
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Mycorrhiza is the mutual symbiotic relationship between green plants and fungi. The term “Mycorrhiza” is used to define the role of fungus in the plant’s rhizosphere which is the root system. In this association, both are mutually beneficial - the plant through photosynthesis makes organic molecules.
Read Also: Salient Features of Kingdom
| Table of Content |
Key terms: Photosynthesis, Fungus, Mycorrhiza, Phosphorus, Sugar, Root cells.
The plant through photosynthesis makes organic molecules like sugar which it gives to fungus and the fungus in turn supplies the plant with additional nutrients and moisture. One of the most nutrients required by the plant is phosphorus, which is obtained from the fungus.

Mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Mycorrhiza translates literally to “fungus-root”. Mycorrhiza is a mutually beneficial relationship between plants and fungi.
The fungi primarily colonizes the root system of the plants, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF or AM) or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. The fungi provide the plants with essential nutrients and minerals. This association also gives fungus a direct and stable source of carbohydrate like glucose. In most cases the association is mutually beneficial, but there are some cases where the fungus is slightly harmful for the plant or the plant feeds from the fungus. This exchange has a very important role to play in nutrient cycle, ecology , preventing soil erosion and physiology of plants.

Mycorrhiza
Mycorrhizal plants are more skilled at surviving than non-mycorrhizal plants. But all plants do not require such an association, mostly in places where there is an abundance of water and nutrients in soil, the plants can easily obtain it without the help of the fungus. In such an environment, even mycorrhizal fungi can germinate and process their own carbohydrates. Mycorrhizas are present in about 92% of the studied plant species, with arbuscular being the predominant form in the plant kingdom.
Read More:
Types of Mycorrhizae
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
There are mainly 2 types of Mycorrhizae on the basis of where the fungi colonize on the plant:
- Ectomycorrhiza: They form mutual symbiotic association with woody plants like oak, pine, beech. The distinguishing feature of the relationship is the intercellular surface which is known as the Hartig Net. The structure consists of highly branched hyphae connecting the epidermal and cortical root cells. Ectomycorrhiza forms dense hyphal sheets surrounding the root surface. Ectomycorrhizal fungi live on the outside of the root. This type of association is found in only a few terrestrial plant species.
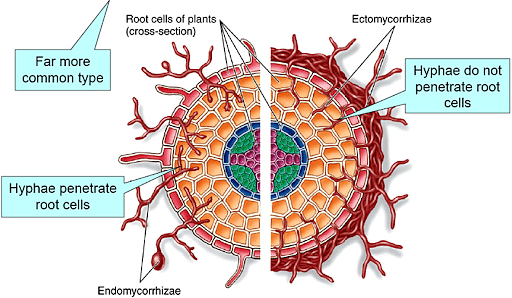
Ectomycorrhiza
- Endomycorrhiza: This is the common form of association which is found in most plant species. Endomycorrhiza have an exchange mechanism on the inside of the root with the fungi hyphae extending outside of the root. It can be subdivided into a few types: Arbuscular Mycorrhizae, Ericaceous Mycorrhizae, Arbutoid Mycorrhiza, and Orchidaceous Mycorrhizae.
Read Also: Difference between Algae and Fungi
Examples of Mycorrhiza
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Orchid Mycorrhiza: In this type, the orchid requires the fungi to initiate germination as it cannot obtain enough nutrients alone to grow.

Orchid Mycorrhiza
- Arbuscular Mycorrhiza: This type has a high affinity for phosphorus and other nutrient intake and also the most widespread association. They form arbuscules which become the site for such nutrient exchange. The fungi which form this association belong to the zygomycota family, which cannot grow without a plant host.
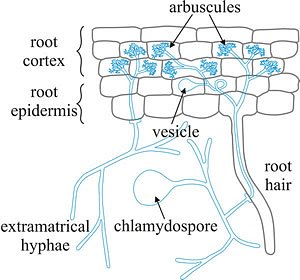
Arbuscular Mycorrhiza
- Ericaceous Mycorrhiza: This type does penetrate and invaginate the root cells but do not form arbuscules. They help the plant to obtain and regulate minerals like iron, manganese and aluminium.

Ericaceous Mycorrhiza
- Arbutoid Mycorrhiza: It is a type of endomycorrhizal fungi which look very much like ectomycorrhizal fungi. They form a fungal sheath that encompasses the roots of the plant.

Arbutoid Mycorrhiza
Benefits of Mycorrhiza
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
- It enhances the water and nutrient intake.
- The association reduces irrigation requirements.
- Need for artificial fertilizers reduces.
- Plant health thrives and becomes stress tolerant.
- Higher transplanting success.
- Makes the plants better at surviving.
- It makes the plants more resistant to diseases and droughts.
- Mycorrhizal plants release chemicals which keep the insects away from it.
- It makes the plants more resistant to toxins present in the environment.

Benefits of Mycorrhiza
Things to Remember
- It is a mutual beneficial association between host plant and fungi
- The association is crucial in maintaining nutrient cycles and balance in ecology.
- The plant receives essential nutrients and moisture from the fungi.
- The fungi gets its carbohydrate requirements from the plant.
- There are mainly 2 types of mycorrhizae - ectomycorrhiza and endomycorrhiza.
- Sometimes mycorrhizal association can be harmful to the plant at high colonization sites of fungi.
- The association helps the plants to keep the insects away and improve the plant health.
- This association also regulates the environment around the plant to make it suitable for its growth.
Also Read:
Previous Years Questions
- The imperfect fungi which are decomposers of litter … (NEET 2015)
- Cell wall of fungi is composed of …
- Identify the odd one out … (KCET 2021)
- A hyphae which is multinucleated and asptate is known as … (WBJEE 1999)
- Puccinia forms uredia and … (NEET 1998)
- A clone is ......… [KCET 2011]
- Animals which possess cleidoic eggs exhibit….[KCET 2011]
- Which among these is not a post fertilization event ?...[KCET 2016]
- Type of asexual reproduction found in Hydra is..[KEAM]
- Which of the following is having longitudinal binary fission ?….[KEAM]
- In grafting, the stock and scion should be joined….
- The mode of asexual reproduction in Euglena is….[CUCET 2010]
- Archaebacteria differ from eubacteria in...(NEET 2014)
- Azotobacter and Bacillus polymyxa are the examples of...(NEET 1996)
- Apomixis in plant means development of a plant… [BHU UET 2008]
- Which one of the following plants reproduces vegetatively by epiphyllous buds?
Sample Questions
Ques: One of the benefits that plants get from mycorrhizal association? (1 mark)
a) Increased photosynthesis efficiency
b) Increased access to soil nutrients and moisture.
c) Resistance to harmful animal activities
d) None of the above
Ans: Increased access to soil nutrients and moisture. (The photosynthesis activity might increase but its efficiency doesn’t improve, also it is resistant to insects but not harmful animal activities.)
Ques: Which of the following is not a category of mycorrhiza? (1 mark)
a) Exomycorrhiza
b) Endomycorrihiza
c) Ectomycorrhiza
d) Ericoid mycorrhiza
Ans: Exomycorrhiza ( “ exo '' means external, the term used for mycorrhiza that do not penetrate the root cells is ectomycorrhiza, not endomycorrhiza)
Ques: Mycorrhizal relationships improve plants defense against pests and pathogens by the following mechanisms except: (1 mark)
a) Physical interaction with the root that it protects.
b) Stimulation of the production of pathogen/insect repelling metabolites.
c) Stimulation of the production of antibodies against the invading pathogen/pest.
d) Taking essential nutrients away from pathogens/pests.
Ans:Taking essential nutrients away from pathogens/pests. (The plant essentially form chemical which repel insects)
Ques: What are the disadvantages of Mycorrhizae? (2 marks)
Ans: The association is usually beneficial for both parts but in high colonization density, the mycorrhizal fungi might deem to be harmful for the plant, as it competes with the nutrients intake of the plant. Sometimes they also start interfering in other interactions as well.
Ques: How long does Mycorrhiza take to work? (2 marks)
Ans: The mycorrhizae takes around 4 weeks to form a symbiotic relationship with the host plant after its application to a growing plant. It takes around 8 weeks for the benefits to be visible.
Also Check Out:





Comments