
Content Writer
Distillation is the process of separating components from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and subsequent condensation. It is a process in which water vapors convert into volatile liquids and separate through selective boiling. Distillation can be used to either increase the concentration of a particular component in the mixture or to obtain pure components from the mixture.
- Distillation is carried out between liquids having different boiling points.
- Distillation is a physical reversible process which means that it can be returned to the original state of matter.
- A plant that performs distillation is known as a distillery.
- The apparatus used to perform the process of distillation is called a still.
In order to separate a mixture of liquids, the liquid is heated to force components with different boiling points, into the gas phase. The gas is then condensed back into liquid form and is collected. The repetition of the process of distillation on the collected liquid to improve the purity of the product is called double distillation.
Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Key Terms: Distillation, Fractional Distillation, Steam Distillation, Vacuum Distillation, Condensation, Boiling Point, Vapor Pressure, Partial Pressure
What is Distillation?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Distillation is defined as the selective boiling and subsequent condensation of a component in a liquid mixture. It is a process of separating two or more components or substances by converting the liquid into vapor and then substantially condensing back the vapors into a liquid state.
- Distillation is useful in obtaining a pure liquid from non-volatile impurities.
- It is also used to raise the absorption of the specific component in a mixture.
- Distillation is a physical separation process and not a chemical reaction.
- It is a reversible process, i.e. the process can be reversed back to the original state of matter.
- Dry distillation is a chemical process that involves the destructive distillation of solid products to convert them into gaseous products.
- If distillation is performed again on the pure liquid to increase the purity of the liquid, then, the process is called Double Distillation.
- The plant in which distillation is carried out is called a distillery.
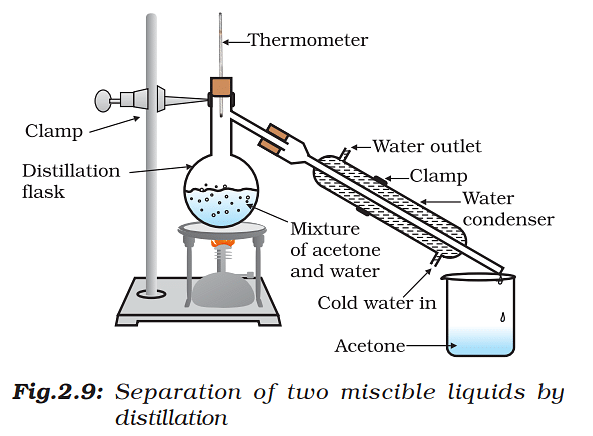
Distillation
Role of Raoult’s Law and Dalton’s Law
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Distillation is dependent on Dalton’s law of partial pressures and Raoult’s law for a mixture of liquids.
| Raoult’s Law: “The partial pressure of a single liquid component in an ideal liquid mixture is equal to the product of the vapor pressure of the pure component and its mole fraction.” |
| Dalton’s Law: “The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equivalent to the sum of the partial pressures of all the constituent gases.” |
The vapor pressure of the individual components increases when a mixture of liquids is heated. This, in turn, increases the total vapor pressure. Thus, the mixture cannot have numerous boiling points at a given composition and pressure.
Why Can't We Obtain a Completely Pure Mixture by Distillation?
All the volatile constituents boil at the boiling point of a mixture of liquids. However, the quantity of a constituent in the resulting vapor is dependent upon its contribution to the total vapor pressure of the mixture. This is the reason why the compounds with higher partial pressures are concentrated in the vapors whereas the compounds having low partial pressures can be concentrated in the liquid.
| “As a component in the mixture cannot have zero partial pressure, it is impossible to obtain a completely pure sample of a component from a mixture via distillation.” |
However, we can obtain samples of high purity when one of the components in the mixture has a partial pressure that is close to zero.
Read More: Organic Chemistry Important Questions
Types of Distillation
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The key types of distillation are explained as follows:
Simple Distillation
- Simple Distillation involves the immediate change of liquid state to vapor state and condensing of vapors by cooling.
- This method is only applicable for mixtures wherein the boiling points of the liquids have a minimum difference of 25 degrees.
- The purity of the distillate or the purified liquid is regulated by Raoult’s law.
- Examples include chloroform, benzene, toluene, acetone, etc. heating the liquid mixture to the boiling point and immediately condensing the resulting vapors.

Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is often used to separate mixtures of liquids whose boiling point difference is more than 25 degree Celsius. It is also used for liquids that have similar boiling points. This method of distillation is also known as rectification. The apparatus or setup required to perform a fractional distillation on a mixture is as follows:
- Distilling Flask or Round-bottom Flask
- Source of heat (fire or a hot bath)
- Receiving flask to collect the condensed vapors
- Fractioning Column
- Standard Glassware
- Thermometer
- Condenser

The liquid mixture is converted into vapors on heating that rise into the fractioning column. The vapors then cool and condense on the walls of the condenser. The hot vapors coming from the distilling flask heat the condensed vapor, creating new vapors. A lot of vaporization-condensation cycles take place and the distillate purifies better with each cycle.
Steam Distillation
- Steam distillation is a process involving heat-responsive compounds in a mixture.
- The process is performed by passing steam through the mixture to vaporize some of it.
- It establishes a high heat-transfer rate.
- The resulting vapor is then condensed to afford the required distillate.
- Steam distillation is used to obtain essential oils from several aromatic flowers and herbs.

Vacuum Distillation
- Vacuum distillation is best for high boiling point mixtures.
- In this method, the pressure of the surroundings is lowered.
- The low pressure enables the component to boil at lower temperatures.
- It is then converted into vapor once the vapor pressure of the component is equal to the surrounding pressure.
- The vapors are condensed and collected as the distillate.
- This method is used to obtain high-purity samples of compounds that decompose at high temperatures.

Read More: Organic Chemistry MCQs
Air Sensitive Vacuum Distillation
- Air-Sensitive Vacuum Distillation is used for compounds that are sensitive to air and readily react with it.
- In this, the vacuum must be replaced with an inert gas once the process of vacuum distillation is complete.
Short Path Distillation
- Short path distillation is used for the purification of a small quantity of a compound that is unstable at high temperatures.
- It is done under lower pressure levels and involves the distillate traveling a very small distance before being collected.
- The less distance traveled by the distillate also reduces the wastage along the walls of the apparatus.
Zone Distillation
- Zone distillation involves the partial melting of a substance and the condensation of the resulting vapors in order to obtain a pure distillate.
- Zone distillation is carried out in a long container with the help of a zone heater.
Applications of Distillation
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Distillation has a considerable number of applications which are described below:
- It is used in laboratories for chemical and pharmaceutical research.
- Distillation is used to purify water as it contains various impurities that can be removed.
- Distillation is used in desalination plants to obtain clear water from seawater.
- Alcoholic beverages like rum and whisky are produced by distilling ferment material which is a mixture of fruit and animal materials that results in produces ethyl alcohol.
- A number of products such as gasoline, wax, fuel oil, lubricating oil, and other petrochemical products, separate at different boiling points when crude oil undergoes distillation.
- Perfumes and food flavorings are obtained from herbs and plants through the process of distillation.
- Fractional distillation is used to separate acetone and methyl alcohol.
- Air contains a mixture of various gases like oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, argon, etc. For this, cryogenic distillation is useful.
Things to Remember
- Distillation is defined as the process of separating components of a liquid mixture based on different boiling points.
- Distillation involves selective boiling and subsequent condensation of a component in a mixture.
- Distillation makes use of the difference in the boiling points of the components in the liquid mixture by forcing one of them into a gaseous state.
- There are various types of distillation such as Fractional distillation, Steam distillation, Vacuum distillation, Zone distillation, etc.
- Fractional distillation seems to be more effective and suitable for volatile liquid mixtures.
- To separate components with high boiling points, vacuum distillation is used.
- Heat-sensitive compounds are separated via steam distillation.
- Uses of distillation include desalination, crude oil refining, purification of alcohol, and making liquefied gases from the air.
Previous Years’ Questions
- Distillation under reduced pressure is employed for…
- A liquid that decomposes at its boiling point can be purified by… [AMUEEE 2014]
- Which one of the following methods can be used to obtain highly pure… [NEET 2021]
- Calcium acetate when dry distilled gives…
- How will you separate a solution (miscible) of benzene…
- It is possible to obtain oxygen from air by fractional distillation… [NEET 1989]
- The most suitable method of the separation of a mixture of ortho… [NEET 1999]
- Which of the following techniques is most suitable for the purification of… [NEET 1997]
- Lassaigne's test for the detection of nitrogen fails in… [NEET 1994]
- Aniline is separated from the aniline-water mixture by… [KEAM]
Sample Questions
Ques. What is Distillation? (3 Marks)
Ans. Distillation is the process that involves the conversion of a liquid into a vapor that is subsequently condensed back to liquid form. The separation of liquids is based on the boiling points of the liquid components in the mixture. Distillation is a physical process and not a chemical reaction. It is a physical separation technique that can be used to either increase the concentration of a particular component in the mixture or to obtain pure components from the mixture.
Ques. Give any three applications of distillation. (3 Marks)
Ans. The applications of distillation are:
- Water purification procedures rely heavily on distillation which is used to get drinking water from seawater.
- Distillation is used to make perfumes and food flavorings from herbs and plants.
- Distillation is used to purify liquid products obtained through chemical synthesis.
Ques. What is Short Path Distillation? (3 Marks)
Ans. The small quantity of the components that are unstable at a high temperature is purified using short-path distillation. Short-path distillation is basically done at a lowered pressure due to which the distillate that is formed travels a very small distance before it gets collected. This reduced distance between the collected distillate and the path traveled by it eventually reduces the wastage of the distillate that gets accumulated in the wall of the apparatus.
Ques. Why is distillation considered an ideal way to separate two liquids? (2 Marks)
Ans. In Distillation, the liquids boil until they reach their boiling points. It then evaporates or vaporizes and passes through the condenser where heat is far away from the vapor and it turns back into a cool, clean reusable liquid. Thus, it is the best way to separate two liquids.
Ques. What is the difference between distillation and evaporation? (3 Marks)
Ans. Evaporation is the method of turning liquid into a gas by adding heat to the liquid so that the molecules on the surface will quickly transform into a gas. Distillation is the method of producing liquid vapor or steam. This is done by heating the liquid to acquire gas and then, condensing the obtained gas into the appropriate liquid form.
Ques. Differentiate between Simple and Fractional Distillation. (3 Marks)
Ans. The difference between Simple and Fractional Distillation is as follows:
| Simple Distillation | Fractional Distillation |
|---|---|
| It is used to separate mixtures of miscible liquids with relatively large differences in their boiling point. | It is used when the mixtures have a relatively less difference in their boiling points. |
| It does not require any additional equipment. | It uses additional equipment called the ‘fractionating column’. |
| Example: Purification of Seawater | Example: Refining of Crude Oil |
Ques. What is Vacuum Distillation? (3 Marks)
Ans. Vacuum distillation is a type of distillation that is used for separating liquids that have very high boiling points from liquid mixtures.
- Thus, it becomes impossible to increase the temperature to reach the high boiling point of the liquids.
- Thus, in this case, the pressure is lowered instead.
- The lowering of the vapor pressure allows the liquid with a high boiling point to boil at a much lower temperature.
- When the vapor pressure of the component becomes equal to the pressure of the surroundings, then the liquid is converted into its vapors.
- The vapors are then condensed and collected in the distillate.
Ques. Does the boiling point of a liquid vary with the pressure surrounding it? (2 Marks)
Ans. Yes, the boiling point of a liquid varies according to the pressure surrounding it. For instance, the boiling point of water at sea level is 100℃, however, the boiling point of water at an altitude of 1905 meters is 93.4℃ as the atmospheric pressure is relatively lower at high altitudes.
Ques. Define chromatography. Give any one application of chromatography. (3 Marks)
Ans. Chromatography is a technique used for the separation of a mixture of solutes brought about by the distribution of dissolved material between two immiscible phases, one of which is the mobile phase and the other part is the stationary phase. It is useful in forensic science to detect and identify trace amounts of substances in the contents of the bladder or stomach.
Ques. What is fractional distillation? (3 Marks)
Ans. Fractional distillation is a type of distillation that involves the separation of miscible liquids in a mixture. The process of fractional distillation involves repeated distillations and condensations and the mixture is usually separated into component parts. The components are separated when the mixture is heated at a certain temperature where fractions of the mixture start to vaporize.
Check-Out:





Comments