
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Axon and dendrite form two of the three most essential parts of the neuron, the third being the cell body. Neurons are special kinds of cells that form an integral part of the nervous system. Neurons in our body detect, receive and transmit all sorts of stimuli. On the contrary to human beings, animals and other vertebrates, the nervous system of invertebrates belonging to lower species functions in a simpler way. Let’s discuss the differences between the axon and dendrite.
| Table of Content |
Nervous System in Human
To understand the axon, dendrite and their differences, it is essential to know about the nervous systems present in humans. The human nervous system is divided into two components:
- Central Nervous Systems
- Peripheral Nervous Systems
Central Nervous System
The Central nervous system is the part of the nervous system which deals with information processing and control. The Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord. Therefore, it forms the bedrock of the Nervous System on which the other functions of the Nervous System work.
Peripheral Nervous System
The functioning of the peripheral nervous system revolves around the central nervous system. Peripheral Nervous System is divided into two components based on their functioning:
- Somatic Nervous System
- Autonomic Nervous System
The Somatic Nervous system is the carrier of signals from the Central Nervous System to the skeleton-muscular system of the body, while the autonomic nervous system acts as the carrier of signals from the Central Nervous System to involuntary parts of the body.
Neuron
Neurons are one of the most essential components of the human nervous system. Neurons are the fundamental reasons why human beings can detect, receive, and transmit different bodily reactions and stimuli.
Axon, dendrite and cell body form the essential components of the neuron. The cell body consists of Nissl's granules that are typically a cytoplasm having a granular body.
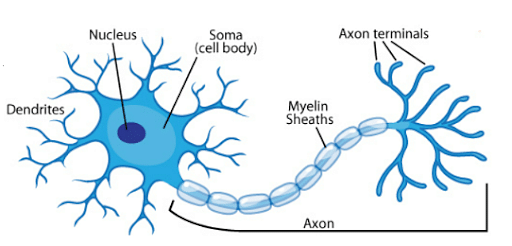
Neuron
Dendrites are the short fibres that protrude out from the cell body. Furthermore, the dendrite carries and transmits signals to the cell body. Axon is a long fibre that has a branch-like structure in one of its ends. The axon carries and transmits signals away from the cell body.
The roots of each branch of axons resemble the bulb structure which is also known as the synaptic knob. There are synaptic vesicles within the synaptic knob. These synaptic vesicles contain a chemical called neurotransmitters.
Classification of Neurons
Neurons are classified into three kinds based on the number of axons and dendrites. Those three kinds are Unipolar, bipolar and multipolar.
- A unipolar neuron contains a cell body with only one axon. The neuron of this kind is mainly found in the embryonic stage.
- A bipolar neuron contains a cell body with one axon and one dendrite. Neurons of this kind are primarily found in the retina of the eyes.
- Multipolar neurons contain a cell body with one axon and two or more dendrites. Neurons of this kind are found in the cerebral cortex.
- Axon is further classified into two types: myelinated and non-myelinated.
- Myelinated nerve fibres are surrounded by Schwan cells that form a sheath or layer around the axon.
- Non-myelinated nerve fibres are surrounded by Schwan cells that do not form sheath or layer around the axon.
- The gap or space between two nearby myelinated layers is called the Nodes of Ranvier.
Also Read: A Labelled Diagram of Neuron
Difference between axon and dendrite
Following are the differences between axon and dendrite.
| Axon | Dendrite |
|---|---|
| Axon is relatively longer in length | Dendrite is relatively shorter |
| Only one axon is present per nerve cell. | Multiple dendrites are present with a nerve cell. |
| Axons transmit signals away from the cell body. | Dendrite transmits signals towards the cell body. |
| Absence of Nissl’s granules. | Nissl’s granules are present. |
| Uniformity of thickness is maintained throughout their length. | There is no uniformity. The ends of the dendrites conclude into branches. |
| Axons are present in the discharging end of the neuron. | Dendrite is present in the receiving end of the neurons. |
| The root of each axon has a synaptic vesicle. | There is no synaptic vesicle in the dendrite. |
Things to Remember
- Axons, dendrite and cell body are the three most essential components of neurons.
- Neurons in our body detect, receive and transmit reactions and stimuli.
- The human nervous system is divided into two types- central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
- The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system which deals with information processing and control.
- Peripheral Nervous System is divided into the somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system.
- Dendrites are the short fibres that protrude out from the cell body. They carry and transmit signals to the cell body.
- Axon is a long fibre that has a branch-like structure in one of its ends. It carries and transmits signals away from the cell body.
Also Read: Diagram of Human Brain
Important Questions
Ques: What are the three most essential components of the nervous system? Describe with a diagram. (3 Marks)
Ans: The three most essential components of the nervous system are the cell body, axon and dendrite. The cell body consists of Nissl's granules that are typically a cytoplasm having a granular body. Dendrites are the short fibres that protrude out from the cell body. Furthermore, the dendrite carries and transmits signals to the cell body. Axon is a long fibre that has a branch-like structure in one of its ends. Furthermore, the axon carries and transmits signals away from the cell body.
Following is the diagram of :

Neuron
Ques: What is the main function of the human hind-brain? What are the two most essential components of the hind-brain and what are their functions? (3 Marks)
Ans: The primary function of the human hind-brain is to control the reflexes and actions of involuntary organs of the human body. The two most essential components of the hind-brain are the cerebellum and medulla oblongata. Following are their functions:
Cerebellum: Cerebellum is that part of the brain that oversees the posturing and movement of the human body. In a way, the cerebellum controls the functioning of bodily movements.
Medulla Oblongata: Medulla Oblongata is the part of the brain that controls the functioning and regulation of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Functions like sneezing, coughing, vomiting, etc. are overseen by medulla oblongata.
Ques: Explain reflex action and the reflex arc. (3 Marks)
Ans: Reflex action is the process in which when our body is subjected to extreme stimulus, there is an involuntary action that happens as a response to safeguard from the perceiving danger. For e.g., when you unknowingly touch a very hot object, you respond by pulling out your hand in a rapid manner. This is what is called reflex action.
Reflex Arc is the route followed by the nerve signal to materialize reflex action.
Ques: Explain Visceral Nervous System. (3 Marks)
Ans: Visceral Nervous System is an important part of the peripheral nervous system. The main function of the visceral nervous system is to carry the signals and impulses from the central nervous system to the visceral parts of the body and from visceral organs to the central nervous system. The visceral organs of the body include the ganglia, plexus and fibres.
Ques: Explain sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. (3 Marks)
Ans: Sympathetic Nervous System: Sympathetic Nervous System is the nervous system that induces a fight-or-flight response system. The sympathetic nervous system is mainly located in the spinal cord. The sympathetic Nervous system controls the palpitation of the heart, respiratory rate, etc.
Parasympathetic Nervous System: Parasympathetic Nervous System is the nervous system that induces a calming effect in the human body. Contrary to the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic system reduces the activity rate of the heart, respiratory rate, etc.
Ques: What are receptors? What are the different types of receptors? (3 Marks)
Ans: Receptors are the part of nerve fibres that receive information from the external atmosphere. Different types of receptors are:
- Phono-receptor: Important for hearing function.
- Photo-receptor: Important for vision-related functions.
- Olfactory-receptor: Important for smelling.
- Thermo-receptor: Important to experience stimulus.
- Gustatory-receptor: Important for taste-related functions.
Ques: Explain Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. (5 marks)
Ans: The nervous system is divided into two types: central and peripheral nervous system.
Central Nervous System
The chief nervous system is the part of the nervous system which deals with information processing and control. The Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord. Therefore, the Central Nervous System forms the bedrock of the Nervous System on which the other functions of the Nervous System work.
Peripheral Nervous System
The functioning of the peripheral nervous system revolves around the central neural system. Peripheral Nervous System is divided into two components based on their functioning:
- Somatic Nervous System
- Autonomic Nervous System
Ques: What are axon and dendrite? What are the differences between axon and dendrite? (5 Marks)
Ans: Dendrites are the short fibres that protrude out from the cell body. Furthermore, the dendrite carries and transmits signals to the cell body. Axon is a long fibre that has a branch-like structure in one of its ends. Furthermore, the axon carries and transmits signals away from the cell body.
Following are the differences between axon and dendrite.
| Axon | Dendrite |
|---|---|
| Axon is relatively longer in length | Dendrite is relatively shorter |
| Only one axon is present per nerve cell. | Multiple dendrites are present with a nerve cell. |
| Axons transmit signals away from the cell body. | Dendrite transmits signals towards the cell body. |
| Absence of Nissl’s granules. | Nissl’s granules are present. |
| Uniformity of thickness is maintained throughout their length. | There is no uniformity. The ends of the dendrites conclude into branches. |
| Axons are present in the discharging end of the neuron. | Dendrite is present in the receiving end of the neurons. |
| The root of each axon has a synaptic vesicle. | There is no synaptic vesicle in the dendrite. |





Comments