
Content Curator
eV or Electron volt and Joule are proportionate to each other. Electron volt is a unit used to measure energy. On the other hand, Joule is the measure of the amount of work done. Any change in electron volt would instill a change in the measure of joules as well. The relation between eV and Joule can be established by using a simple conversion formula.
Key Terms: Electron volt, Joule, Energy, SI unit, work done
Electron Volt (eV)
eV is the short form for electron volt. It is a unit used to measure energy.
One eV is defined as the total energy required for an electron to gain one volt of energy.
In other words,
One eV is the energy change that occurs when an electron of charge 1.6 x 10-19 C is taken through a potential difference of one-volt magnitude.
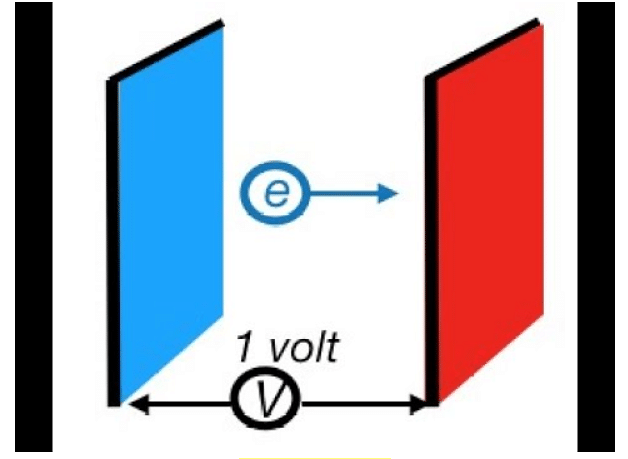
Electron Volt (eV)
eV can also be expressed in other forms such as KeV, MeV, GeV, TeV, etc. The formula to obtain energy in terms of eV is given as,
1 J = 6.2415 × 1018 eV
Also Read:
Joule
Joule is the SI unit used to measure energy.
One Joule is defined as the amount of energy transferred to an object when a force of magnitude one Newton, in the direction of the motion of the object, acts on it for a distance of one meter.
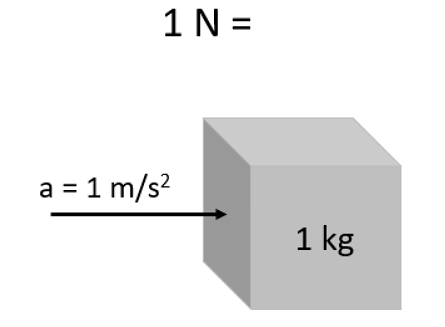
One Joule
The amount of work done instead of energy transferred, under similar conditions, can also be accounted for by one Joule. The formula to obtain energy in terms of Joules is given as,
1 eV = 1.602 × 10-19 J
Relation Between eV And Joule
This relation between eV and Joule can be given by the below equation,
1 eV = 1.602 × 10-19 J
It is to be noted that both these units are used to measure energy but they come from two different systems of units. Joule is the SI unit of energy.
Also Read: Unit of Electric Charge
Conversion Table For Energy
One can easily convert energy from eV to Joule by simply following the equation,
1 eV = 1.602 × 10-19 J
Similarly, one can easily convert energy from Joule to eV by simply following the equation
1 J = 6.2415 × 1018 eV
The table below shows the conversion of some standard energy values.
| Energy (in eV) | Energy (in Joules) | Energy (in Joules) | Energy (in eV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 eV | 1.602 × 10-19 J | 1 J | 6.242 × 1018 eV |
| 2 eV | 3.204 × 10-19 J | 2 J | 1.248 × 1019 eV |
| 3 eV | 4.806 × 10-19 J | 3 J | 1.872 × 1019 eV |
| 4 eV | 6.408 × 10-19 J | 4 J | 2.497 × 1019 eV |
| 5 eV | 8.010 × 10-19 J | 5 J | 3.121 × 1019 eV |
| 6 eV | 9.613 × 10-19 J | 6 J | 3.745 × 1019 eV |
| 7 eV | 1.121 × 10-18 J | 7 J | 4.369 × 1019 eV |
| 8 eV | 1.281 × 10-17 J | 8 J | 4.993 × 1019 eV |
| 9 eV | 1.442 × 10-18 J | 9 J | 5.617 × 1019 eV |
| 10 eV | 1.602 × 10-18 J | 10 J | 6.242 × 1019 eV |
| 50 eV | 8.010 × 10-18 J | 50 J | 3.121 × 1020 eV |
| 100 eV | 1.602 × 10-17 J | 100 J | 6.242 × 1020 eV |
| 500 eV | 8.010 × 10-17 J | 500 J | 3.121 × 1021 eV |
| 1000 eV | 1.602 × 10-16 J | 1000 J | 6.242 × 1021 eV |
Significance Of eV And Joule
The simple relation between eV and Joule is quite significant in physics. Scientists use this relation to obtain magnitudes of many energy-related problems in day-to-day life. Particle physics, nuclear physics, solid-state physics, and atomic state physics are some of the major branches of physics where the relation between eV and Joule plays a significant role. Apart from energy, scientists also use eV to determine values of physical quantities such as distance, momentum, mass, temperature, and time of an object.
Also Read: Bridge Rectifier
Things to Remember
- 1 eV is the energy change that occurs when an electron of charge 1.6 x 10?¹? C is taken through a potential difference of 1 volt magnitude.
- The conversion formula for eV to Joule is 1 eV = 1.602 × 10-19 J
- 1 Joule is defined as the amount of energy transferred to an object when the force of magnitude 1 Newton, in the direction of the motion of the object, acts on it for a distance of 1 meter.
- The conversion formula for Joule to eV is 1 J = 6.2415 × 1018 eV
- The relation between eV and Joule has wide use in particle physics, nuclear physics, solid-state physics, and atomic state physics.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the conversion value of 1eV to 1 kg? What is the conversion value of 1kg to 1 eV? [2 Marks]
Ans. There is no direct relationship between the mass of a particle whose unit is kg and the energy of the particle whose unit is eV. But scientists have derived an indirect relation between these two. According to the conversion processes determined by scientists,
1 eV = 1.782 x 10-36 kg and
1 kg = 5.609 x 1035 eV.
Ques. The total energy required to break one bond in DNA is 10-21 J. Then what is the energy required to break the same DNA bond in eV? [2 Marks]
Ans. It is given that:
The total energy required to break one bond in DNA = 10-21 J
It is known that:
1 J = 6.2415 × 1018 eV
Hence,
10-21 J = \(\frac{6.2415 \times 10^18 eV \times 10^{-20} J}{1 J}\)
10-21 J = 6.2415 × 10-2 eV
∴ The energy required to break the same DNA bond in eV is 6.2415 × 10-2 eV.
Ques. What is the significance of MeV/C2? [2 Marks]
Ans. MeV/C2 is a unit that relates mass with energy. The relationship of a unit mass with energy can be given through this unit. MeV is mega electron volts and C is the charge. The energy of a particle can be given by calculating it in terms of MeV/C2.
Also Read:
Ques. The kinetic energy of an air molecule is 10-21 J. What will be the magnitude of the same energy in eV? [2 Marks]
Ans. It is given that:
The kinetic energy of an air molecule = 10-21 J
It is known that:
1 J = 6.2415 × 1018 eV
Hence,
10-21 J = \(\frac{6.2415 \times 10^18 eV \times 10^{-21} J}{1 J}\)
10-21 J = 6.2415 × 10-3 eV
∴ The magnitude of the same energy in eV is 6.2415 × 10-3 eV.
Ques. What is the relation between eV and Joule? [2 Marks]
Ans. The relation between eV and Joule is given by a simple mathematical expression. Joule is a derived unit of energy and eV is the SI unit of energy. Both these units show a direct relationship. It can be said that eV is directly proportional to Joule. This relation between eV and Joule can be expressed using the equation,
1 eV = 1.602 × 10-19 J
Also Read:
| Types of Motors | Types of Switches | Types of DC Motor |
| Types of Transistors | Types of Friction | Balanced Force |
Ques. Give the values of eV for different prefixes such as mega, kilo, giga, tera, peta, and exa. [3 Marks]
Ans.
| eV | eV | 1 eV |
|---|---|---|
| Mega-eV | MeV | 106 eV |
| Kilo-eV | KeV | 103.eV |
| Giga-eV | GeV | 109 eV |
| Tera-eV | TeV | 1012 eV |
| Peta-eV | PeV | 1015 eV |
| Exa-eV | EeV | 1018 eV |
Ques. What is gf-cm? What is the conversion value of 1 MeV to gf-cm? [2 Marks]
Ans. The term gf-cm is a unit used to express momentum and torque. Its full form is gram force - centimeter. MeV is a symbol for Mega electron volt. There is a direct equation to give the conversion value of MeV to gf-cm.
∴ 1 MeV = 0.0000000016 gf-cm.
Ques. What is energy? What is the unit of energy? [2 Marks]
Ans. The capacity of a body to do work is called energy possessed by the body. It is a scalar quantity and is measured in joule (J). Generally, for practical purposes, a bigger unit called kilojoule (kj) is used (1 kj = 1000 J).
Also Read: Branches of Physics
Ques. Calculate the work done against gravity. [2 Marks]
Ans. Suppose a body of mass m is lifted vertically upwards through a distance h. In this case, the force required to lift the body will be equal to the weight of the body, mg (where m is mass and g is acceleration due to gravity).
Now,
Work done in lifting a body = Weight of body × Vertical distance
W = mg × h = mgh
Where,
W = Work done
h = Height through which the body is lifted
Ques. Four men lift a 250 kg box to a height of 1 m and hold it without raising or lowering it. [3 Marks]
(a) How much work is done by the men in lifting the box?
(b) How much work do they do in just holding it?
(c) Why do they get tired while holding it? (g = 10 ms-2)
Ans. (a) F = 250 kg × 10 ms-2 (g = 10 ms-2) = 2500 N
s = 1 m
W = F.s
= 2500 N × 1 m
= 2500 Nm = 2500 J
(b) Zero, as the box does not move at all while holding it.
(c) In order to hold the box, men are applying a force that is opposite and equal to the gravitational force acting on the box. While applying the force, muscular effort is involved. So, they feel tired.
Also Read:





Comments