we must exert constant effort until the load is overcome.
As an example, consider a doorknob, a spanner, a bicycle paddle, and so on.

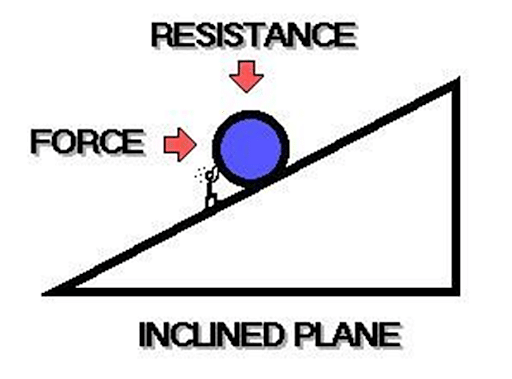
Inclined Plane
A simple machine with a sloping surface is an inclined plane. An inclined plane's VR is always greater than one. Inclined planes are used to raise heavy bodies. The steeper the slope, more nearly the force approaches the actual weight. It is mathematically expressed as
F= W sinθ
Where,
F= force required to move the object on upwrds on the inclined plane
W= Weight of the object
θ= Angle the inclined plane makes with the horizontal
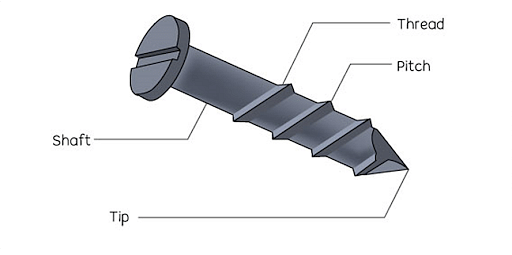
Screw
A screw is a modified inclined plane with a raised spiral line running through it. Screw nail, Jackscrew, driller, and so on are some examples.
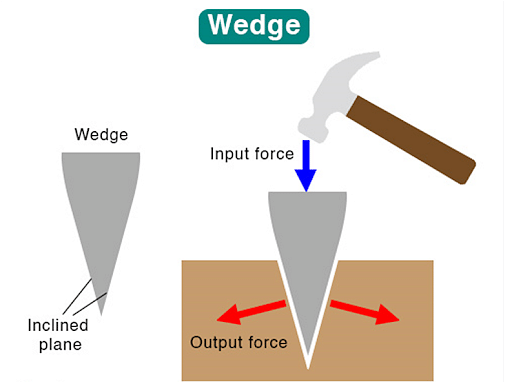
Wedge
A wedge is a simple machine with two ends, one sharply pointed and the other thick. As an example, consider the following: axe, knife, wedge, and so on.
Moment
The turning effect produced by a force is referred to as moment. Newton-metre is the SI unit of the moment (Nm).
Force (F) x Moment Arm = Moment (r)
Uses of Simple Machines
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Simple machines are beneficial because they reduce effort or enable people to perform tasks that are beyond their normal abilities.
- Screws and livers are simple machines which increase the distance over which the reduced force acts.
- They are used in lifting heavy loads.
- Riding a bicycle
- Cutting paper with scissors
Advantages of Simple Machines
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Simple Machine Applications (Benefits) include
- It aids in the multiplication of force.
- It aids in changing the force direction.
- It aids in increasing work speed.
- It aids in the completion of tasks in a safe manner.
Mechanical Advantage
The mechanical advantage of a simple machine is the load-to-effort ratio.
MA = Load (L) / Effort (E)
- MA has no unit because it is the ratio of two loads.
- MA is affected by friction and machine weight.
- Lubricants and other products can be used to reduce frictional force and other various forces that result in a decrease in MA in order to increase the MA of machines.
- The Velocity Ratio (VR) of a simple machine is the ratio of effort distance to load distance.
Mathematically,
VR = Effort Distance (ED) / Load Distance (LD) (LD)
- VR has no unit because it is the ratio of two distances.
- It is not affected by friction or machine Efficiency of a machine (η): Efficiency of a machine is defined as the percentage ratio of a machine's output work to its input work.
i.e., η= Output Work (L x LD) / Input Work (E x ED) x 100% or,
η = MA / VR x 100%weight
Ideal Machine
The Ideal Machine is not affected by friction.
- An ideal machine is one that has 100% efficiency.
- The input work is always equal to the output work in this type of machine.
- In practice, no machine is frictionless, so this is not a practical machine.
Things to Remember
- Simple machines are devices that are simple in construction and make our work easier and faster by changing the direction of force (s).
- There are 6 types of simple machines. The lever, pulley, screw, inclined plane, wedge, wheel, and axle are all examples.
- The Ideal Machine is not affected by friction. An ideal machine is one that has 100 percent efficiency.
- The efficiency of a machine is defined as the percentage ratio of a machine's output work to its input work.
- Simple machines aid in the completion of tasks in a safe manner.
Also Check:
| Important Topics From Chapter 11: Work, Power and Energy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gravity | Weightlessness | Density of Water |
| Density of Air | Angular Acceleration Formula | Angular Velocity Formula |
| Relative Velocity | Gravity Waves | Lenz Law |
Sample Questions
Ques: A 20cm long spanner is used to apply 60N of force to a rusted nut on a motorcycle. Calculate the produced moment. (2 marks)
Ans: Here,
The moment arm (r) is equal to 20 cm.
Force (F) =60 N
F x r = Moment
=60 x 20
=1200 Nm
Ques: To open a rusted nut, a 25cm long spanner is used. Calculate the effort used if the moment produced is 8Nm. (2 marks)
Ans: Moment = 8Nm in this case.
The moment arm (r) equals 25cm = 25/100 m = 0.25 m.
Now, the applied effort (F) = Moment / r = 8 / 0.25 = 32 N.
Ques: The radius of the wheel in a wheel and axle is 50 cm, and the radius of the axle is 20 cm. Calculate MA, VR, and efficiency if a load of 2000N is lifted with an effort of 1000N. (3 marks)
Ans: Here,
Load (L) =2000N
Effort (E) = 1000 N
As a result, MA = L/E = 2000/1000 = 2
And,
The wheel's radius (R) is 50 cm.
The axle radius (r) is equal to 20 cm.
As a result, VR = R/r = 50/20 = 2.5
Now, the wheel and axle efficiency = MA / VR x 100 percent = 2/2.5 x 100 percent = 80%
Ques: An effort of 1000 N is applied in an inclined plane to lift a load. The incline plane's MA and VR are 2 and 3, respectively. Determine the efficiency and effort required. (3 marks)
Ans: MA = 2
VR = 3
Thus, efficiency = MA / VR x 100%
= 2/3 x 100%
= 66.66%
Furthermore, Load (L) = 1000N
We know that MA = Load / Effort, or that Effort
= MA / L
= 1000/2
= 500 N.
As a result, the effort expended is 500 N.
Ques: Determine a lever's efficiency if its MA and VR are 3 and 4, respectively. (2 marks)
Ans: MA = 3 VR = 4
Efficiency = MA /VR x 100 percent
= 3/4 x 100 percent
= 75%
Ques: Determine the efficiency of a four-wheeled pulley system when it is used to lift a 500 N load with a 300 N effort. (2 marks)
Ans: VR = 4
Since, Load = 500N,
Effort = 300N in a four-wheeled pulley system
Load / Effort MA = 500/300
MA = 1.67
Now, Efficiency = MA / VR x 100%
= 1.67/ 4 x 100%
= 41.67%
Ques: Why are simple machines important? (2 marks)
Ans: Most simple machines are designed to reduce the amount of effort (force) required to perform a simple task. To accomplish this, the applied force must act over a greater distance or over a longer period of time, resulting in the same amount of work being performed by a smaller force. Screws, levers, and inclined planes are designed to increase the distance over which a small force acts, allowing us to push or pull with less effort. This design's effect is commonly referred to as providing a mechanical advantage.'
Ques: List the activities where simple machines are used in our day-to-day activities. (2 marks)
Ans: The list of daily activities that include simple machines are:
Stairs are examples of inclined planes.
Scissors are constructed from levers and wedges.
Pulleys: A rolling pin is a wheel as well as an axle.
Another pulley: An inclined plane is a sledding hill.
Also Read:





Comments