Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Difference between resistance and resistivity is that one opposes the flow of electric current, while the other is the resistance of a material per unit length for a unit cross-section.
Resistance is an aspect that opposes the flow of free electrons. Resistivity is the property of a material that gives resistance to that material. Resistors are used in a heater, toaster, microwave, electric stove, etc., due to their nature of generating heat when conducting current. Resistivity, symbolized by rho, ρ, is quantitatively equal to the resistance R of a specimen. The unit of resistance is ohm.
Key Terms: Resistance, Resistivity, Ohm’s Law, Electric Current, Temperature Coefficient, Electron, Voltage
What is Resistance?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
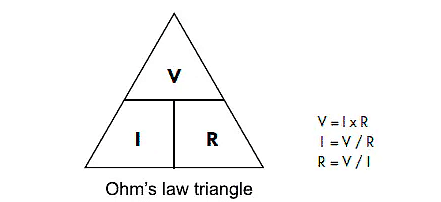
Resistance is the physical property of a substance and a measure of opposition to the flow of electric current. Thus, from Ohm's law relation,
| V = IR |
Where,
- V → Voltage
- I → Current
- R → Constant of proportionality.
Further, the constant of Proportionality (R) is called the resistance of the conductor. Thus, electrical resistance can be defined as the opposition to the flow of charge(electrons) via the conductor.
Factors Affecting Resistance
Resistance depends on the following factors:
- Length and Area of the Cross-section - The resistance depends on the dimensions like length and area of the conductor.
- Temperature - The resistance also depends on temperature, which is the physical state of the conductor.
Formula and Unit of ResistanceThe resistance is said to be 1 ohm when an ampere of current flows through the conductor due to the potential difference of one volt between its ends. It can be expressed as follows: R = V/I Therefore, 1 ohm =1 volt/1 ampere Ohm is the SI unit of resistance, and it is denoted by the symbol Ω.
Ohm’s Law Triangle |
The video below explains this:
Resistance Formula Detailed Video Explanation:
What is Resistivity?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Resistivity can be defined as the resistance of one cubic meter of a wire. It is the property of the material from which the wire is made.
Experimentally, it is proven that the resistance of a wire is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the wire.
Thus, Resistivity is given by the expression:
The SI unit of resistivity is ohm-meter, and it is denoted by the symbol Ωm.

Factors affecting Resistivity
Resistivity depends on factors like :
- The nature of the material
- The temperature of the material
- Resistivity is independent of the dimensions of a conductor.
Effect of temperature on Resistance and ResistivityThe resistance and resistivity of a substance depend on the temperature. As the temperature of the conductor increases, the amplitude of the vibration of the atoms in the lattice increases. As a result, the collision cross-section of atoms increases. Then the atoms offer a bigger target. This increases the likelihood of their collision with free electrons. Thus, the resistance of a conductor increases with an increase or rise in temperature. Experimentally, it has been found that the changes in resistivity of a metallic conductor with temperature are linear over a significant range below and above 0 Cº. This means that the resistivity is not zero at 0 °C. |
What is Temperature Coefficient of Resistance?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The temperature coefficient of resistance is the slight change in resistance of a substance per kelvin.
Thus, mathematically it is expressed as follows:
a = R t – R 0 / R 0t
Where
R 0 → Resistance of material at 0 °C.
R t → Resistance of material at t temperature.
t → Change in temperature.
α → Temperature coefficient of resistance.
What is Temperature coefficient of Resistivity?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The temperature coefficient of resistivity is the slight change in resistivity of a material per kelvin. Thus, mathematically it can be expressed as follows:
a = ρ t – ρ 0 / ρ 0t
Where
ρ 0 → Resistivity of material at 0 °C.
ρ t → Resistivity of material at temperature t °C.
t → Change in temperature
α → Temperature coefficient of Resistivity.
The SI unit of the temperature coefficient of resistance / resistivity (α) is per kelvin ( 1/K or K -1 )
Difference between Resistance and Resistivity
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
| Resistance | Resistivity |
|---|---|
| Resistance is the property of the material that opposes current flow in an electric circuit. | Resistivity provides the resistance of a material that has a fixed dimension or size. |
| Resistance is the ratio of the length (L) and cross-sectional area (A) of the conductor. | The resistivity of the material is the ratio of the product of the resistance and the area to the length of a conductor. |
| Resistance is given by the formula, R = ρ l/a | Resistivity is given by the formula, ρ = R*a/l |
| The SI unit of resistance is Ohm. | The SI unit of resistivity is Ohm-meter. |
| Resistance is represented by the symbol R. | Resistivity is represented by the symbol ρ. |
| Resistance depends on factors like the length, the cross-section, and the area of the conductor. | The resistivity depends on the nature and temperature of the material. |
| The property of resistance finds its application in various places like heaters, fuses, stabilizers, etc. | Electrical resistivity measurement concept is used as a quality control test for calcareous soil. |
Things To Remember based on Difference Between Resistance and Resistivity
- Resistance is the physical property of a substance and a measure of opposition to the flow of electric current.
- Resistivity provides the resistance of a material that has a fixed dimension or size.
- Resistivity can be defined as the resistance of one cubic meter of a wire.
- The SI unit of resistance is ohm (Ω).
- The SI unit of resistance is ohm-meter (Ωm).
- Both resistance and resistivity depend on temperature.
- Resistivity does not depend on the dimensions of the conductor.
Previous Year Questions
- Find the current through a resistance of 2 ohm if the voltage across the resistance is 6V
- State And Explain Joules Law Of Heating
- Why is the curve representing Ohm's law linear?
- State Ohm’s law. How can it be verified experimentally?
- Define 1 volt and the Potential difference.
- The resistance R= V/I, where V=100 ± 5.0V and I = 10 ± 0.2A. What is the total error in R?
- An electric lamp of 100 Ohms, a toaster of resistance 50 Ohms, and a water filter of resistance 500 Ohms are connected in parallel to a 220 V source.
- A battery of 9 V is connected in series with resistors of 0.2 Ohms, 0.3 Ohms, 0.4 Ohms, 0.5 Ohms, and 12 Ohms respectively. How much current would flow through the 12-ohm resistors?
- A small bulb has a resistance of 2 ohms when it is cold. It draws 0.4-ampere current from a source of4V and then starts glowing. Calculate the resistance when it is glowing
- A current of 1 ampere flows in a series circuit containing an electric lamp and a conductor of 5 Ω when connected to a 10 V battery. Calculate the resistance of the electric lamp.
Sample Questions based on Difference Between Resistance and Resistivity
Ques. Three resistors of 10Ω, 10Ω, and 15Ω are connected in parallel. Find their equivalent resistance. (2 marks)
Ans. The given resistors are R1 = 10Ω, R2 = 10Ω, R3 = 15Ω and R1, R2 and R3 are connected in parallel, then the equivalent resistance (R) is given by the formula,
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
= 1/10 + 1/10 + 1/15
= 16/60
Hence equivalent resistance, R = 60/16 = 4.25 Ω.
Ques. What is the formula of resistivity? (2 marks)
Ans. Resistivity is commonly symbolized by the Greek letter rho, and is represented by the symbol ρ. Resistivity is given by the formula, ρ = RA/l.
Ques. What is a resistivity example? (2 marks)
Ans. The resistivity of copper is usually given as: 1.72 x 10 -8 Ωm. The resistivity of a specific material is measured in Ohm-Metres (Ωm) which is also affected by its temperature.
Ques. Explain how resistivity is directly proportional to resistance? (2 marks)
Ans. Resistivity ρ is an intrinsic property and Resistance is an extrinsic quantity that depends on the length(L) and cross-sectional area(A)of a resistor. Thus, resistivity is directly proportional to resistance.
Ques. Do conductors have a very low resistance? (2 marks)
Ans. Yes, conductors have a very low resistance to electrical current.
Ques. Is resistivity directly proportional to temperature? (2 marks)
Ans. No, Resistivity is indirectly proportional to the temperature. In other words, if the temperature of material increases, their resistivities will decrease.
Ques. What causes resistance ? (2 marks)
Ans. An electric current flows when electrons travel through a conductor, for example, a metal wire. Moving electrons can collide with ions in the metal. This makes it more difficult for current to flow and thus causes resistance.
Ques. State ohm's law. (2 marks)
Ans. Statement of Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s Law states that the electric current I flowing through a given conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference (voltage) V across its ends (provided that the physical conditions—temperature, pressure, of the conductor remain same).

where R is a constant of proportionality. It is called the resistance of the conductor. The unit of resistance, volt per ampere, is given a special name ohm and a Greek symbol Ω (Omega).
Ques. What is meant by electrical resistivity of a material? Derive its S.I. unit. (2 marks)
Ans. Mathematically, resistivity of the conducting material is given by
p = R x A/J
If l = 1 m, A = 1 m2, then p = R
Hence, the resistivity of the material is defined as the resistance offered by a metallic wire having a unit length and a unit area of cross-section. Since unit length and unit area of cross-section forms a cube, the specific resistance or resistivity can also be defined as the resistance offered by a cube of a material of 1 m when current flows perpendicularly through the opposite faces. In SI system, its units is

Ques. The figure below shows three cylindrical copper conductors along with their face areas and lengths. Discuss in which geometrical shape the resistance will be highest. (2 marks)

Ans. 
Ques. Calculate the resistance of 1 km long copper wire of radius 1 mm. Resistivity of the copper is 1.72 x 10 -8 ? m. (2 marks)
Ans. 
Ques. Out of the two wires X and Y shown below, which one has greater resistance? Justify your answer. (2 marks)

Ans. Wire ‘Y’ has greater resistance as it has more length than wire ‘X’. It is because resistance of wire is directly proportional to the length of wire.
Ques. What happens to resistance of a conductor when its area of cross-section is increased? (2 marks)
Ans. Restistance decreases as 
Ques. A given length of a wire is doubled on itself and this process is repeated once again. By what factor does the resistance of the wire change? (2 marks)
Ans. Length becomes one-fourth of the original length and area of cross-section becomes four times that of original.

So, new resistance is (1/16)th of original resistance.
Also check:



Comments