
Content Strategy Manager
Lewis acids and Lewis bases are named after an American Chemist Gilbert Newton Lewis. He postulated the Lewis theory to explain the Lewis acid-base reactions. According to this theory, electron-pair acceptors ‘Lewis Acid and electron pair donors 'Lewis Base' react to form a coordinate covalent bond referred to as a Lewis adduct.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Lewis Acid, Lewis base, Covalent Bond, Electron pair, Electrophile, Ion, Hydogen, Ammonia
Lewis Acid
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The chemical species with empty orbitals that can accept a pair of electrons from the Lewis bases are called Lewis acids. They contain an unoccupied p-orbital and have a trigonal planar shape. The electrophiles are Lewis acids as they tend to accept a pair of electrons. Lewis acids use the Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (LUMO) to form a bond with the Lewis base.

Applications of Lewis Acid
- Lewis acids are used as catalysts in a variety of reactions. In Friedel – Crafts alkylation reaction, AlCl3 accepts a lone pair of chloride ions and forms AlCl4-. This produces a highly acidic electrophilic carbonium ion. The reaction for the same is given below:
XCl + AlCl3 → X+ + AlCl4–
- Lewis acids are active in photochemical, electrochemical, hydrogenation, and Prins reactions.
- Lewis Acids are widely used to carry out many cationic and pseudo-cationic reactions.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wilkinsons Catalyst | Uses of Sulphur Dioxide | Manufacturing of Sulfuric acid through contact process |
| Bonding in Metal Carbonyls | Effects of Nitrogen Oxide | Ligands |
Lewis base
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A Lewis base is a species that has a lone pair of electrons and can donate a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. The most strongly located HOMO (Highest Molecular Occurrence Orbital) atomic or molecular chemical species serve as Lewis bases. These chemical species can donate a pair of electrons to a certain Lewis acid to produce an adduct.

Anything like the OH- ion that can transfer a few electrons that are not bonding are the Lewis base. Thus, an electron pair donor is a Lewis base. Ammonia, alkyl amines and other typical amines are the most common Lewis bases. Lewis
bases are usually anionic, and their base strength usually depends on the pKa of the parent acid.
As Lewis bases are electronically rich, they can be categorized as nucleophiles and so contribute electron pairs.
Lewis base: Examples
- The compounds in which Oxygen, Sulphur, Selenium and Tellurium exhibit an oxidation state of -2 are often Lewis bases. Water and ketones are examples of such chemicals.
- Pyridine and the derivative of pyridine is the most common example of Lewis base as they are capable of acting as an electron-pair donor.
- The strong conjugate Lewis bases have weak Lewis acids. Besides that, because of its ability to donate electron-pairs, some chemical species with lone pairs of electrons such as CH3- and OH- are also recognized as the Lewis bases.
- CN-, CH3COO-, H2O are some other examples of Lewis Bases.
- The simple anions which have an electron pair can also act as Lewis bases by donating the electrons. For example, H- and F-.
- The complex anions such as sulfates also behave as Lewis Base.
Applications of Lewis bases
- Lewis bases have tremendous applications in the modification of the selectivity and activities of metallic catalysts.
- Asymmetric catalysis is a key aspect of enantioselective synthesis in the manufacturing of medicinal products. Chiral Lewis bases frequently are used to confer chirality on catalysts in order to enable asymmetric catalysis.
- Few Lewis bases are ‘multi-dented’; so that they can form bonds with Lewis acids. These Lewis bases are known as chelates.
The reaction between Lewis acids and Lewis bases
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The formation of an adduct takes place when a Lewis acid takes an electron from a Lewis base, and this results in the formation of a covalent bond or coordinate bond between the two reactants.
Let Lewis acid be A and Lewis base be B
Lewis acid, A is an electron acceptor while Lewis base, B is an electron donor. A coordinate covalent bond exists between A and B.

Given below are some examples of the reactions between Lewis acid and Lewis base to yield a Lewis adduct.
- Lewis base H2O water and Lewis acid H+ hydrogen ion react to form Lewis adduct hydronium ion H3O+.
The oxygen atom tends to donate an electron to the hydrogen ion to form the coordinate covalent bond.

- Lewis base NH3 ammonia and Lewis acid H+ hydrogen ion react to form Lewis adduct ammonium ion NH4+.
The nitrogen atom tends to donate an electron to the hydrogen ion to form the coordinate covalent bond.

- Lewis base NH3 ammonia and Lewis acid Ag+ silver ion react to form Lewis adduct with the chemical formula Ag(NH3)2+
The nitrogen atom tends to donate an electron to the silver ion to form the coordinate covalent bond.

- Lewis base F- fluoride ion and Lewis acid BF3 Boron trifluoride react to form Lewis adduct with the chemical formula BF4- tetrafluoroborate ion.
The fluoride ion tends to donate an electron to the Boron trifluoride to form the coordinate covalent bond.

-
Lewis base NH3 ammonium ion and Lewis acid BF3 Boron trifluoride react to form Lewis adduct with the chemical formula NH3BF3 ammonia boron trifluoride.
The NH3 ammonium ion tends to donate an electron to the BF3 Boron trifluoride to form the coordinate covalent bond.

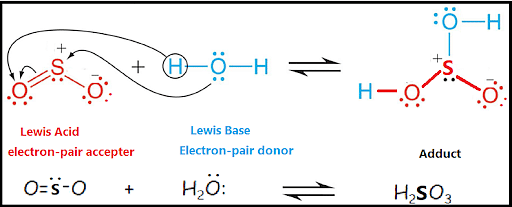
- Lewis base H2O and Lewis acid sulphur dioxide SO2 reacts to form a Lewis adduct with a chemical formula H2SO3 that is, Sulfurous acid.
The oxygen atom tends to donate an electron to the sulphur atom in SO2 while the hydrogen atom tends to donate an electron to the oxygen atom in SO2 to form the coordinate covalent bond.
Things to Remember
- The chemical species with empty orbitals that can accept a pair of electrons from the Lewis bases are called Lewis acids.
- A Lewis base is a species that has a lone pair of electrons and can donate a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond.
- Lewis acids are used as catalysts in a variety of reactions.
- Lewis bases are used in the modification of the selectivity and activities of metallic catalysts.
- When a Lewis acid takes an electron from a Lewis base, a covalent bond or coordinate bond between the two reactants and the formation of an adduct takes place.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques: Which of the following are Lewis Acids? (1 Mark)
H2O, BF3, H+ and NH4+
Ans: Among these compounds, BF3 and H+ ions are Lewis acids.
Ques: Select the Lewis acid and Lewis base in
SnCl4 + 2Cl– → [SnCl6]2-. (1 Mark)
Ans: In the given reaction, SnCl4 is acid and Cl is a base.
Ques: Why does boric acid act as Lewis acid? (1 Mark)
Ans: Boric acid acts as a Lewis acid by accepting electrons from hydroxyl ions. The reaction is given below:
B(OH)3 + 2HOH → B(OH)4- + H3+O.
Ques: Classify the following species into Lewis acids and Lewis bases and show how these can act as Lewis acid/Lewis base? (2 Marks)
OH– ions
F–
H+
BCl3
Ans: (a) OH– ions can donate an electron pair and act as Lewis base.
(b) F– ions can donate an electron pair and act as Lewis base.
(c) H+ ions can accept an electron pair and act as Lewis acid.
(d) BCl3 can accept an electron pair as the Boron atom is electron deficient. So, BCl3 is a Lewis acid.
Ques: (i)Select Lewis acids and Lewis bases from the following: Cu2+, H2O, BF3, OH.
(ii) Give two examples of cations that can act as Lewis acids. (2 Marks)
Ans: (i) Lewis acids: Cu2+, BF3
Lewis base: H2O, OH.
(ii) Two cations that act as a Lewis acid are- Ag+, H+.
Ques: BF3 does not have protons but still acts as an acid and reacts with NH3. Why is it so? What type of bond is formed between the two? (2 Marks)

Ans: In BF3, the octet of B is not complete. So it is an electron deficient species and can accept electron pairs. That is why it acts as Lewis acid and reacts with NH3.
Ques: In the reaction between BF3 and C2H5OC2H5 which one of them will act as an acid. Justify your answer. (3 Marks)
Ans: The reaction between BF3 and C2H5OC2H5 is

As BF3 is electron-deficient and accepts a pair of electrons from C2H5OC2H5. Therefore, BF3 is the Lewis acid.
Ques: Write the applications of Lewis Acid and Lewis Base. (3 Marks)
Ans: Some applications of Lewis Acid and Lewis Base are-
Lewis Acid-
- Lewis acids are used as catalysts in a variety of reactions. For example Friedel – Crafts alkylation reaction-
XCl + AlCl3 → X+ + AlCl4 –
- Lewis acids are active in photochemical, electrochemical, hydrogenation, and Prins reactions.
- Lewis Acids are widely used to carry out many cationic and pseudo-cationic reactions.
Lewis Base-
- Lewis bases are used in the modification of the selectivity and activities of metallic catalysts.
- Chiral Lewis bases frequently are used to confer chirality on catalysts in order to enable asymmetric catalysis.
- Few Lewis bases are ‘multi-dented’; so that they can form bonds with Lewis acids.
Ques: Why NH3 ammonium ion tends to donate an electron to the BF3 Boron trifluoride to form the coordinate covalent bond? (3 Marks)
Ans: Lewis base NH3 ammonium ion and Lewis acid BF3 Boron trifluoride react to form Lewis adduct with the chemical formula NH3BF3 ammonia boron trifluoride. In the reaction, the ammonium ion donate an electron to Boron trifluoride to form the coordinate covalent bond.

For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments