Namrata Das Exams Prep Master
Exams Prep Master
A fungus is a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms like yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. Found free-living in soil and water, fungi are the organisms that belong to the kingdom Fungi. They are the most widely distributed organism on the globe as it possesses medicinal properties. Most fungi are multicellular. They are unique in having cell walls made from chitin. Most fungi survive on dead matter or soil. Other examples of fungi are rusts, stinkhorns, puffballs, truffles, mildews, and mushrooms. The characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is the chitin in their cell walls. In this article, we will be discussing the various reproduction processes and the life cycle of fungi in detail.
Read Also:- Sexual Reproduction in Fungi
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Fungus, Reproduction, Mushrooms, Spore, Bacteris, Multi-cellular, Cell wall.
Life Cycle of Fungi
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. While some fungi reproduce sexually, others reproduce asexually. Most of the molds indoors are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium.

Life Cycle of Fungi
Some of the characteristic features of fungi are:
- They are eukaryotic, non-vascular, non-motile, and heterotrophic organisms.
- They may be unicellular or filamentous.
- They reproduce by means of spores.
- They exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation.
- They lack chlorophyll and thus are incapable of photosynthesis.
Read More:
Sexual Reproduction of Fungi
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
- Spore (Haploid): This stage marks the beginning of the life cycle of all fungi. In this phase, all the spores are haploid- that is; they have only a single copy of their entire genetic material. These spores then migrate over long distances through the air, carried by various organisms. On locating a favorable living environment, the spores grow a bunch of root-like structures called mycelium. The mycelium is responsible for the transfer of nutrients for the development of the spores.
- Mycelium (Diploid): During its growth and development, the mycelium may encounter other fungi. If the two fungi are compatible, one cell from a mycelium fuses with one from the other mycelium, to form a single new cell. This new cell is diploid as it has two copies of its genetic formation.
- Meiosis: After the formation of mycelium, the fungus enters the next stage called meiosis. During this process, a single cell splits into two daughter cells and the genetic materials from both parents are equally distributed. The daughter cells have unique features and thus do not look similar to each other or their parents.
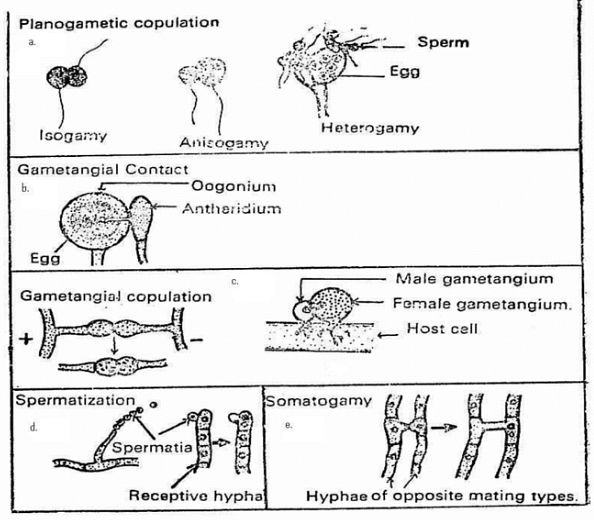
Sexual Reproduction of Fungi
Asexual Reproduction of Fungi
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- During the mycelium stage, the fungus has the choice of reproducing sexually or asexually.
- During its asexual life cycle, the fungus produces mitospores, which are identical to its parent.
- These mitospores later grow into a new set of mycelium and the entire life cycle repeats itself.
Besides regular sexual reproduction with meiosis, certain fungi, like those within the genera Penicillium and Aspergillus, may exchange genetic material via parasexual processes, initiated by anastomosis between hyphae and plasmogamy of fungal cells.
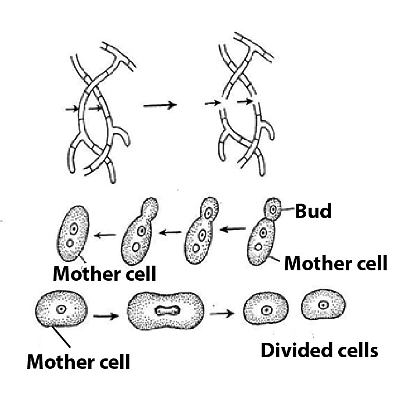
Asexual Reproduction of Fungi
In conclusion, reproduction in fungi may be a complex process, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this diverse kingdom of organisms. Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states that cause the creation of specialized structures for sexual or asexual reproduction.
Read Also:- Gemmule Formation
Points to Remember
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
- Fungi are heterotrophs, that is, they absorb dissolved molecules, by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Unlike plants, they do not perform photosynthesis.
- Reproduction in fungi may occur in two well-differentiated stages within their life cycle, the teleomorph (sexual reproduction) and the anamorph (asexual reproduction).
- Most fungi grow as hyphae, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length.
- The branch of biology dealing with the systematic study of fungi is called mycology. It also studies their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy, and their use to humans as a source of medicine, food, and psychotropic substances consumed for religious purposes, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or infection.
- Fungi grow in a wide range of habitats, including extreme environments such as deserts or areas with high salt concentrations, or ionizing radiation, as well as in deep-sea sediments.
- Some can survive the extreme UV and cosmic radiation encountered during spaceflight. Most grow in terrestrial environments, though several species live partly or solely in aquatic habitats.
Also Read:
Previous Years Questions
- The imperfect fungi which are decomposers of litter … (NEET 2015)
- Cell wall of fungi is composed of …
- Identify the odd one out … (KCET 2021)
- A hyphae which is multinucleated and asptate is known as … (WBJEE 1999)
- Puccinia forms uredia and … (NEET 1998)
- A clone is ......… [KCET 2011]
- Animals which possess cleidoic eggs exhibit….[KCET 2011]
- Which among these is not a post fertilization event ?...[KCET 2016]
- Type of asexual reproduction found in Hydra is..[KEAM]
- Which of the following is having longitudinal binary fission ?….[KEAM]
- In grafting, the stock and scion should be joined….
- The mode of asexual reproduction in Euglena is….[CUCET 2010]
- Archaebacteria differ from eubacteria in...(NEET 2014)
- Azotobacter and Bacillus polymyxa are the examples of...(NEET 1996)
- Apomixis in plant means development of a plant… [BHU UET 2008]
- Which one of the following plants reproduces vegetatively by epiphyllous buds?
Sample Questions
Ques. Do fungi need light? (2 marks)
Ans. While plants need sunlight to supply their food via photosynthesis, fungi do not need light. All plants have a green pigment called chlorophyll which is liable for capturing sunlight. Fungi do not contain chlorophyll and hence, do not require any light.
Ques. Do all fungi have an equivalent life cycle? (2 marks)
Ans. The life cycle of fungi has various patterns based on the species of the fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. While some fungi reproduce sexually, others reproduce asexually.
Ques. What are the main differences between animals and fungi? (4 marks)
Ans. Fungi and animals are very different from one another and classified as completely separate kingdoms. At the cellular level, both animals and fungi are composed of eukaryotic cells. Fungal cells differ from plant cells in that they do not have chloroplast and cannot perform photosynthesis to form their own food. They are almost like animal cells in that fungal cells have centrioles, the structures that organize the spindle during mitosis. Like plants, fungi have a cell wall but it is composed of chitin, a polymer of n-acetyl glucosamine, instead of cellulose, a polymer of glucose. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs. Fungi secret enzymes externally digest food then these nutrients are absorbed. Animals ingest (eat) food followed by internal digestion and absorption of nutrients. Some fungi have stages in their life cycle that are motile in liquid, for instance, water molds.
Ques. Why do fungi need water? (2 marks)
Ans. Fungi mainly absorb water and digest sugars and starches which they use to grow. Fungi have adapted to several environments and may be found in the air, in the ground, in water, or on plants. All of those places provide the nutrients, warmth, and moisture fungi need.
Ques. How are spores formed in fungi? (2 marks)
Ans. Fungi commonly produce spores, as a result of sexual, or asexual, reproduction. Spores are usually haploid and grow into mature haploid individuals through mitotic division of cells. Diploid cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores.
Ques. What is budding in fungi? (2 marks)
Ans. Budding, which is another method of asexual reproduction, occurs in most yeasts and in some filamentous fungi. During this process, a bud develops on the surface of either the yeast cell or the hypha, with the cytoplasm of the bud being continuous with that of the parent cell. In this way, a sequence of cells may be produced.
Ques. Are fungi heterotrophic or autotrophic? (2 marks)
Ans. All fungi are heterotrophic, which suggests that they get the energy they need to live from other organisms. Like animals, fungi extract the energy stored within the bonds of organic compounds like sugar and protein from living or dead organisms. Many of these compounds also can be recycled for further use.
Ques. Why is a fungus called saprophytic? (2 marks)
Ans. Fungi cause decay by releasing enzymes onto the dead animal or plant. These break down complex compounds into simple soluble ones which will be absorbed by decomposers. Organisms that prey on dead material in this way are called saprophytes.
Ques. What are the uses of fungi? (3 marks)
Ans. Fungi are important to everyday human life. Fungi are important decomposers in most ecosystems. Fungi, like food, play a role in human nutrition in the form of mushrooms, and also as agents of fermentation in the production of bread, cheeses, alcoholic beverages, and various other food preparations. Humans also use fungi for pest control. Additionally, fungi can be used to produce citric acid, antibiotics, and human hormones. Fungi are model research organisms also.
Also Check Out:




Comments