Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Biome and ecosystem both are very closely related terms but with different ecological concepts. Biome refers to a major life zone that encompasses all plants and animals that naturally occur in a region. These organisms share common characteristic features, specific to their living environment. Whereas an ecosystem refers to a system in the environment that includes both living and nonliving things. It is a functional unit where these living and nonliving components interact with each other and sustain life.
| Table of Content |
Key Takeaways: Biome, Ecosystem, Biotic, Abiotic, Climate
What is Biome?
A biome is a vast geographical area that encompasses living organisms (plants and animals) that share similar characteristic features. These organisms are adapted to a particular terrain and climatic conditions of an area. Biomes are formed as a result of living organisms’ responses to the environmental conditions around them. It refers to a major life zone characterized by large-scale vegetative and climatic traits. Species in a biome share many common adaptive features. They appear similar in appearance and behavior due to the similarity in the patterns of natural selection. Each biome is named after the predominant vegetation found in the zone. Hence, we have five major types of biomes- forest, aquatic, grassland, desert, and tundra.

Types of Biome
What is Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a functional unit in the environment, where living and nonliving things interact with each other and sustain life. It includes the interaction of biotic and abiotic components in a given environment or area. The biotic factors include animals, plants and other living organisms. The abiotic elements include soil, water, temperature, atmosphere, climate, sunlight etc.
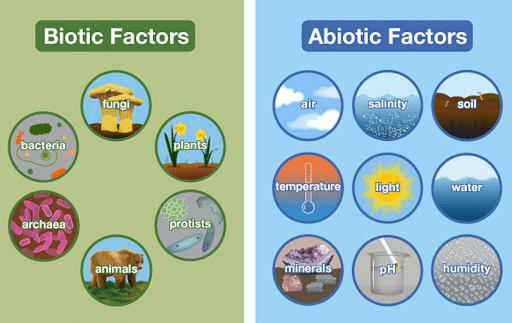
Biotic and Abiotic Components
In an ecosystem, energy moves in a unidirectional path. The living things interact with themselves via processes like competition, symbiosis, predation, parasitism etc. They also interact with abiotic factors. Such interactions help in maintaining the flow of matter and energy in an ecosystem. There exists a hierarchy in the ecosystem consisting of living entities.
This hierarchical structure consists of producers, consumers and decomposers. They interact with each other through different processes and give rise to food chains in an ecosystem. A group of food chains forms the food web. It is through these food chains and webs that the ecosystem survives. In an ecosystem, the abiotic components provide all conditions for the biotic components to survive and flourish. An ecosystem is part of a biome. A biome can have many numbers of ecosystems. An ecosystem is small when compared to biomes as it is widely distributed.
Difference between Biome and Ecosystem
| Biome | Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| A large area with distinct climatic conditions, animal and plant species. | Ecosystem refers to the interaction of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components in an environment. |
| It indicates a large geographical area | It indicates a small geographical region. |
| A biome consists of multiple ecosystems | Ecosystem forms a part of biome |
| A biome depends on climatic conditions like snow, temperature, rainfall, ice etc. | Ecosystem does not depend on climatic factors. It focuses on interactions between living and nonliving components. |
| Has large diversity. Biomes consist of a variety of plants and animal species. | Smaller compared to biomes and have less diversity. |
| In a biome all organisms may not interact with each other. | The primary function in an ecosystem is the interaction between organisms. These interactions are essential in sustaining life in an ecosystem. |
| Influenced by latitude | Not influenced or affected by latitude. |
| Examples: aquatic, desert, tundra, grasslands, forests are some biomes. | An ecosystem consists of animals, plants, ponds, coral reefs, etc. |
Things to Remember
- A biome refers to a large area characterized by distinct vegetation, species and climatic conditions. Ecosystem primarily focuses on the interaction between biotic and abiotic components in an environment.
- A biome is larger than an ecosystem, since it is distributed throughout the earth surface.
- A biome consists of many and different types of ecosystems.
- A biome is strongly influenced by climatic conditions, whereas an ecosystem is not.
- Interactions in an ecosystem sustains life on earth. It possesses food chains and webs that ensure flow of matter and energy through the ecosystem.
- An ecosystem is independent of latitude, whereas a biome is influenced by latitude.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques: What are the factors that influence a biome? (3 marks)
Ans: A biome refers to a large area having distinct species of plants, animals and climatic conditions. A biome is influenced and affected by climatic conditions and latitude. The different types of biomes are characterized by the climatic conditions like temperature, rainfall, snow, ice etc they possess. Unlike an ecosystem, they are not influenced by the interactions between organisms. In a biome organisms may or may not interact with each other. There is no necessity that all organisms must interact with other organisms. But that is not the case of the ecosystem.
Ques 2: Define an ecosystem. (3 marks)
Ans: Ecosystem is a functional unit where living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) entities interact in their environment. The biotic factors include animals, plants and other living organisms. The abiotic elements include soil, water, temperature, atmosphere, climate, sunlight etc. Ecosystem forms a part of the biome and it indicates a small geographical region. There exist an internal hierarchy within the ecosystem consisting of living entities. This hierarchical structure consists of producers, consumers and decomposers. They interact with each other through different processes like predation, competition, symbiosis, parasitism etc and give rise to food chains in an ecosystem. Food chains and food webs are essential in sustaining life in an ecosystem.
Ques 3: Mention the different ecosystem services? Out of these, which is the most important service? Who gave the price tags on nature’s life support services? (5 marks)
Ans. Ecosystem services are as follows:
- Nutrient cycling
- Forest (ecosystem) purify air and water
- Creates and improves soil fertility
- Mitigate floods and Droughts
- Provides habitat for wildlife vegetations and animals
- Promotes Pollination
- Maintain Biodiversity, thereby maintaining the ecological balance of earth.
- Provide cultural, aesthetic and spiritual values.
Out of these, soil formation is considered as the greatest ecosystem service.
Robert Constanza is the one who gave price tags to ecosystem services.
Ques 4: how is the flow of energy in an ecosystem? (2 marks)
Ans: There is a lack of direction in case of the flow of energy in an ecosystem. This means that the energy flow takes place from one trophic level to the other. It doesn’t revert back and follows a single direction. For instance, the energy from the sun is utilized by the plants or producers, and when these plants are eaten by the consumers, the energy gets transferred to the next trophic level.
Ques 5: Describe the type of biomes. (5 marks)
Ans: The different type of biomes are:
- Forests
Forest biomes are characterised by trees. They cover one-third of the earth's surface. These biomes possess the largest terrestrial biodiversity, which includes birds, plants, mammals and insects. Forest biomes are of three major types- tropical forests, temperate forests, and boreal forests. These biome types possess different climatic conditions and features.
- Aquatic Biomes
Aquatic biomes are related to water bodies. Aquatic biomes consist of sub-categories like freshwater biome, wetland biome, marine biome, coral reefs biome and estuary biome. Freshwater biomes refer to water bodies surrounded by land. Marine biomes encompass all oceans of earth. Wetland biome refers to those shallow water bodies which includes marshes, swamps, mudflats, bogs. Coral reefs are found in the shallow parts of the ocean. Coral reefs provide habitat for many underwater aquatic organisms and species. Coral reefs are calcified remains of coral animals. Estuaries are formed where the ocean meets fresh water. Estuary biomes are an important breeding ground for aquatic species like crustaceans.
- Grasslands
Grassland biomes are generally open regions, dominated by grass. They have a dry, warm climatic condition. Grassland biomes can be divided into two subtypes- savannas or tropical grasslands and temperate grasslands. Savannas or tropical grasslands are generally found close to the equator. Savannas receive heavy rainfall for several months, followed by drought. Temperate grasslands are found away from the equator. This biome includes prairies, veldts and steppes.
- Deserts
Desert biomes are generally dry areas that receive less than 20 inches of rainfall annually. They possess high temperatures. Most desert biomes are found in the subtropical regions. Due to the extreme climatic conditions, very less biodiversity is found in these biomes. The wildlife and vegetation found in these biomes are those which can adapt with the extreme climatic conditions. Desert biomes can fall into four categories according to their climatic conditions and geographic location- hot and dry, semiarid, coastal, and cold.
- Tundra
Out of the five types of biomes, tundra is the most inhospitable, coldest biome. These biomes are treeless and possess very low temperatures. They receive very less rainfall annually. They encompass plants, generally grass, shrubs, mosses, lichens, liverworts and sedges. Tundra biomes can be classified as alpine tundra and arctic tundra. The alpine tundra is generally found on mountains and arctic tundra usually found north of the taiga or boreal forests.
Ques 6: What are the components of an ecosystem? (5 marks)
Ans: Ecosystem is a functional unit consisting of biotic & abiotic factors where they interact among themselves & with the physical environment. Ecosystem consists of two major components:-
- Biotic Components:
Biotic components can be classified as producers, consumers and decomposers.
- Producers:- The living organisms which produce food and nutrients for themselves & for all living organisms from inorganic raw material with the help of solar energy are called producers. They are also called autotrophs.
- Consumers:- they are the heterotrophic organisms in an ecosystem and they consume the food synthesized by the producers. They are broadly classified as.
- Primary consumers:- Primary consumers are the ones who are directly dependent on producers called herbivores. E.g. goat, rat, deer, cow etc.
- Secondary consumers:- These are organisms that use primary consumers as their food. They are called carnivores. E.g. Tiger, fox cats, lions.
- Tertiary consumers:- These are top carnivores which prey upon both carnivores, & herbivores
- e.g. crow, man.
- Decomposers:- Organisms that break up the dead bodies of plants, animals & waste materials are called decomposers e.g. bacteria, Fungi etc.
- Abiotic Components:
They are non-living elements in an environment. They include inorganic substances like phosphorus, sulphur, carbon, nitrogen hydrogen etc. And organic substances like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids etc.
Climatic conditions like humidity, rainfall, temperature also are abiotic factors of an ecosystem.





Comments