Namrata Das Exams Prep Master
Exams Prep Master
Zinc Chloride, with the formula ZnCl2, can be prepared by a direct reaction or simply by evaporating the aqueous solution formed in various reactions. It is a chemical solvent that demonstrates hygroscopic dispositions. Zinc chloride is a colorless or white fluid that captivates and apprehends the water molecule that is existing in the background. It is like an ionic salt, necessary for the synthesis of lubricants, protein, and cholesterol may result in the burning of the eyes, skin burning, and mucous covering. This chemical compound is mildly corrosive towards metal. It contours granules that are white and deliquescent. Zinc Chloride is A deadly acid deliquescent that is used mainly as a drying agent, catalyst & wood preservative. It is used in Dry cells as an electrolyte. Let’s have a closer look at the chemical compound and discuss some important questions.
| Table of Content |
Keywords— Zinc chloride, the formula of Zinc Chloride, uses zinc Chloride, the chemical compound, Zinc dichloride.
What is Zinc Chloride?
Zinc chloride is a chemical compound with the formula ZnCl2 and its hydrates. There are nine different crystalline forms of zinc chloride which are currently known. Zinc chlorides are basically colorless or white, and are highly soluble in water. This chemical compound is strongly deliquescent or water-absorbing, which is utilised as a drying agent and as a flux.

Zinc chloride possesses hygroscopic qualities, which means it attracts and captures the water molecules in its environment. The five known hydrates of zinc chloride have the general formula of ZnCl2 (H2O)n in which the values of n can be 1, 1.5, 2.5, 3, and 4. Again, solid ZnCl2 shows polymorphism and can become one of the following crystal structures: tetragonal, monoclinic, and orthorhombic.
Also check:
Structure of Zinc Chloride
Zinc chloride is referred to as an inorganic binary salt, and a molecule of zinc chloride exhibits ionic bonding between the zinc cation (Zn2+) and the chloride anions (Cl–). The structure of a ZnCl2 molecule is shown below.
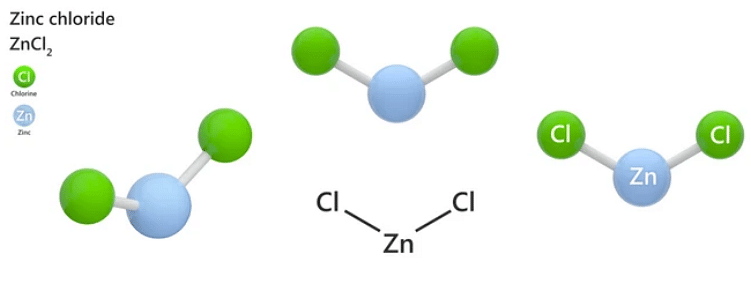
It must be noted that the zinc-chlorine bond in ZnCl2 have some covalent characteristics, which accounts for its low melting point and its solubility in ethereal solvents.
Also check:
Formula of Zinc Chloride
The formula of Zinc Chloride is ZnCl2, we should keep one thing in our mind before writing this formula that Zn keeps its most familiar valency is +2 which indicates that it can contribute 2e^- a. On the other hand, Chloride is -1, which tells that it can accumulate e^ - 80. Zn ^2+ provides 2e^ -s, & 2cl^- increase 1e^- each & that’s how ZnCl2 is stabilized.
It can also be described as follows:
ZnCl2
Zinc= Zn^2+
Chloride= Cl^1-
So the chemical formula formed will be ZnCl2.
Properties of Zinc Cgloride
Chemical Data
| Zinc Chloride | ZnCl2 |
|---|---|
| Molar Mass | 136.315 grams per mole |
| Density | 2.907 grams per cubic centimetre |
| Melting Point | 563 K (290°C) |
| Boiling Point | 1005 K (732°C) |
Physical Properties of Zinc Chloride
The physical properties of Zinc Dichloride include all the things that are relatable to the physical formation of Zinc Chloride.
It can be discussed as given below—
- The molecular weight is 136.315 GMS/mole
- The boiling point is 732° C
- The melting point is 290° C
- The density is 2.907
- Zinc Chloride contours odorless, white, very deliquescent granules.
Chemical Properties of Zinc Chloride
The chemical properties of Zinc chloride can be explained through these points –
- The solution becomes acidic when ZnCl2 is dissolved in water & the pH level of this solution consists of a concentration peer of 6M is approximately 1.
- The hydrated forms of Zinc Chloride lose water after getting heated and then the small multitudes of ZnCl COH are attained.
- It is soluble in alcohol, glycerol, ethen & water
- Zinc Chloride should be safeguarded from all sources of moisture.
Preparation of Zinc Chloride
- The reaction between Zinc and hydrogen chloride gives an anhydrous form of Zinc Chloride. The Chemical equation for the same as follows-
Zn+ 2HCl >Zncl2 + H2
- Hydrochloric acid can be used to treat zinc, in order to obtain a hydrated form of the compound, instead of hydrogen chloride. Hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc sulphide as well in order to form zinc chloride and hydrogen sulphide. The chemical equation for this reaction is as follows:
ZnS+2Hcl > ZnCl2 + H2S
- In the samples of Zinc Chloride, there are some impurities due to the sanctification but it is simply due to its oxidation state
Znas+2
- The purification can also be done with the sublimation with HCl has followed by the pursuing heating of the sublimate to around 400°C with dry nitrogen gas.
- Another way to purify it is by heating it with thionyl Chloride.
Also check:
Uses of Zinc Chloride
Zinc Chloride is vastly used in industries in different ways. Let’s have a look over the industry uses of Zinc Chloride:
- In the chemical industry- The chemical Zinc Chloride is used in the chemical industry in high amounts for the manufacturing of many dyes, solvents, antiseptic mouthwash & intermediate chemicals.
- In Metallurgical Industries- In the soldering process Zinc Chloride is used as petroleum and a cleaning agent. Zinc Chloride is also used in the making of magnesium cement.
- Uses in petroleum- Zinc Chloride helps separate oil from water. It is vastly used in wearing oil from water by the petroleum industry.
- In Printing Industries- 64% of Zinc Chloride in water can be used as a dissolver to silk cellulose & starch.
- In Dry cells- It is extensively used in dry cells as an electrolyte.
- Some other uses- Apart from the above, It is used as a disinfecting agent, condensing agent, dehydrating agent, wood preservative it is used making deodorants.
Things to Remember
- If Zinc Chloride is dissolved in water then the solution becomes acidic.
- Zinc chloride is a chemical compound with the formula ZnCl2 and its hydrates. There are nine different crystalline forms of zinc chloride which are currently known. Zinc chlorides are basically colorless or white, and are highly soluble in water.
- Matter Zinc Chloride is dense with a moderately low electrical conductivity.
- The chemical formula of Zinc Chloride is ZnCL2.It is used as an electrolyte in dry cells.
- The hydrated forms of Zinc Chloride lose water after getting heated & then the small multitudes of ZnCl COH are attained.
- In the soldering process Zinc Chloride is used as petroleum & a cleaning agent. Zinc Chloride is also used in the making of magnesium cement.
Sample Questions
Ques: How to calculate the molar mass of Zinc Florida? (2 marks)
Ans: The molar mass of Zinc Chloride can be calculated as follows-
- The molar mass of Zinc= 65.38u
- The molar mass of Chlorine= 35.453u
- Molar Mass of ZnCL= 65.38×2×35.453 = 136.286u
- The molar of zinc Chloride is 146.286u.
Ques: Is Zinc Chloride safe for consumption? (2 marks)
Ans: Zinc chloride is considered to be highly corrosive if ingested and if inhaled, this is also a strong irritant. Zinc chloride is highly corrosive and ingestion of even 10 mL of a 35 % solution can lead to oropharyngeal and gastric burns, epigastric tenderness, pharyngeal oedema, melaena, and haematemesis.
Ques: Write the valency Of Zinc. (2 marks)
Ans: Zinc is a D-block element that belongs to the transition metal, valence shell contains 2 electrons that iareus2 which means that it can lose two electrons located in ts orbital & then it becomes Zn2+. So the valency of Zinc is 2.
Ques: Write the formation of Zinc Chloride? (3 marks)
Ans: The reaction between Zinc and hydrogen chloride gives an anhydrous form of Zinc Chloride. The Chemical equation for the same as follows-
Zn+ 2HCl >Zncl2 + H2
Hydrochloric acid can be used to treat zinc, in order to obtain a hydrated form of the compound, instead of hydrogen chloride. Hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc sulphide as well in order to form zinc chloride and hydrogen sulphide. The chemical equation for this reaction is as follows:
ZnS+2Hcl > ZnCl2 + H2S
Ques: Write the formula of Zinc Chloride? (2 marks)
Ans: The formula of Zinc Chloride is ZnCL2. Where Zn stands for Zinc & CL for chlorine & 2 is the valence of Zinc.
Ques: Are zinc & Zinc Chloride are same? (2 marks)
Ans: No, Zinc and Zinc chloride is different from each other. Zinc chloride is a chemical compound that is made of a mixture of Zinc and hydrogen chloride gas.
Ques: What are the applications of zinc chloride? (4 marks)
Ans: The uses of zinc chloride are as follows:
- In the chemical industry- The chemical Zinc Chloride is used in the chemical industry in high amounts for the manufacturing of many dyes, solvents, antiseptic mouthwash & intermediate chemicals.
- In Metallurgical Industries- In the soldering process Zinc Chloride is used as petroleum and a cleaning agent. Zinc Chloride is also used in the making of magnesium cement.
- Uses in petroleum- Zinc Chloride helps separate oil from water. It is vastly used in wearing oil from water by the petroleum industry.
- In Printing Industries- 64% of Zinc Chloride in water can be used as a dissolver to silk cellulose & starch.
- In Dry cells- It is extensively used in dry cells as an electrolyte.
Ques: Is zinc chloride considered as a reducing agent? (2 marks)
Ans: The reducing agent is a substance for which reduction takes place by losing electrons. The oxidizing agent is a substance for which oxidation occurs by accepting electrons. The zinc causes the sulfur to gain electrons and become reduced. This is why the zinc is called the reducing agent.
Ques: What are the chemical properties of zinc chloride? (4 marks)
Ans: The chemical properties of Zinc chloride are:
- The solution becomes acidic when ZnCl2 is dissolved in water & the pH level of this solution consists of a concentration peer of 6M is approximately 1.
- The hydrated forms of Zinc Chloride lose water after getting heated and then the small multitudes of ZnCl COH are attained.
- It is soluble in alcohol, glycerol, ethen & water
- Zinc Chloride should be safeguarded from all sources of moisture.



Comments