Namrata Das Exams Prep Master
Exams Prep Master
The electrical circuit is an interconnection of electrical components in order to perform a specific function. These circuits use two types of power, alternating current and direct current. The power may increase or decrease suddenly when this current is flowing through devices. Fuse is a safety device in the form of a wire which is present inside an electrical circuit. This wire melts immediately and stops current flow as soon as it detects a fault like current overload. Circuit breakers are electrical switches designed to protect the electrical device from short circuits. They can be found everywhere, starting from households to industries. There is a huge point of difference between the two. Let us take a closer look at them.
| Table of Content |
Also check: Potential Energy
What is a Fuse?
Fuse basically sounds like the powerhouse or the center place of all the electrical circuits of the house in one single box. In simple terms, a fuse can be defined as an electrical safety device responsible for regulating the current in the entire electrical circuit. A fuse holds a very important place in electrical engineering. It is solely concerned with the function of providing or distributing an equal or required amount of current.
The fuse can be actually called as a backup. For example, if the wires get heated enough and start running excessive current, ending up producing a lot of heat energy, the fuse can be utilized to remove the power from such a faulty system.
Also read:
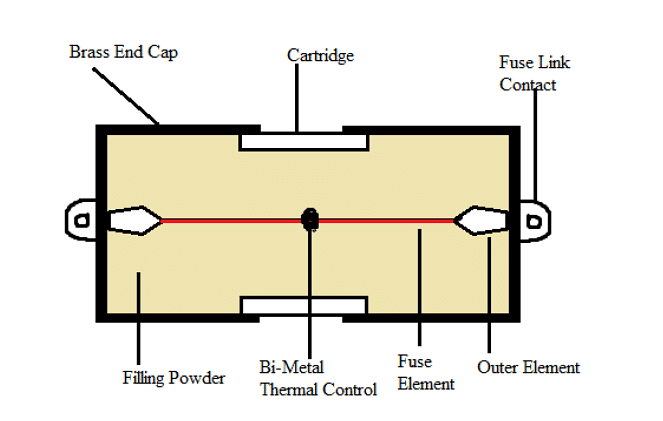
Structure of a Fuse
A fuse is made up of a metal strip placed between a pair of electrical terminals. It is covered by housing which is non-combustible in nature. The fuse must carry the current efficiently all the way through the protected circuit, which is why it is arranged in the manner of a series. As current flows, heat is produced by the resistance of the element. When a high current starts flowing, the temperature of the element rises. This results in the melting of the element itself or the melting of a soldered joint inside the fuse. The fuse element can be zinc, copper, silver, or aluminum. The heating effect depends upon the shape of the fuse element. Current is divided between multiple strips of the metal element. Some outside materials may be used as a catalyst to speed up the quenching of the arc. This may be the air that surrounds the fuse element or even silica sand.
Functions of a Fuse
A fuse is associated with the following functions:
- A fuse is responsible for preventing short circuits
- Acts as a barrier between the human body and the circuit
- The fuse prevents a device from breaking down due to short circuits
- Fuse keeps any kind of blackouts from happening
Also read:
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is an electrical switch solely concerned with protecting an electrical circuit from any kind of damage. This damage may be caused by current overload or a short circuit. It has the ability to be operated both by manual means and automatically. It stops the current flow as soon as it detects any fault. It need not be replaced completely after a fault and can be reset to normal working.
Circuit breakers come in different sizes. The small ones are restricted to a single household while the larger ones are responsible for controlling the current of an entire city. The idea of circuit breakers came a little later after Thomas Alva Edison invented the light bulb back in 1879.
Also read:
Structure of a Circuit Breaker
There are different types of circuit breakers like a vacuum circuit breakers, air circuit breakers, molded-case circuit breakers, etc. Molded-case circuit breakers are very commonly used in the case of low voltage circuits. The economic cost and the sizes of these circuit breakers are what makes it so promising. The important components of this circuit breaker are
- frame/molded case
- Operating mechanism
- Arc extinguisher
- Trip units

The frame of this circuit breaker serves as an insulated cover mounted at the top to cover all the components of the machine. The material of this frame may be glass polyester or resin. Different sizes of circuit breakers have different frame designations.
The operating mechanism of a circuit breaker is responsible for the opening and closing of contacts. Upon holding the handle in the on position, the breaker is bound to trip. Therefore the position of the handle implies the state of the contacts. It may be closed, open, or tripped depending upon the handle movement.
Also read:
When the circuit breaker stops or disturbs the current flow due to faults, an arc is created. This arc extinguisher must divide the arc by extinguishing it for smooth functioning. These extinguishers are made of a stack of steel plates. There are two insulator plates present which hold this stack in position. Trip init can be called the engine of the whole circuit breaker. When a short circuit takes place, the trip unit trips the operating mechanism. These trip units provide protection to a great extent against short circuits, overloads, and arcing ground faults.
Function of a Circuit Breaker
A circuit breaker serves two primary functions. These are:
- The basic function of a circuit breaker is to prevent any further supply of current as soon as it has detected any fault or overload. It immediately stops the current flow.
- When the fault has been rectified, the circuit breaker resumes the normal flow of current again.
Also read:
Difference between a Fuse and a Circuit Breaker
The major differences between a fuse and a circuit breaker are as follows:
| Fuse | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|
| Fuse can be defined as a safety device responsible for protecting an electrical circuit in case of a current override. | Circuit breakers are an electrical switch that protects the electrical circuit from damage. |
| A fuse is known to operate for almost about 0.002 seconds. | A circuit breaker’s operating time ranges from 0.02-0.05 seconds. |
| A fuse constitutes a low breaking capacity. | A circuit breaker has a high breaking capacity. |
| Fuse is highly economic and affordable. | Circuit breakers have a high operational cost. |
| Fuse is the ultimate backup for a faulty electric system and therefore can be only used once. | There is no restriction on the number of users of circuit breakers. |
| The working mechanism of a fuse is dependent on the nature of the conducting material as well as its thermal properties. | A circuit breaker is based on the principle of electromagnetism. It is known to switch principles while undergoing its function. |
| In the case of an overload of currents, a fuse provides protection. | The circuit breaker is concerned with providing protection against overloads as well as short circuits. |
| A fuse does not indicate or give any warning at the time of an overload. | A circuit breaker always gives an indication during overloads. |
| Fuses have the ability to perform automatically. | Apart from being automatic, circuit breakers may require manual operation to function. |
Things to Remember
- A fuse is a safety device responsible for controlling the flow of current. It is the center point of all the electrical circuits in the house which is why it is very important in electrical engineering. The material of the fuse element may be zinc or copper.
- A fuse is associated with the function of stopping the current flow in situations like current overload, and short circuits. They also serve as a protection of the human body from such circuits, preventing blackouts and mishaps. Fuses also prevent the device from failing completely because of such faults.
- Fuses have an operating time of about 0.0002 seconds. They don't provide any indication at the time of overload but are automatic in nature. They have a low breaking capacity and are extremely affordable. However, once used, a new fuse has to be used or installed.
- A circuit breaker is an electrical switch that protects the electrical circuit from being damaged. They can be handled either manually or automatically. After stopping the current flow during a fault, it has the ability to reset the device back to normal working mode.
- Circuit breakers have a high operational cost and work on the principle of electromagnetism. They always give an indication in case of overloads and operate for about 0.02-0.05 seconds. Circuit breakers have a high breaking capacity. A molded-case circuit breaker is a very common type of circuit breaker used by people.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques: What is a fuse? Name its types. (2 marks)
Ans: A fuse is a device or a safety device present inside an electrical circuit or plug. It stops or interrupts the flow of current as soon as it detects a fault like a short circuit. Some of the types of fuses are DC fuse, AC fuse, cartridge fuse, high voltage fuse, and SMD fuse.
Ques: What is the function of a fuse? (2 marks)
Ans: The fuse is primarily associated with functions like,
- Preventing short circuits
- Prevention of blackouts
- Barrier with the human body and short circuits
- Prevents the machine from breaking down
Also check:
Ques: What are the different types of circuit breakers available? (2 marks)
Ans: There are many kinds of circuit breakers available. Each of them is unique and serves its individual function. The different types of circuit breakers are,
- Single pole circuit breakers
- Molded case circuit breakers
- Air circuit breaker
- GFCI circuit breaker
- Vacuum circuit breaker
Ques: Name the uses of a circuit breaker. (2 marks)
Ans: The basic use of a circuit breaker is, it is specifically designed to protect an electrical circuit from an overload of current. It trips and cuts off the power supply when it detects a fault.
Also check:
Ques: Name some important differences between a fuse and a circuit breaker. (3 marks)
Ans: A fuse does not give any indication at the time of a current override whereas circuit breakers provide an indication. Fuse is automatic and cannot be handled manually. On the other hand, a circuit breaker can be handled both automatically as well as by manual operation. Fuse is easily affordable and well within people’s reach whereas circuit breakers are a bit expensive.
Ques: Name some characteristics of a fuse. (3 marks)
Ans: Some important characteristics of a fuse are as mentioned below,
- Fuse has an operational time of 0.002 seconds
- Easily affordable
- Low breaking capacity
- Works automatically
- Fuse can be used once, and later needs replacing
Also check:
Ques: What are the components of a fuse? (2 marks)
Ans: The thin strip of metal and the casing or the cartridge are considered as the main components of a fuse. The presence of a filling powder and the brass cap is essential as well.
Ques: Describe the structure of a fuse. (4 marks)
Ans: A fuse is made up of a metal strip placed between a pair of electrical terminals. It is covered by housing which is non-combustible in nature. The fuse must carry the current efficiently all the way through the protected circuit, which is why it is arranged in the manner of a series. As current flows, heat is produced by the resistance of the element. When a high current starts flowing, the temperature of the element rises. This results in the melting of the element itself or the melting of a soldered joint inside the fuse. The fuse element can be zinc, copper, silver, or aluminum. The heating effect depends upon the shape of the fuse element. Current is divided between multiple strips of the metal element. Some outside materials may be used as a catalyst to speed up the quenching of the arc. This may be the air that surrounds the fuse element or even silica sand.
Also check:









Comments