Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
Instantaneous Speed is the speed of an object at a specific instant of time. It can be defined as a short distance traveled by an object divided by the corresponding time taken.
- It refers to the actual speed of an object at a particular moment.
- Instantaneous speed may change with every passing moment.
- When plotted on graphs, it is the slope of the tangent at any point in the journey.
For instance, the speedometer shows the instantaneous speed with which the car is moving. At one moment, the instantaneous speed may be 50 kmph, and in the next moment, it may change to 54 kmph.
Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Motion in a Straight Line
Key Terms: Instantaneous Speed, Speed, Average Speed, Instantaneous Speed Formula, Instantaneous Velocity, Magnitude, Distance
What is Speed?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Speed is the rate at which an object changes its position in any direction.
- It is the ratio of distance to the time taken to cover that distance.
- The SI unit of speed is ‘meters per second’ (m/s).
- The dimensional formula of speed is M0L1T-1.
- It is a scalar quantity as it has only magnitude.
Speed Formula is given as
| \(Speed = {Distance \over Time}\) |
Speed of a Car
There are three major types of speed which are as follows:
- Uniform Speed
- Variable Speed
- Average Speed
- Instantaneous Speed
Read More:
What is Instantaneous Speed?
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Speed is the rate at which an object changes its location over time. The speed of an object may fluctuate as it moves.
- Instantaneous Speed is defined as the speed of an object at a specific point in time.
- If the position is a function of time, the speed is determined by how the position changes as time passes.
- As the time interval reaches zero, the distance traveled also approaches zero.
- However, the limit of the ratio of distance and time is non-zero and is called instantaneous speed.
- Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of instantaneous velocity at a given moment.
- It is a scalar quantity with only direction.
Unit of Instantaneous Speed
- The unit of instantaneous speed is the same as the speed.
- The SI unit of instantaneous speed is meter per second (m/s).
- The CGS unit of instantaneous speed is given as cm/s.
Instantaneous Speed
Read More: Motion in a Straight Line Important Questions
Instantaneous Speed Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Instantaneous Speed is the ratio of distance to the time taken. Instantaneous Speed Formula is given as:
| \(Speed_{(i)} = {ds \over dt}\) |
Where
- ds: Distance Traveled
- dt: Time Interval
- Speed(i): Instantaneous Speed
Solved ExampleExample: Calculate the instantaneous speed at t = 3 s with distance being given as x(t) = 10t2 – 5t + 1. Solution: Given that,
Using the Instantaneous Speed Formula, \(Speed_{(i)} = {ds \over dt}\) Speed(i) = d(10t2 – 5t + 1)/dt Speed(i) = (20t – 5) Speed(i) = (20(3) – 5) = 60 – 5 = 55 m/s. Thus, the instantaneous speed is 55 m/s. |
Read More: Relation Between Torque and Speed

Instantaneous Speed
Difference between Average Speed and Instantaneous Speed
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Average Speed and Instantaneous Speed are the two types of Speed along with Uniform speed and Variable speed. Average speed is the ratio of the total distance traveled by an object to the total time taken. On the other hand, the speed of an object at any instant of time is known as instantaneous speed.
The difference between Average Speed and Instantaneous Speed are as follows:
| Parameter | Average Speed | Instantaneous Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Average Speed is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time spent. | Instantaneous Speed is defined as the speed at a particular instant of time. |
| Formula | Average Speed = Total Distance/Total Time | Instantaneous Speed = Distance at Particular Instant/Time at Particular Instant |
| Uniformity | Average Speed remains constant. | It is not constant and may vary from time to time. |
| Example | The average speed is 40 miles per hour for a car at 40 miles per hour. | A speedometer can tell you how the car is going at any given moment such as 50 kmph. |
Read More: Motion in a Straight Line MCQs
Difference between Instantaneous Speed and Instantaneous Velocity
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Instantaneous Velocity is the rate of change of position for a time interval that is very small or almost zero. On the other hand, instantaneous speed is the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity.
The difference between Instantaneous Speed and Instantaneous Velocity is as follows:
| Instantaneous Speed | Instantaneous Velocity |
|---|---|
| Instantaneous Speed is the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity of an object. | Instantaneous velocity is the rate of change in the position of an object that takes place at a very small interval of time. |
| Instantaneous speed is a scalar quantity with only magnitude and no direction. | Instantaneous velocity is a vector quantity with both direction and magnitude. |
| Instantaneous Speed Formula is \(Speed_{(i)} = {ds \over dt}\). | Instantaneous Velocity Formula is \(V_{(i)} = lim_{\Delta t \rightarrow 0}{ds \over dt}\). |
Check More:
Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 Handwritten Notes
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Here are the handwritten notes on Class 11 Motion in a Straight Line and related topics:




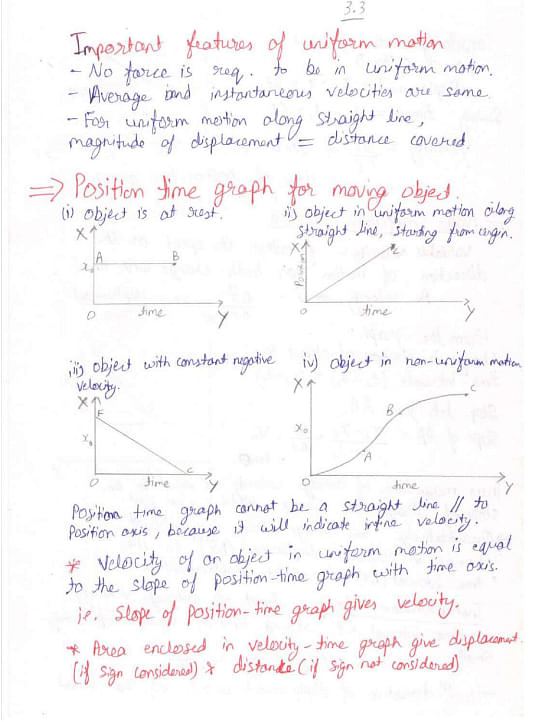



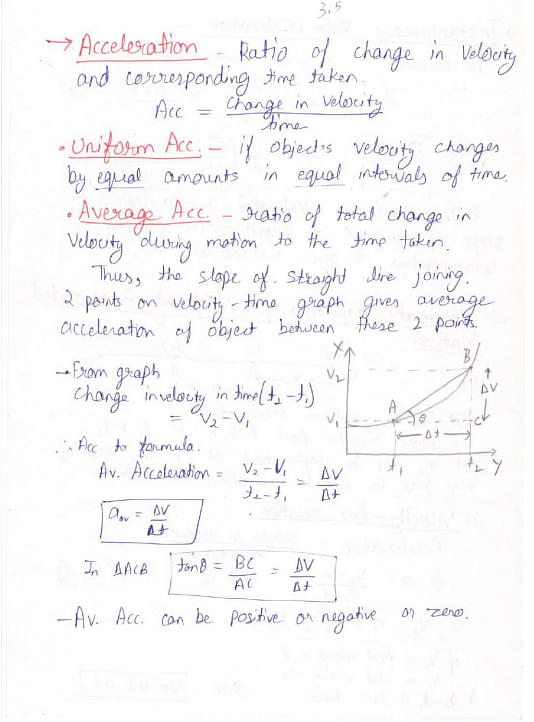







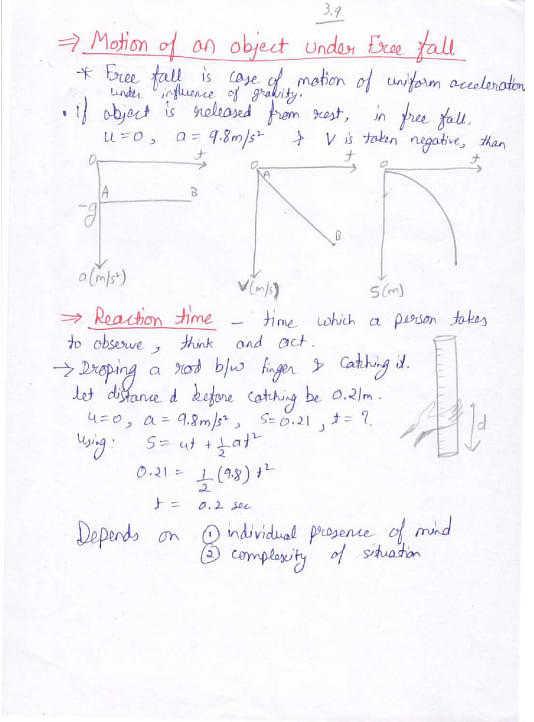
Things to Remember
- Speed is defined as the pace at which an object's position changes over time.
- The speed of an object might fluctuate as it moves.
- Instantaneous speed of an object is defined as its speed at a specific point in time.
- Instantaneous speed is calculated using the absolute value of instantaneous velocity, which is always positive.
- At a particular time, the slope of a position-versus-time graph shows instantaneous velocity.
- Instantaneous Speed Formula is given as \(Speed_{(i)} = {ds \over dt}\).
Previous Years’ Questions
- In one-dimensional motion, instantaneous speed…
- Speedometer of a car measures…
- The position of an object moving along the x-axis is given by…
- A velocity of a particle at an instant is 10m/s. After… (Haryana PMT 2006)
- A particle moving with an initial velocity… (AMUEEE 2016)
- The x−t plot shown in the figure below describes the motion… (KEAM)
- A ball A is thrown up vertically with a speed...[KEAM]
- From a balloon is moving upwards with velocity….[KEAM]
- A bullet fired into a fixed wooden block loses….[KEAM]
- A bullet when fired into a target loses half of its velocity….[KEAM]
- A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly to….[KEAM]
- A train of length L move with a constant speed….[KEAM]
- A particle is moving with constant acceleration….[KEAM]
Sample Questions
Ques. Define Instantaneous Speed. (3 Marks)
Ans. Instantaneous Speed is the speed at which the distance of an object varies over time.
- Instantaneous speed is never zero or less than zero.
- It is a scalar quantity as it has only magnitude and no direction.
- The instantaneous speed of uniform motion is constant.
- The magnitude of instantaneous velocity can be defined as the magnitude of instantaneous speed at any given time.
Ques. What will be the instantaneous speed for an object that travels the distance x(t) = 5t3 – 16t +100 m at t = 8s? (3 Marks)
Ans. It is given that,
- x(t) = 5t3 – 16t +100 m
- t = 8s
Using the Instantaneous Speed Formula,
Sinst = limt->T (dx/dt)
= limt->8 d[x(t)]/dt
= limt->8 d[5t3 – 16t + 100] / dt
= limt->8 [15t2 – 16]
= 15(8)2 – 16 = 15(64) – 16
Sinst = 944 m/s
Thus, the instantaneous speed of the object is 944 m/s.
Ques. A telescope takes an image of a meteor traveling a distance of 100 km in 0.001 seconds. Calculate the instantaneous speed of this meteor at the instant the picture is taken. (3 Marks)
Ans. Since the time duration is very short, the instantaneous speed of the meteor will be given by the formula,
Speed = Distance/Time
Speed = 100 km/0.001 seconds
Speed = 1,00,000 km/second.
Thus, the instantaneous speed of the meteor will be 1,00,000 km/second.
Ques. What is the instantaneous speed of a vehicle? (1 Mark)
Ans. The speed displayed on the speedometer of the vehicle is its instantaneous speed. It is the speed at that specific point in time.
Ques. Determine the instantaneous speed of an object that travels the distance given by the function x(t) = 2t2 + t + 10 cm at a time interval of 2s. (3 Marks)
Ans. According to the question,
- x(t) = 2t2 + t + 10 cm
- t = 2s
Using the Instantaneous Speed Formula,
Sinst = limt->T (dx/dt)
= limt->2 d[x(t)]/dt
= limt->2 d[2t2 + t + 10] / dt
= limt->2 [4t + 1]
= 4(2) + 1 = 9 cm/s
Thus, the instantaneous speed of the object is 9 cm/s.
Ques. When an object is dropped and gravity acts on it, the position of the object changes according to the function x(t) = 4.9t2, where x(t) is in meters. Using the Instantaneous Speed Formula, what is the instantaneous speed at t = 10.0 sec? (3 Marks)
Ans. The Instantaneous Speed Formula is given as
\(V = \lim_{\Delta t\rightarrow 0}\frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}\)
V = limΔt→0[x(t+Δt)]−x(t)/Δt
= limΔt→0[4.9(t+Δt)2]–4.9t2/Δt
= limΔt→0[4.9(t2+2tΔt+Δt2)]–4.9t2/Δt
= limΔt→04.9t2+9.8tΔt+4.9Δt2–4.9t2/Δt
= limΔt→009.8tΔt+4.9Δt2/Δt
= limΔt→0(9.8t+4.9Δt)
V = 9.8 t = 9.8(10.0) m/s = 98.0 m/s
Thus, the instantaneous speed is 98.0 m/s.
Ques. An automobile comes to a complete stop at a traffic light before continuing on a straight road. The function x(t) = 6t2 determines the car's distance from the light. At t = 5.00 s, what will be the instantaneous speed? (3 Marks)
Ans. Using the Instantaneous Speed Formula,
\(V = \lim_{\Delta t\rightarrow 0}\frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}\)
= limΔt→0[x(t+Δt)]−x(t)/Δt
= limΔt→0[6(t+Δt2]–6t2/Δt
= limΔt→0[6(t2+2tΔt+Δt22]–6t2/Δt
= limΔt→06t2+12tΔt+6Δt2–6t2/Δt
= limΔt→012tΔt+6Δt2/Δt
= limΔt→0(12t+6Δt)
V = 12t = 12(5.0) m/s = 60.0 m/s
The instantaneous speed of the car at t = 5.00 s is 60 m/s.
Ques. Prove that a particle's average velocity over a time interval is either less than or equal to the particle's average speed over the same period. (2 Marks)
Ans. The ratio of total displacement to total time is known as average velocity. The ratio of the total distance to total time is the definition of average speed. The average velocity is less than or equal to the average speed because displacement is less than or equal to distance.
Ques. When chased by a lion, a man runs in a straight line at a constant pace of 4m/s towards his car. The distance between the car and the individual is d meters. The lion is running at a constant speed of 6 m/s and is 26 meters behind the victim. The individual arrives at the car safely. What is d's highest potential value? (3 Marks)
Ans. The lion must approach the car at the same time as the person to grab the person over the distance d.
The lion must traverse a total distance of d + 26 m in the time it takes the guy to reach the car, t.
- Velocity of Man vman = d/t
- t = d/vman = d/4
- Velocity of Lion vlion = d/t
- t = d/vlion = d+26/6
d/4 = d+26/6
6d = 4d + 104
d = 52 m
Thus, the maximum possible distance is 52 m.
Ques. What is Instantaneous Velocity? (3 Marks)
Ans. Instantaneous velocity is defined as the change of position that takes place at a very small time interval.
- Instantaneous velocity is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction.
- Its unit of measurement is meters per second (m/s).
- Instantaneous velocity formula is given as \(V_{(i)} = lim_{\Delta t \rightarrow 0}{ds \over dt}\).
Check-Out:







Comments