Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Multinodular goiter is characterised by the presence of several lumps (nodules) within the thyroid gland. As you already know, hormones are responsible for regulating the body’s cellular function. There are some illnesses that can be caused due to deficiency and exceeding levels of hormones. However, this can only happen when hormones function slower or not at the required level. One such illness that can be caused by the disturbance in hormones is called Multinodular Goiter.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Goiter, Hormones, illness, Lumps, Nodules, Thyroid gland, Neck
What is Multinodular Goiter?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Thyroid is a little gland in the neck that produces hormones which regulate a variety of body activities. An enlarged thyroid gland is referred to as goiter.
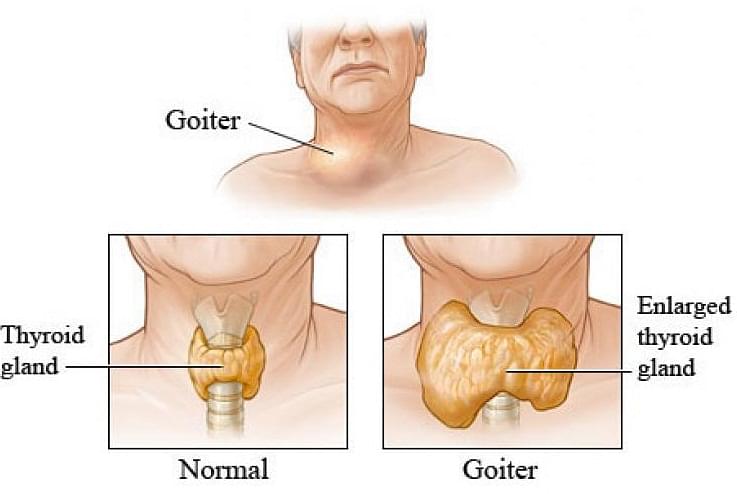
Goiter
Multinodular goiter is a form of goiter in which separate multiple lumps (nodules) are formed on the thyroid gland. It is caused because of many nodules that may act normally, abnormally, or exceedingly. However, the nodules can only be seen via scan or examination. Sometimes, it is non-functional or sometimes it can turn into thyroid cancer.

Multinodular Goiter
In most cases, the cause of multinodular goiter is unknown, but iodine deficiency (a lack of iodine in the diet) and some genetic factors have been linked to the development of multinodular goiter. Females in the age group of 35-50 with nodular growth in the midline of the neck are more likely to have multinodular goiter. However, this is still a ratio of (M:F=1:3).
Also Read:
Risk Factors of Multinodular Goiter
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Iodine is used by the thyroid to make hormones. The thyroid can't work properly if it doesn't get enough iodine. This is the reason why food manufacturers add iodine to salt. This can reduce the chances of thyroid dysfunction.

Types of Goiter
However, other than this there are other risk factors as well that can give birth to multinodular goiter. These are:
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Graves' disease are cases of autoimmune thyroid conditions.
- By sex, nodules and thyroid disorders are more common in women.
- By age, thyroid nodules are more likely to form in older women.
- Thyroid hormone production is influenced by genetic factors.
- A history of multinodular goiter in the family.
- Smoking, stress, or drugs
- Nodular disease
Also, when the thyroid gland produces insufficient thyroid hormone, the pituitary gland in the brain releases more thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH overproduction can cause the thyroid to expand, resulting in a multinodular goiter.
Read Also:
Signs And Symptoms of Multinodular Goiter
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Multinodular goiter does not always show symptoms. Sometimes it can be asymptomatic. However, the majority of multinodular goiters are identified during a routine physical check or during a test performed for another reason. Also, a person with a toxic multinodular goiter may experience hyperthyroidism symptoms.

Enlarged Thyroid gland is a sign of Multinodular Goiter
The nodules can be felt right over the thyroid, which is found in both men’s and women's necks just below Adam's apple. Some of the signs and symptoms of multinodular goiter are:
- Hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty tolerating heat
- Fast heart rate, even when at rest
- Irritability
- Nervousness
- Weight loss or inability to gain weight
- Difficulty sleeping
Read here: Thyroid Gland
Treatment of Multinodular Goiter
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A thorough history and physical exam should be performed if a multinodular goiter is discovered or suspected. Although, there are some other treatments as well that can be done to diagnose multinodular goiter.
Some additional tests can be done that includes:
- Thyroid function tests: This can be done by taking blood samples that can be used to determine how much TSH the pituitary gland produces, as well as how much T-4 and T-3 the thyroid produces.
- Biopsy: Ultrasound is used to direct a very little needle into the thyroid to acquire a tissue or fluid sample from nodules during a fine-needle aspiration biopsy. The samples are examined to see if they contain leukemia cells.
- Ultrasonography: Ultrasonography creates a digital image of the tissues in the neck using sound waves. The technician performs the test by passing a wand-like device (transducer) around your neck.
- Uptake of radioactive iodine: In this test, the patient will be given a little amount of radioactive iodine. A technician can measure the amount and pace at which your thyroid absorbs it using a particular scanning gadget.
Other than these tests, it can also be treated with a physical examination in which a doctor examines a patient's neck for swollen neck veins. Also, some other treatments can be apart from the tests such as Thyroid medication and Thyroidectomy.
Also Read:
Goitrogenic Foods To Avoid For Thyroid
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Goitrogenic foods are foods that can impair T4 thyroid hormone absorption and negatively interfere with thyroid hormone function.

Goitrogenic Food
Because goitrogenic foods are known to boost the processes of autoimmune illnesses, they may be especially harmful for persons with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. The foods that come under goitrogenic are:
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- Brussels sprouts
- Broccoli
- Turnips
- Mustard greens
- Kale
- Cassava root
- Lima beans
- Sweet potato
- Millet
- Soy and soy products
- Green tea
It is suggested that one shouldn't have to completely eliminate goitrogenic foods from his or her diet if they have other health benefits, however, he should avoid eating them uncooked.
Also Read:
Foods For Thyroid Healing
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are some nutrients that are classified as thyroid-healing foods. Thus, if someone is suffering from thyroid problems, he or she can consider increasing the consumption of the following nutrients:
- Tyrosine (amino acid)
- Selenium
- Zinc
- Copper
- Iron
- Vitamins B2, B3, and B6
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
Thyroid hormones primarily affect metabolism, weight regulation and growth & development. The proper functioning of the thyroid gland is based on a careful balance of hormones and nutrients. Thus, if the thyroid is taken care of in a good way, a person cannot have a problem with multinodular goiter.
Also Read: Genetics
Things to Remember
- An enlarged thyroid gland is referred to as goiter.
- The occurrence of many lumps (nodules) within the thyroid gland is known as multinodular goitre.
- Multinodular goiter sometimes is non-functional or sometimes it can turn into Thyroid cancer.
- Multinodular goiter can be caused by the deficiency of iodine.
- Sometimes, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) overproduction can cause the thyroid to expand, resulting in a multinodular goiter.
- Hoarseness, irritability, difficulty in sleeping are some symptoms of multinodular goiter.
- Some tests, a thorough physical examination, Thyroid medication, and Thyroidectomy are some of the treatments used to detect or treat multinodular goiter.
- Intake of some selected Goitrogenic foods needs to be avoided to make thyroid healthy.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. What are the major functions of the thyroid gland? (2 marks)
Ans. The thyroid gland is in charge of nearly all of the cells in the human body. Thyroid gland controls the metabolic rate of the body, managing heart, muscle, and digestive function, as well as brain growth and bone maintenance. Moreover, the pituitary gland and the thyroid operate together. The thyroid's hormone production is controlled by the pituitary gland.
Ques. What is a toxic multinodular goiter? (2 marks)
Ans. Toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG), also known as multinodular toxic goiter (MNTG), is hyperthyroidism-related active multinodular goitre. Generally, toxic multinodular goiter is a common cause of hyperthyroidism in which excess thyroid hormone production (TSH) from functionally autonomous thyroid nodules do not require thyroid stimulating hormone activation.
Ques. Which illness is produced by an iodine deficiency? (2 mark)
Ans. Iodine insufficiency can cause thyroid enlargement, hypothyroidism, and intellectual abnormalities. Moreover, the most serious consequences of iodine deficiency include brain damage and irreversible mental retardation as well.
Ques. Define hypothyroidism? What are the causes of hypothyroidism? (2 marks)
Ans. Hypothyroidism is a disorder in which the thyroid produces and releases insufficient thyroid hormone into the bloodstream. Hypothyroidism is also known as underactive thyroid that can cause fatigue, weight gain, and an inability to handle cold temperatures. Some of the primary causes of Hypothyroidism are:
- Thyroid inflammation)
- Iodine deficiency
- Hereditary conditions
- Radiation and surgical removal of the thyroid
Ques. Describe the Grave’s disease of the thyroid in brief? (2 marks)
Ans. Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid to become overactive, meaning it works harder than it should. It is one of the most common problems of the thyroid and the most common cause of hyperthyroidism as well. Graves' disease occurs when the immune system attacks the thyroid, causing it to overproduce hormones, resulting in a variety of problems throughout the body. It is more common in women and affects people between the ages of 30 and 50.
Ques. What are the different types of goiters? (2 marks)
Ans. There are several types of goiters that include:
Multinodular goiter: Multiple nodules grow in the thyroid in multinodular goiter.
Retrosternal goiter: A goiter of this type can develop behind the breastbone.
Diffuse smooth goiter: Diffuse smooth goiter occurs when the entire thyroid expands.
Ques. What is done in radioactive iodine treatment? (2 marks)
Ans. An overactive thyroid gland can be treated with radioactive iodine. The radioactive iodine dose is taken orally. The thyroid absorbs radioactive iodine, which causes thyroid cells to die. The treatment reduces or eliminates hormone production, which may lead to a reduction in goiter size.
Ques. State the warning signs of thyroid problems? (2 mark)
Ans. Some warning signs of thyroid problems are:
- Weight gain and loss
- Fatigue
- Slow and increase heart rate
- Sensitivity of heat and cold
Also Read:




Comments