Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
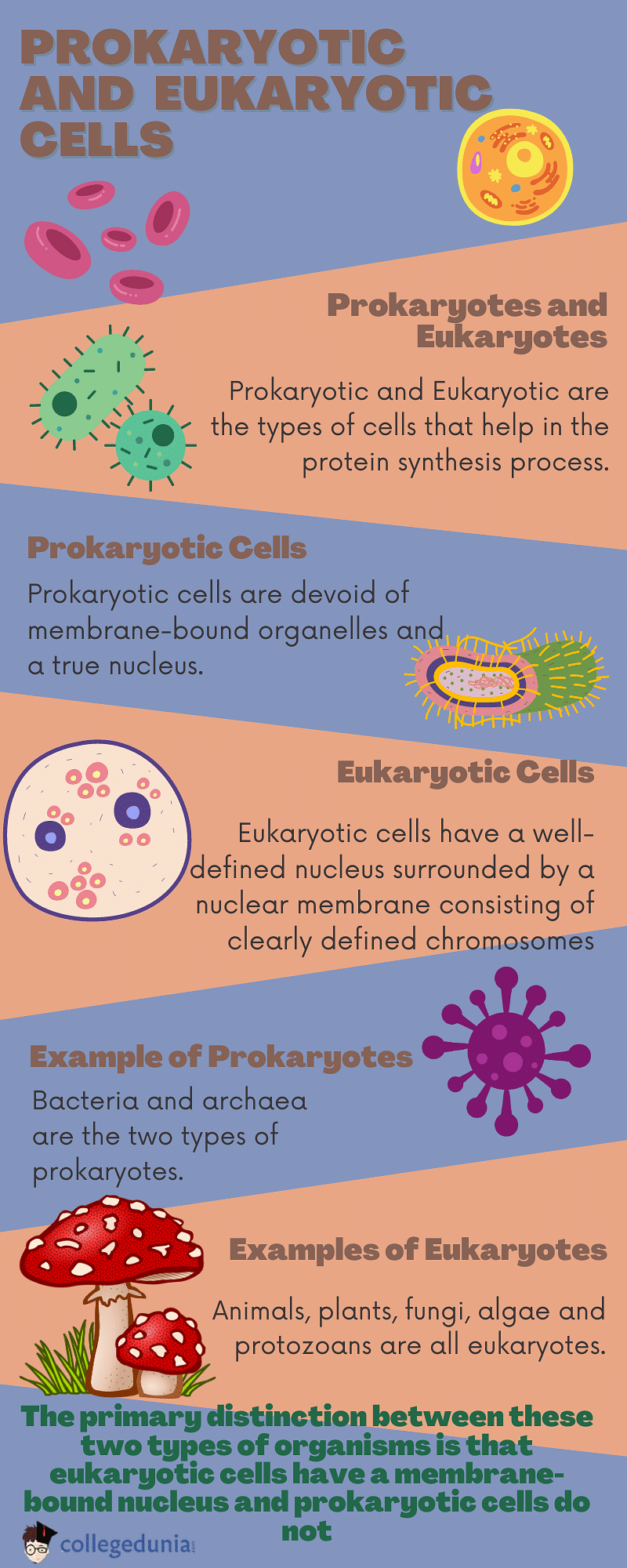
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic are the types of cells that help in the protein synthesis process. Every living organism is composed of one of two groups: eukaryotes or prokaryotes. The cellular structure shows which group an organism belongs to.
- Prokaryotic cells are devoid of membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus.
- Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane consisting of clearly defined chromosomes.
- According to scientists, eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes around 2.7 billion years ago.
- The first form of life was prokaryotes.
Read more: Packaging of DNA
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells, Protein, Protein synthesis process, Membrane, Nucleus, Chromosomes, Nuclear membrane
Read Also: Proteins
What are Prokaryotic Cells?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The term 'prokaryote' is derived from the two Greek words pro (means earlier or before) and Karyon (means kernel). It is simply translated before the nucleus.
- The prokaryotic cells are the most primitive cell which was discovered nearly 3.4 billion years ago.
- These prokaryotic cells are found in ancient environments.
- Some of the cells use chemical energy while some of them use solar energy from the sun.
- It can be specified by their internal structure.
- The prokaryotic cells have no nuclear membrane around them.
- The prokaryotic cells are smaller in size and simple structure.
- The organisms consist of prokaryotic cells termed prokaryotes.
These cells have an absence of a nucleus and the reproduction in the organisms made up of prokaryotic cells is done by the binary fission process. The structure of prokaryotic cells has a capsule-like structure that works as a protective layer for the cell.
Important Components of Prokaryotic Cells
The following are the important components of prokaryotic cells:
- Plasma Membrane - It's an outer layer that covers the cell and separates the cell from the outer environment. It consists of phospholipid molecules.
- Cytoplasm - It is present inside the cell having a jelly-like structure. The cellular components are found in the cytoplasm. It mainly contains salts and enzymes.
- Ribosomes - It is one of the important components of prokaryotic cells where protein synthesis occurs.
- DNA - DNA is the genetic material of the cell circular and directs the protein created by the cells and its functions.
Prokaryotic cells are devoid of nuclear membranes, mitochondria, or Golgi bodies, there are various other components that are a part of the structure which include:
- Nucleoid - The nucleoid is a genetic material present within the cell’s cytoplasm that is generally spherical, rod-like, or spiral-shaped.
- Cell Wall - The wall of the cell is the exterior layer of a cell and provides shape and structure to the cell.
- Capsule - A capsule helps in the protection of the bacterial cells, retaining moisture and attaching themselves to the different surfaces of nutrients.
- Flagella - Flagella refers to the long tail-like structures that help the prokaryotic cells to move from one place to another.
- Pili - They are fine hair-like structures that are in the form of outgrowths that help the cells to attach themselves to other prokaryotic cells.
| Sample Questions Ques. Is the nucleus present in prokaryotes? Ans. The nucleus is not present in prokaryotes. However, prokaryote DNA can be found in a central region called the nucleoid. Prokaryote DNA is usually found as a single chromosome of circular DNA. These organisms do not have other membrane-bound structures such as the endoplasmic reticulum. Ques. Do prokaryotes have mitochondria? Ans. No, prokaryotes do not possess mitochondria. Mitochondria can only be found in eukaryotic cells. |
Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells
The prokaryotic cells have various specific characteristics which are as follows:
- It does not contain a nuclear membrane or nucleus.
- The mitochondria, Golgi bodies, and chloroplasts are not found in prokaryotic cells.
- The genetic material of prokaryotic cells' DNA is circular.
- The prokaryotic cells have a small size and simple structure. The size of cells ranges from 0.5 to 5 micrometers.
- Reproduction is done by the Binary fission process.
Examples of Prokaryotic Cells
The most common examples of prokaryotic cells are bacteria, cytoplasm, blue and green algae, amoeba, onion peel cells, plants, animals, fungi, protozoa, etc.
Also Read:
| Related Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Single Cell Protein | Locomotion and Movement | Gene and DNA |
| Chromosome and Chromatin | Difference between Cilia and Flagella | Differences between Cell Membrane and Plasma Membrane |
What are Eukaryotic Cells
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The term Eukaryotes is derived from the two Greek words EU (means good) and Karyon (means kernel).
- This means the cell has a good nucleus.
- It contains almost all the kingdoms of organisms.
- Eukaryotic cells have larger and more complex structures as compared to prokaryotic cells.
- The cell's nuclear membrane covers the outer surface of the cell called the eukaryotic cell.
- The organisms having a nucleus covered with a nuclear membrane are called eukaryotes.
The eukaryotic cells have a well-organized structure. In these cells, the cytoplasm consists of mitochondria covered with membranes. The eukaryotic cells have sexual and asexual divisions. In the cellular features, eukaryotic cells are a well-organized structure as compared to prokaryotic cells.
Important Components of Eukaryotic Cells
The eukaryotic cells consist of various components. The main components of eukaryotic cells are as follows:
- Plasma membrane - It covers the outer region of the cell and separates the cell structure from the external environment. It is made up of protein contents and exchanges the substances from the cell.
- Cell wall - The cell wall is made from protein, cellulose, and pectins. It is found only in plant cells and absent in animal cells. It works as a protective shield for the cell.
- Nucleus - Nucleus is the main part of the cells where ribosomes are produced. It also contains nucleoplasm having protein and DNA inside it.
- Ribosomes - Ribosomes are found inside the nucleus of cells made up of ribonucleic acid, and protein. The protein synthesis occurs in the ribosome.
- Lysosomes - These consists of hydrologic enzymes that help in the digestion of proteins like nucleic acid, lipids, carbohydrates, etc.
- Mitochondria - It produces energy and maintains the metabolic activities of the cell. It is called the powerhouse of the cell.
- Cytoskeleton - It is located inside the cytoplasm of the cell. It consists of fibers, microtubes, etc. which lend to shape the cell and are responsible for the movement of the cell.
- Golgi bodies - It is situated close to the nucleus of the cell. These are not found in plant sieve cells and human RBCs. It is disc-shaped and plainly structured.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum - It is a network of structures having small and tubular shapes. It is commonly two types - smooth and rough.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells
The eukaryotic cells have following characteristics mentioned below -
- The nucleus of eukaryotic cells is covered with the nuclear membrane.
- The cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells.
- These cells are split in parts through the mitosis process.
- It comprises a cytoskeleton structure.
- Mitochondria is found in each eukaryotic cell.
- The genetic material found inside the nucleus consists of single and linear-form DNA.
| Sample Questions: Ques. What are the features that every cell has? Ans. All cells, whether prokaryotic or eukaryotic, share these four features:
|
Read Also: Excretion in Plants
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Given below are the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
| Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|
| It does not contain the nuclear membrane-bound. | It contains the nuclear membrane bounded by the nucleus. |
| It is very small in size and has a simple structure. | It is comparatively larger and has a complex structure. |
| It is a unicellular organism. | It is a multicellular organism. |
| The growth of prokaryotic cells is faster. | The growth of eukaryotic cells is slow. |
| Only a single chromosome is present. | More than one chromosome is present. |
| Cell division in prokaryotic cells is done by fission. | Cell division in eukaryotic cells is done by the mitosis process. |
| The nucleolus is not found in these cells. | The nucleolus is present in these cells. |
| It has a complex cell wall, present in all prokaryotic cells. | It has a simple cell wall and is present only in plants and fungi. |
| It has small ribosomes. | It has comparatively large ribosomes. |
| The cytoplasm is present. | The cytoplasm in these cells is also present. |
| Examples - amoeba, blue and green algae, bacteria, and archaea. | Examples - plants, animals, fungi, and protist cells. |
Also Read:
| Related Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| What is Tissue? | Protoplasm | Cell Biology |
| Discovery of Cells | Transportation in Animals and Plants | Energy Currency of the Cell |
Points to Remember
- Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that do not have membrane-bound structures.
- Prokaryotic cells help in nutrient recycling by the decomposition of dead organisms and re-using their nutrients.
- They help in a varied number of metabolic processes.
- Eukaryotes are organisms that have a nucleus and other organelles enclosed by a plasma membrane.
- The cell’s DNA is situated in the nucleus among the eukaryotic organelles.
- Two other important organelles are the chloroplasts and mitochondria.
- The eukaryotic cells help in keeping the disease causing organisms at bay.
Previous Year Questions
- The movement of cilia and flagella is due to the presence of...[JKCET 2013]
- Plasma membrane helps in :...[JKCET 2005]
- Which of the following structure is bounded by single membrane?...[JKCET 2005]
- 70 S ribosomes occur in….[AMUEEE 2014]
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum is actively involved in...[JKCET 2014]
- Perinuclear space is present in...[JKCET 2014]
- Chloroplast lacks….[COMEDK UGET 2005]
- Colour of flower petals is due to...[CUCET 2012]
- Streaming of the cytoplasms within some living cell is known as...[CUCET 2011]
- Example of an oxidative organelle is...[CUCET 2011]
- Lampbrush chromosomes are...[COMEDK UGET 2005]
- Cisternae have a diameter of...[JKCET 2014]
- Cells divide and new cells are formed from pre-existing cells. This concept was given by..[AMUEEE 2010]
- Aleuroplasts in a cell stores...[AMUEEE 2010]
- Axoneme having 9 + 2 doublet microtubule arrangement is found in...[AMUEEE 2009]
- One of the chief functions of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is..[AMUEEE 2009]
- Cilia are :...[JKCET 2004]
- Which is not properly paired?..[JKCET 2004]
- What is true about fluid mosaic model?...[JKCET 2004]
- Besides proteins ribosomes contain :...[JKCET 2004]
Sample Questions
Ques 1. Define prokaryotic cells with examples? (1 mark)
Ans. The prokaryotic cells are the most ancient discovered cells in which the nucleus is not found. It is unicellular. It is a simple and small cell. Algae, amoeba, and bacteria are examples of prokaryotic cells.
Ques 2. Define eukaryotic cells with examples? (1 mark)
Ans. These cells have a well-organized nucleus and nuclear membrane-bounded it. They can be unicellular and multicellular. It is comparatively large and complexly structured. Plants, animals, and fungi are examples of eukaryotic cells.
Ques 3. Cell division in prokaryotic cells are done by which process: (1 mark)
(a) Fission
(b) Mitosis
(c) Reproduction
(d) Enzyme secretion
Ans. a. The cell division in prokaryotic cells is done by the fission process.
Ques 4. The cell division in eukaryotic cells is done by what? (1 mark)
Ans. The cell division in eukaryotic cells is done by the mitosis process.
Ques 5. What is the function of ribosomes? (1 mark)
Ans. The ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in the cell.
Ques 6. Which of the following is called the powerhouse of the cell? (1 mark)
(a) Nucleus
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Mitochondria
Ans. d. Mitochondria produces energy and is responsible for the metabolic processes of the cell. It is also called the powerhouse of the cell.
Ques 7. Which of the following have circular DNA? (1 mark)
Ans. The genetic material DNA in prokaryotic cells has a circular shape.
Ques 8. Which part of the cell protects it from the outer environment? (1 mark)
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Endoplasmic reticulum
(c) plasma membrane
(d) Lysosomes
Ans. c. In the cell the plasma membrane protects the body of the cell from the outer environment. It acts as a protective shield of the cell.
Ques 9. Give 5 differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. (5 marks)
Ans. Differences are:
| Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|
| It does not contain the nuclear membrane-bound. | It contains the nuclear membrane bounded by the nucleus. |
| It is very small in size and has a simple structure. | It is comparatively larger and has a complex structure. |
| It is a unicellular organism. | It is a multicellular organism. |
| The growth of prokaryotic cells is faster. | The growth of eukaryotic cells is slow. |
| Only a single chromosome is present. | More than one chromosome is present. |
Also Check:




Comments