Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Eubacteria and Archaebacteria are two main divisions within the prokaryotic organisms. Eubacteria, also known as the true bacteria, are usually found in the domain bacteria. Eubacteria are single-celled prokaryotic microorganisms with a variety of characteristics that are or can be found in a variety of environments around the whole world.
Read More: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic microorganisms
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Eubacteria, Bacilli, Cooci, Spirilla, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-Positive bacteria
Definition of Eubacteria
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Eubacteria are single-celled prokaryotic microorganisms and are also known as the "true" bacteria that have a variety of characteristics that can be found under various environmental conditions all over the world. Almost all kinds of bacteria fall under this, except archaebacteria.
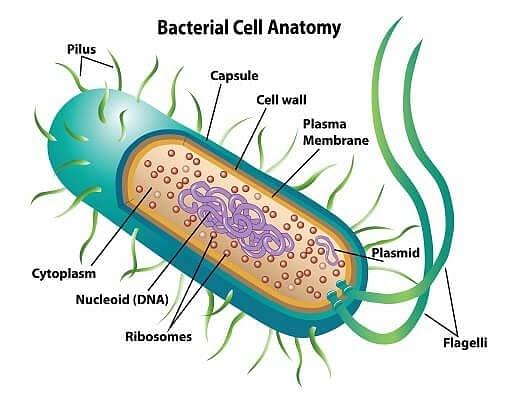
Eubacteria
Eubacteria can form spores and it can cause disease in humans as well as in animals (they can be pathogenic organisms). The mode of reproduction in Eubacteria is through binary fission or by budding, they tend to form large colonies that create "biofilms" i.e. extracellular structure that helps to protect the colony in unique ways. There are mainly three types of eubacteria based on their shapes:
- Bacilli
- Cocci
- Spirilla
Whereas Eubacteria are classified or we can say are typically classified as:
- Gram-Positive
- Gram-Negative
- Miscellaneous
Also Read:
Types of Eubacteria
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
There are three types of bacteria that are mainly classified based on the shape they take: Bacilli, Cocci, Spirilla. The shapes of bacteria are often used as a classification system. Bacteria are linked after the division, forming different shapes and structures such as clusters, filaments, and tight coils. Let us discuss the three shapes in detail.
- Bacilli: They are rod-shaped bacteria.
- Cocci: They are spherical in nature.
- Spirilla: They tend to have spiral or wave-shaped structures in nature.
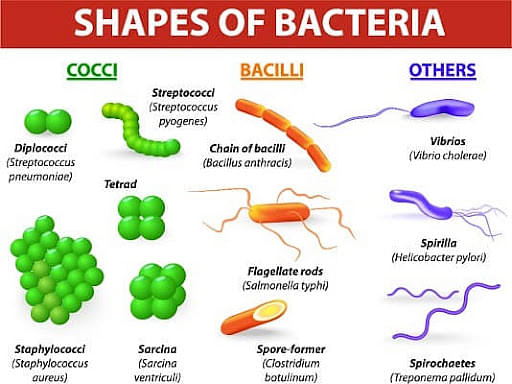
Classification of bacteria based on their shapes
Eubacteria are typically classified based on different factors such as,
- Gram-positive
- Gram-Negative
- Miscellaneous Eubacteria
As there are numerous phyla of eubacteria under the domain bacteria, these relationships are switching constantly and are still defined based on new DNA experiments. The outer membrane of the bacteria is an additional layer that surrounds the cell walls of bacteria.
When this additional layer cannot be stained with gram- stain, they are known as Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria contain certain species that are harmful to humans.
Those bacteria which can be seen with the help of gram stains are known as Gram-Positive bacteria and they are either harmless or beneficial to human health.
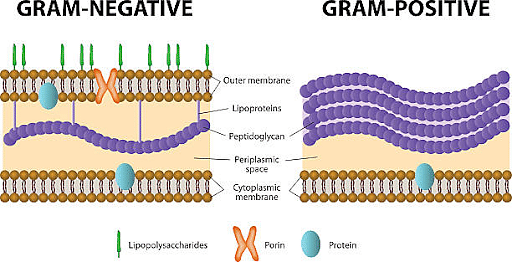
Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
Characteristics of Eubacteria
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Eubacteria is also known as the "true bacteria."
- Peptidoglycans form the stiff cell wall in Eubacteria.
- Flagella are used for locomotion.
- A few bacteria have pili, which are small appendages on the surface of the cell that helps or assist the bacteria in sexual reproduction. Pili also helps or assists in the attachment of pathogens to their hosts.
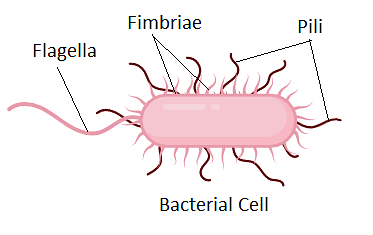
Pili in Bacteria
- Depending on the type of the cell wall and the gram stain they take, they are classified as gram-positive or gram-negative. where gram-negative is harmful to humans and gram-positive is beneficial to human health.
- The two examples of eubacteria are Rhizobium and Clostridium.
Read more : Saprophytes
Mode Of Nutrition of Eubacteria
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
Mode of nutrition in Eubacteria is heterotrophic, but both the organisms, be it autotrophic or heterotrophic organisms feed on eubacteria. Heterotropic are those who consume food from other plants, organic carbon sources, or animal matter whereas autotrophs are those who produce their food through the process of photosynthesis.
Read more : Lichens
Examples of Eubacteria
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some examples of Eubacteria are streptococcus pneumonia which causes pneumonia infection in humans. Lactobacillus, which is present in our gut, is a good bacteria. Some more examples of typically classified bacteria are proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, chlamydias, spirochetes.
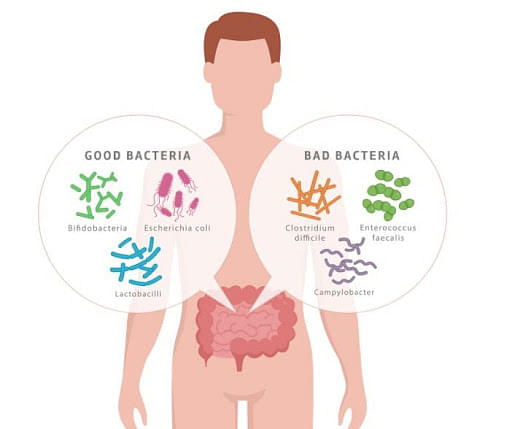
Eubacteria in Humans
Read more : Mycorrhiza
Things of Remember
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
- Eubacteria are single-celled prokaryotic microorganisms and are also known as the "true" bacteria.
- The mode of reproduction in Eubacteria is through binary fission or by budding.
- There are three types of bacteria that are mainly classified based on the shape they take: Bacilli, Cocci, Spirilla.
- Eubacteria are typically classified on the basis of different factors i:e Gram-positive, Gram-Negative, and Miscellaneous Eubacteria.
- Gram-negative is harmful to humans and gram-positives are beneficial to human health.
- Some examples of Eubacteria are streptococcus pneumonia, Lactobacillus, proteobacteria, cyanobacteria, chlamydias and spirochetes.
Also Read:
Previous Year Questions
- The taxonomic unit phylum in the classification of animals is… [UPSEE 2016]
- Cell wall is absent in… [NEET 2015]
- Membrane-bound organelles are absent in… [NEET 2010]
- A free living nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium which can also… [NEET 2004]
- Which fungal disease spreads by seed and flowers… [NEET 2002]
- Match Column - I with Column - II… [NEET 2019]
- The thalloid body of a slime mould (Myxomycetes) is known as… [NEET 2006]
- There exists a close association between the alga… [NEET 2005]
- After karyogamy followed by meiosis, spores are produced… [NEET 2018]
- Archaebacteria differ from eubacteria in… [NEET 2014]
- Azotobacter and Bacillus polymyxa are the examples of… [NEET 1996]
- Bacteria lack alternation of generation because there is… [NEET 1991]
- Bacterial leaf blight of rice is caused by a species… [NEET 2008]
- Barophilic prokaryotes… [NEET 2005]
- BGA (blue green algae) are included in which of the following groups… [NEET 1996]
- Which type of DNA is found in bacteria?….[NEET 1996]
- Lichens grow by….[NEET 1996]
- Which of the following is free-living aerobic and ...[NEET 1997]
- Genophore/bacterial genome or nucleoid is made of…..
- Bacteria lack alternation of generation because there…..[NEET 1991]
Sample Questions
Ques. What are the differences between Archaea and Eubacteria? (2 marks)
Ans. Differences between Archaea and Eubacteria are:
| Eubacteria | Archaea |
|---|---|
| Single-celled simple organisms. | Single-Celled complex organisms. |
| Capable of living in extreme conditions. | Capable of living in normal conditions. |
| Reproduction is through asexual methods. | It can reproduce by both sexual and asexual methods. |
Ques. Define Eubacteria. Give two examples of Eubacteria. (2 marks)
Ans. Eubacteria are single-celled prokaryotic microorganisms and are also known as the "true" bacteria that have a variety of characteristics that can be found under various environmental conditions all over the world. Almost all kinds of bacteria fall under this, except archaebacteria. Eubacteria can form spores and it can cause disease in humans as well as in animals ( they can be pathogenic organisms ). The mode of reproduction in Eubacteria is through binary fission or by budding, they tend to form large colonies that create "biofilms" i:e extracellular structure that helps to protect the colony in unique ways. Examples of Eubacteria are: Streptococcus pneumonia, and Lactobacillus.
Ques. What are the types of eubacteria on the basis of their shape. Explain? (3 marks)
Ans. There are mainly three types of eubacteria based on their shape. The shapes of bacteria are often used as a classification system. Bacteria are linked after the division, forming different shapes and structures such as clusters, filaments, and tight coils. :-
- Bacilli: They are rod-shaped bacteria.
- Cocci: They are spherical in nature.
- Spirilla: They tend to have spiral or wave-shaped structure in nature
Ques. Write three Characteristics of Eubacteria. (3 marks)
Ans. Three characteristics of Eubacteria are as follows:
- Peptidoglycans form the stiff cell wall in Eubacteria.
- Flagella are used to help it to move.
- A few bacteria have pili, which are small appendages on the surface of the cell that helps or assist the bacteria in sexual reproduction. Pili also helps or assists in the attachment of pathogens to their hosts.
Ques. What is the mode of nutrition of Eubacteria. (2 marks)
Ans. The well-known mode of nutrition in Eubacteria is heterotrophic, but both the organisms, be it autotrophic, or heterotrophic organisms both feed on eubacteria. Heterotropic are those who consume food from other plants, organic carbon sources or animal matter whereas autotrophs are those who produce their food through the process of photosynthesis.
Ques. Explain Gram-negative and Gram-positive eubacteria. (2 marks)
Ans. The outer membrane of the bacteria is an additional layer that surrounds the cell walls of bacteria. This additional layer cannot be stained with gram- stain. Due to this reason, they are known as Gram-negative. These bacteria contain certain species that are harmful to humans. Those bacteria which can be seen with the help of gram stains are known as Gram-Positive bacteria and they are either non-harmful or beneficial to human health.
Ques. How is Eubacteria different from archaebacteria. (2 marks)
Ans. Eubacteria and Archaebacteria are two main divisions within the prokaryotic organisms. Eubacteria are also known as the true bacteria and are usually found in the domain bacteria, whereas archaebacteria are usually found in the domain Archaebacteria. Eubacteria are single-celled prokaryotic microorganisms with a variety of characteristics that are or can be found in a variety of environments around the whole world.
Ques. What is the role of bacteria in increasing soil fertility? (2 marks)
Ans. Some bacteria, which are present in the root nodules of leguminous plants or free-living, fix the atmospheric nitrogen in the soil which is ultimately used up by the plants. Hence they increase the fertility of the soil. For example, Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Azospirillum, etc.
Ques. Explain why antibiotics do not work against flu or any infection caused by viruses. (2 marks)
Ans. Viruses cannot be killed by using antibiotics as their cell pathways are different from that of bacteria. It means taking antibiotics to get rid of flu or any other viral infection is useless, because it does not reduce the strength of the virus, nor does it reduce the duration of the infection. But, however, antibiotics will work if we get attacks of viral infection and bacterial disease at the same time. Even then, it will cure bacterial disease only but not a viral infection.
Ques. Explain canning. (2 marks)
Ans. Canning is a process used for food preservation. Heat, at a certain temperature and for a limited period of time, is used to kill harmful microorganisms as well as enzymes. This method also involves the removal of oxygen gas and avoiding post-process contamination by airtight sealing of food items.
Ques. What is the action mechanism of the antibiotic penicillin? (2 marks)
Ans. Penicillin, discovered by the Scottish doctor Alexander Fleming in 1928, is a drug that inhibits enzymes necessary for the synthesis of peptidoglycans, a constituent of the bacterial cell wall. With the inhibition, the bacterial population stops growing because there is no new cell wall formation.
Ques. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells, i.e., they do not have a membrane-delimited nucleus. Eukaryotes have cells with a delimited nucleus. Where in these types of cells can DNA be found? (2 marks)
<Ans. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is found within the cell nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, DNA is found dispersed in the cytosol, the fluid space inside the cell. Other DNA molecules can also be found within mitochondria and chloroplasts, specialized organelles of eukaryotic cells.
Ques. Are bacteria the only prokaryotic beings? (2 marks)
Ans. Prokaryotic beings are classified into two big groups: archaebacteria and bacteria (this is also known as eubacteria). Compared to bacteria, archaebacteria have basic differences, like the chemical compositions of their plasma membrane and cell wall and different enzymes related to DNA and RNA metabolism.
Ques. Mention the types of parasexual methods used by eubacteria? (3 marks)
Ans. The three types of parasexual methods in eubacteria are transformation, transduction, and conjugation.
- Transformation is the process in which bacteria takes up the foreign DNA from its surroundings and gets transformed into another kind.
- Conjugation is the process in which F plasmid with fertility factor is transferred from one bacterium (the donor) to another with the help of sex pilus.
- Transduction is the process of transfer of genetic materials from one bacteria to another through the agency of bacteriophages.
Ques. What are the hyperthermophilic organisms growing in highly acidic (pH 2) habitats called? (3 marks)
Ans. Thermophiles live in very hot places, typically from 60° to 80°C. Many thermophiles (some eubacteria and archaebacteria) are autotrophs and have metabolisms based on sulphur. Some thermophilic archaebacteria form the basis of food webs around deep-sea thermal vents, where they must withstand extreme temperature and pressures. Archaebacteria can grow in highly acidic (pH =0.7) and very basic - (pH =11) environments.
Also Read:




Comments