Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Respiration in fish or anything living in the water varies from that of human beings. Organisms like fish, existing in water, need oxygen to breathe for cells to endure. Fish has their specific structures to carry out the respiratory purpose, helping them inhale oxygen dissolved in water. Oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolves in water, and maximum fishes exchange dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide in water by way of the gills. Water taken in constantly through the mouth passes backwards among the gill bars and over the gill filaments, where the exchange of gases is taken place. The blood capillaries in the gill filaments are near to the gill surface to take up oxygen from the water and to give up the excess of carbon dioxide to the water.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Respiration, Fish, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Water, Gills, Blood Vessels, Bony Fish, Breathing, Blood, Respiration in Fish, Exchange of Gases
Respiration in Fish
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Respiration in fish proceeds with the help of gills. Many fishes possess gills on either side of their head. Gills are tissues made of feathery structures termed gill filaments which provide a huge surface. A large surface area is critical for gas exchange in aquatic organisms as water holds a very little amount of dissolved oxygen. The filaments in fish gills are prepared in rows of the gill arch. The filament holds lamellae which are discs provided with capillaries. Blood flows in and out of the gills through those small blood vessels. Though gills in fish occupy only a small section of their body, the extensive respiratory surface produced by the filaments reduces the whole organism with effective gas exchange.
Fishes take in oxygens rich water through their mouths and pump it over their gills. When water transfers over the gill filaments, the blood within the capillary network goes up the dissolved oxygen. The circulatory system then supplies oxygen to every tissue of the body and lastly to the cells while taking up carbon dioxide that is removed over the gills of the body. It exists in the body of the fish and then water moves out of the gills over the openings given in the sides of the throat or through the operculum. A flap is generally found in bony fish which covers and safeguards the gills.

Respiration in Fish
Numerous fish, like lampreys and sharks, have several gill openings. Rohu which is a bony fish has a single gill opening on both sides.

Fish Gill
Concurrent Exchange Mechanism
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In a few of the molluscs and fishes, this mechanism significantly improves the efficiency of gills as water flows through the gills, in the opposite route of blood flow. This raises the efficiency of gills by 90%, through which the dissolved oxygen can be recovered.
- Gills are secured by gill which covers both sides of the throat which is called the pharynx.
- Fishes exchange gasses by pulling the oxygen-rich water content over their mouth and by pumping it through the gills. When the oxygen has been absorbed by the gills and the remaining water is thrown out.
- Bony fishes have merely one-gill openings, but few fishes like lampreys and sharks have various gill openings.
- Gill openings are similarly recognized as gill slits.
- Bony fishes have three pairs of gills, Cartilaginous fishes have five to seven pairs of gills and jawless simple fishes have seven.
There are two kinds of fishes categorized on their breathing methods:
- Obligate Air Breathers: Fishes who breathe air sometimes or suffocate like the African lungfish.
- Facultative Air Breathers: Fishes who just breathe air if they want to and can then depend upon their gills for oxygen like the Catfish also known as Hypothomes Plecostomus.
Check More
Respiration in Bony Fish
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- In the bony fishes, gills exist in a branchial chamber, which is covered by the operculum.
- The Operculum benefits from putting water pressure inside the throat to allow proper ventilation.
- The bony fish’s gill arches do not have any septum. Instead, the gills project from the arch, which is sustained by gill rays.
- In a few bony fishes, external gills are extant.
- Fishes take oxygen-rich water over their mouth, pump it through the gills, later which the oxygen goes into their bloodstream. When the oxygen is absorbed, the lasting water is thrown out through the gill slits.
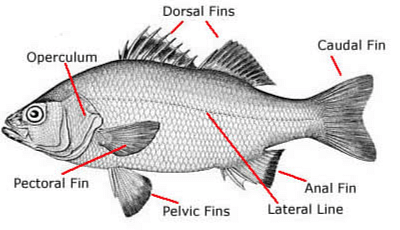
Bony Fish
Respiration in Lampreys and Hagfish
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Gill slits usually lack in few fishes and they possess a spherical pouch-like structure in which they exist.
- They have a round opening on the outside.
- Like other fishes which have gill slits, these fishes have two gills in every pouch.
- The openings are a few times covered and it forms an operculum.
- Hagfish has six to fourteen sets of pouches, although Lampreys have seven pairs of pouches.
Respiration in Cartilaginous Fishes
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Five pairs of gill slits exist in the cartilaginous fishes that open right to the outside.
- They have a long septum, which looks like a sheet and is sustained by the gill array.
- Lamellae is extant beside the gill septum.
- Fishes breathe by sucking water over the opening recognized as a spiracle instead of their mouths. This spiracle comprises a small pseudo branch, which takes just oxygenated blood from the gills.

Structure of Cartilaginous Fish
Read More: Difference between Bony Fish and Cartilaginous Fish
How Do Few Fishes Respire without Gills?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Although most of the fishes in the ecosystem use gills for respiration as others adopt other methods to enable the same. Below mentioned is the utmost importance amongst them:
- Cutaneous respiration which is the gas exchange occurred through the skin of an organism instead of gills or lungs like Reed fish and mudskippers.
- An electric eel could respire over buccal cavities.
- Few fishes like Scolopacidae respire over digestive tracts.
- Few fishes have accessory breathing organs, like labyrinth organs beyond gills in labyrinth fish and more.
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Fishes are cold-blooded animals with streamlined body covered with dermal scales which is waterproof.
- Respiration in fishes takes place through the help of Gills. There are around 4 to 7 pairs of Gills in fishes usually.
- Gills are red in colour because they are filled with blood vessels and are present beside the pharynx and are covered by the operculum.
- The countercurrent exchange mechanism of breathing is used by the fishes mainly. In this process, the water flows opposite the bloodstream, which in turn increases the efficiency of the exchange of gasses by 90%.
- The folded structures of lamellae provide a larger surface area and help in the exchange of gases.
Sample Questions
Ques. Give some details about Gills. (3 Marks)
Ans. Some of the details about Gills are as follows:
- Gills are the respiratory organs of many aquatic organisms just like lungs in Humans.
- Gills have a feathery texture and are present near the head which lets them allow water to enter and help in the exchange of gases.
- Gills are red in colour due to the blood vessels and are present next to the mouth cavity present in the fish.
Ques. How does the fish catch oxygen for respiration? (3 Marks)
Ans. Oxygen is the most significant element that keeps it alive. Similar human fishes take oxygen but with the help of gills. Fish takes water in their mouths by passing it over the gills on every side of their heads. The water absorbs dissolved oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, which is then evicted.
Ques. Why do fishes have a hard time breathing? (3 Marks)
Ans. The gills are equally big, with thousands of tiny blood channels, allowing them to extract the utmost oxygen. Fishes have a far harder time "breathing" as the amount of oxygen in the air among the amount in the water is significantly higher.
Ques. What does the fish take in for respiration? (3 Marks)
Ans. The land animals use their lungs to breathe oxygen from the air and the fishes use their gills to breathe oxygen through water. When a fish gulps water through its mouth, the act of breathing starts. Simultaneously, the waste carbon dioxide in the blood is ejected into the water through the gills.
Ques. Does fish need oxygen to live healthily? (3 Marks)
Ans. Fish like land animals need oxygen to live; but instead of inhaling air, fish gather oxygen from the water nearby them. To increase the quantity of oxygen that their blood can pick up, fish gills embrace a design termed counter-current oxygen exchange.
Ques. Which are the two kinds of fish’s categories on their breathing methods? (3 Marks)
Ans. The two kinds of categories on the breathing approaches:
- Obligate Air Breathers: Fishes who breathe air sometimes or suffocate like the African lungfish.
- Facultative Air Breathers: Fishes who just breathe air if they want to and can then depend upon their gills for oxygen like the Catfish also known as Plecostomus.
Ques. In simpler terms, what do you mean by respiration in the fish? (3 Marks)
Ans. Respiration in fish or anything living in the water varies from that of human beings. Organisms like fish, existing in water, need oxygen to breathe for cells to endure. Fish has their specific structures to carry out the respiratory purpose, helping them inhale oxygen dissolved in water.



Comments