Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
The summer season often seems to be unbearable by some. That is why they often say, "the weather is too humid". Have you ever wondered about the meaning of humidity? In simple words, humidity is the measure of water vapour in the air. Combined with high temperature, humidity increases the distress caused due to heat. Humidity has been termed as the ratio between the vapour pressure of water vapour in the air to the vapour pressure at saturation. Humidity can be expressed at different levels depending on certain factors that affect it. There is no SI Unit for the measurement of humidity. Given below is the detailed information on the units of measurements for humidity used by people to measure the same.
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Humidity, Relative Humidity, Specific Humidity, Absolute Humidity, Air, Water Vapour, Pressure, Atmosphere, SI Unit, Temperature, Heat, Vapour Pressure
Unit of Humidity
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The term humidity is most commonly used in the coastal regions and is defined as the ratio between the vapour pressure of water vapour in the air to the pressure of vapour at saturation. It is expressed at different levels and has no special SI unit.

Humidity
Relative Humidity
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In order to find the content of water vapour in the air, relative humidity is used. It can be defined as the ratio of the amount of moisture in the air at a particular temperature to the amount of moisture that air can withstand at the same temperature. During the rainy season, relative humidity is 100%.
RH= actual vapor density/saturation vapor density% × 100
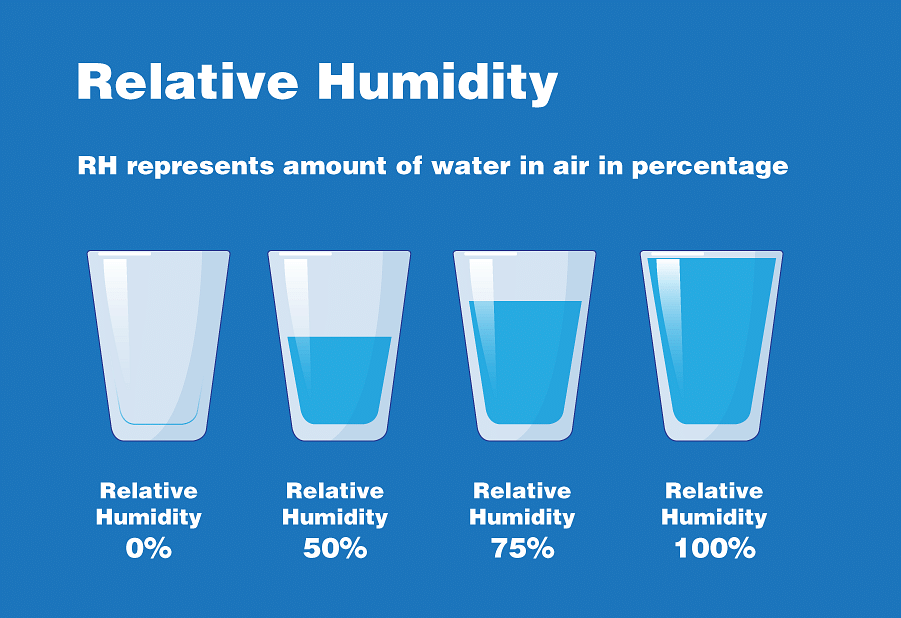
Relative Humidity
Absolute Humidity
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Absolute humidity is used to explain the content of water in the air used to measure water vapour weight per unit volume of air. The unit of absolute humidity is g.m-3, i.e. units of grams of water vapour per cubic meter of air. But, because other factors too affect absolute humidity, the results are likely to be less useful.
Check More:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Types, Applications, Factors Affecting Vaporization | Difference between Evaporation and Transpiration | |
Specific Humidity
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
One of the most reliable units of measuring humidity is known as specif humidity. It measures the weight of water vapour per unit weight of air and is expressed as g.kg-1, i.e. grams of water vapour per kilogram of air.
Things to Remember
- Humidity is defined as the ratio between the vapour pressure of water vapour in the air to the pressure of vapour at saturation.
- RH= actual vapor density/saturation vapor density% × 100
- The unit of absolute humidity is g.m-3.
- Specific humidity is used to describe the weight of water vapour per unit weight of air and is expressed as g.kg-1
Sample Questions
Ques. Distinguish between absolute and relative humidity. (3 Marks)
Ans. Absolute humidity can be defined as the amount of water vapour present in a unit volume of air and is expressed in kilograms per cubic meter.
While Relative Humidity is a measure of how moist or dry the air is. It is the ratio of the amount of water vapour in the air to the amount of vapour the air can hold at that temperature and is expressed as a percentage.
Ques. How is humidity affected by temperature? (3 Marks)
Ans. The amount of water vapour that can be held by air depends upon the temperature. With the temperature getting colder, the air is able to hold less water. The temperature at which the amount of water vapour is present at its maximum limit is known as the dew point of air
As the temperature of the air increases, the relative humidity decreases as air can hold more water molecules while when temperatures drops, relative humidity increases.
Ques. Define humidity. Can relative humidity reach a point of 100? (3 Marks)
Ans. The amount of water vapour in the air is known as humidity. It has no SI unit and can be expressed at different levels.
Yes, relative humidity can be 100% in several cases, especially during the monsoons, when air has a high/maximum amount of moisture.
Ques. Which regions contain more amount of water vapor? (3 Marks)
Ans. The air present in dry regions has less amount of water vapour, while the air in coastal regions contain more amount of water vapour in it.
Tropic regions have the greatest amount of humidity and humidity decreases towards the poles. Humidity is a major determinant of climate and weather and is the most variable in the atmosphere.
Ques. How is relative humidity measured and what are its effects? (3 Marks)
Ans. Relative Humidity is the measure of water vapour present in a water-air mixture compared to the saturation. The device used to measure relative humidity is known as hygrometer.
It effects our daily life, in the way that, when relative humidity is low, i.e. less than 20%, the air seems to be dry. In such cases, the surfaces in our throat and lips tend be dry.
Ques. If the capacity of air to hold water vapour is 10g/m³ and the analysts determine that the air at present holds 8g/m³. Determine the relative humidity. (3 Marks)
Ans. Going by the formula,
RH= actual vapor density/saturation vapor density% × 100
RH= 8/10×100
Thus, RH= 80
Ques. 22 grams of water vapor is present in 6 m³ of air. This maximum amount of water vapor it can hold is 25 grams. Calculate absolute and relative humidity. (3 Marks)
Ans. AH= Amount of water vapour/Cubic meters of air
AH= 22/6
= 3.66g/m³
RH= Actual water vapour/ maximum water vapour×100
RH= 22/25×100
= 88
Check-Out:



Comments