Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Difference between Mitochondria and Chloroplast is based on Presence, Size, Shape, Colour, Membrane, and various other parameters. The double-layered cell organelles present in a eukaryotic cell are nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast. Mitochondria is found both in animal and in plant cells, whereas chloroplast is found only in plant cells. Mitochondria are responsible for generating energy for the cell in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). On the other hand, chloroplasts perform Photosynthesis in a plant cell.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms:- Cell, Mitochondria, cell organelles, membrane, Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), muscle cells.
Also Read:- Vegetative Propagation in Plants
What are Mitochondria?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Mitochondria are small cell organelles which float throughout the cell. They are also referred to as the Powerhouse of the Cell, and are thus found in thousands in muscle cells, as muscles require a lot of energy.
Mitochondria are usually rod-shaped or sausage-shaped, and are double-membraned structures made of an outer membrane which surrounds the organelle, and an inner membrane which contains many finger-like folds called Cristae.
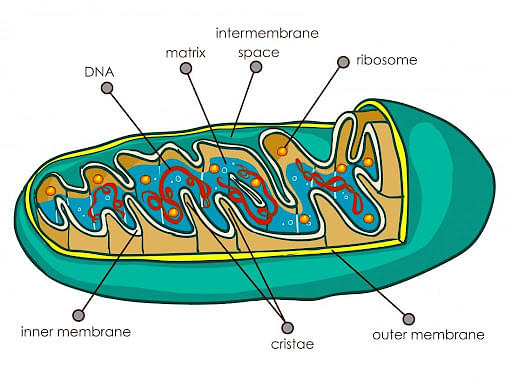
Diagram of Mitochondria
Mitochondria have their own DNA and ribosomes, different from the rest of the cell. Besides generating energy, they also generate heat, store calcium for cell signaling activities, enable cellular differentiation, and promote cell growth.
Also Read:- Energy Currency of the Cell
Parts of Mitochondria
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
A mitochondrion has four main compartments:
- An outer membrane, which is permeable to certain ions and small molecules.
- An intermembrane space, which has a composition similar to cytosol.
- An inner membrane, which has respiratory chain proteins. It is folded into multiple cristae allowing larger space to hold proteins involved in electron transport chains.
- A matrix which forms the inner part of the mitochondrion, and is the site for metabolic reactions.
Given below is a well- labeled diagram of a mitochondria to help in better understanding of its structure.

Structure of Mitochondria
Also Read:- Unicellular Organisms
What are Chloroplasts?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Besides plant cells, chloroplasts are also found in algae. They are located in the cytosol of a cell, and contain chlorophyll to absorb solar energy. They primarily work as the site for photosynthesis, by absorbing light energy and converting it into chemical energy.
Chloroplasts are plate-shaped in Chlorella, cup-shaped in Chlamydomonas, and spherical or ovoid in higher plants. Like mitochondria, they also have their own DNA and reproduce independently from the rest of the cell.
Chloroplasts are also double-layered cell organelles. They consist of thylakoids, which are the site of light-dependent reactions, and a matrix called stroma, which is the site for light-independent reactions. The thylakoids are arranged in stacks known as grana. The chloroplasts are involved in energy metabolism.

Diagram of Chloroplast
Parts of Chloroplasts
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
A chloroplast consists of the following main parts:
- An semi-porous outer membrane, which is permeable to small molecules and ions, and impermeable to large proteins.
- An intermembrane space.
- An inner membrane, which regulates the passage of materials in and out of the chloroplast.
- An aqueous, protein-rich, alkaline fluid called stroma, which is present within the inner membrane. It has the chloroplast DNA, chloroplast ribosomes, starch ribosomes, thylakoid system and many proteins.
- A collection of membranous sacs called thylakoids, which is suspended in the stroma. It stores the chlorophyll and is thus the site for the light reactions of photosynthesis.
Given below is a well-labeled diagram of a chloroplast to help in better understanding of its structure.
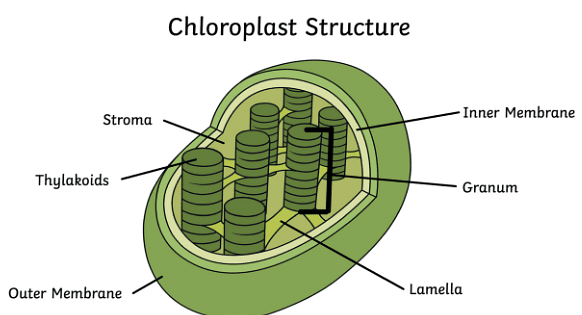
Chloroplast Structure
Also Read:- Transportation in Animals and Plants
Difference Between Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Here are some of the key differences between Mitochondria and Chloroplasts:
| Point of Difference | Mitochondria | Chloroplast |
|---|---|---|
| Presence | All types of aerobic organisms, plants and animals. | Only in exposed cells of green plants and some green algae. |
| Size | Smaller than a chloroplast- 0.5-10µm. | Generally large and more complex than mitochondria. Average diameter is 4-6µm. |
| Shape | Generally cylindrical in outline. | Disc- shaped |
| Colour | Colourless | Green in colour |
| Pigments present | No pigments present. | Various pigments like chlorophyll, carotenoids, and other photosynthetic pigments are present. |
| Membrane | The inner membrane is folded into finger-like structures like cristae. | The inner membrane forms flattened sacs called thylakoids. |
| Chambers | Consists of two chambers- matrix and cristae. | Consists of two chambers- thylakoids and stroma. |
| Main function | Energy metabolism and cellular respiration; also known as the powerhouse of the cell. | The site for photosynthesis in plants. |
Also Read:
Things to Remember
- Mitochondria release energy by breaking down organic food, producing carbon dioxide and water.
- Chloroplasts store energy and use carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose.
- Mitochondria occupy almost 25% of the cell volume. They form a dynamic connected network also called a reticulum.
- Both outer and inner membranes of the mitochondria are made up of phospholipid layers just like the cell’s outer membrane.
- Besides photosynthesis, chloroplasts also carry out functions like the synthesis of fatty acids, amino acids, and membrane lipids.
Also read: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Previous Years Questions
- A major site for synthesis of lipids is….[NEET 2013]
- which one of the following colours of light so as to….[NEET 2005]
- According to fluid mosaic model, plasma membrane is….[NEET 1998]
- Acetabularia used in Hammerling's nucleocytoplasmic...[NEET 1988]
- All types of plastids possess essentially….[NEET 1992]
- An outer covering membrane is absent over….[NEET 1992]
- Balbiani rings are the sites of...[NEET 1993]
- the Golgi apparatus is also concerned with the...[NEET 1994]
- Biological organisation starts with….[NEET 2007]
- A bivalent consists of...[NEET 1989]
- A cell organelle containing hydrolytic enzymes is...[NEET 2016]
- Water soluble pigments found in plant cell vacuoles….[NEET 2016]
- Which of the following are not membrane - bound?….[NEET 2015]
- Electron microscope has a high resolution power…. [NEET 1990]
- Flagella of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells….[NEET 2004]
- Bacterial inclusions are generally covered by….
- Prochromosome is….
- Pili occur in…
- Cellulose of cell wall is synthesised by synthetase enzyme located over….
- Cell wall layer lacking cellulose and containing xylans is..
Sample Questions
Ques. Where does the Krebs cycle take place in the mitochondria? (1 Mark)
Ans. The mitochondrion is a double-membraned organelle responsible for generating ATP for the cell. The Krebs cycle is the middle step of cellular respiration, and takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
Ques. What cell contains the most chloroplasts? (1 Mark)
Ans. Palisade cells contain the largest number of chloroplasts per cell, which makes them the primary site of photosynthesis in the leaves of those plants that contain them, converting the energy in light to the chemical energy of carbohydrates.
Ques. How do mitochondria and chloroplasts work together? (2 Marks)
Ans. Chloroplasts are responsible for converting sunlight into food for plants by a process known as photosynthesis. On the other hand, mitochondria convert this food into energy in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). Chemical reactions taking place in the cell, allowing the release of energy from food.
Ques. What are the similarities between mitochondria and chloroplasts? (2 Marks)
Ans. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are both found in plant cells, however in animal cells, chloroplasts are absent. Both cell organelles are responsible for generating energy for the cells. They are similar structure-wise as well, in the sense that both the organelles comprise outer and inner membranes.
Ques. What is the primary purpose of cristae in the mitochondria? (2 Marks)
Ans. The importance of the cristae comes from the fact that they greatly increase the surface area of the inner membrane of the mitochondria. This is important because this membrane houses the electron transport chain proteins. A larger surface area allows reactions to occur at a higher rate and, thus, more ATP can be generated. The cristae are not essential to protecting the mitochondrial genome or maintaining shape.
Ques. Where do the light reactions take place in the chloroplast? (2 Marks)
Ans. The chloroplast has a very similar structure to the mitochondrion, as it is a double-membraned organelle. The chloroplast is used to house the processes of photosynthesis. The light reactions take place in the thylakoid membrane, while the light independent reactions take place in the stroma.
Ques. Are chloroplasts found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? (2 Marks)
Ans. Mitochondria and chloroplast are two organelles that have been found in eukaryotic cells. Chloroplast is found only in plants, while most eukaryotic cells have mitochondria. Although both organelles are found in eukaryotic cells, both mitochondria and chloroplast are often found in prokaryotic cells.
Ques. What is a mesosome in a prokaryotic cell? Mention the functions that it performs. (3 Marks)
Ans. Mesosome is a membranous structure in a prokaryotic cell, which is formed by the extensions of the plasma membrane into the cell in the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae.
Mesosomes are equal to mitochondria in eukaryotes, as they perform aerobic cellular respiration in prokaryotes. It helps in DNA replication and distribution of genetic material to daughter cells. Mesosomes also help in respiration, increase the surface area of the plasma membrane and enzymatic content and cell wall formation.
Ques. Why are Mitochondria and chloroplast regarded as endosymbionts? (3 Marks)
Ans. According to the endosymbiosis theory which explains the origins of organelles into the eukaryotic cells, mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from endosymbiotic bacteria. Heterotrophic prokaryotes were engulfed which functioned as mitochondria.
Photosynthetic prokaryotes were engulfed, which functioned as chloroplasts. Both mitochondria and chloroplast can work independently because of the presence of their own genetic materials. Thus, mitochondria and chloroplast are called endosymbionts as they both possess their own nucleic acids.
Ques. Name two cell-organelles that are double membrane bound. What are the characteristics of these two organelles? State their functions and draw labelled diagrams of both? (5 Marks)
Ans. Mitochondria and chloroplast are double membrane bound organelles. Mitochondria: Mitochondria are cylindrical or sausage shaped cell organelles and contain two membranes, outer and inner.
The inner compartment is called the matrix containing DNA, RNA, ribosomes, enzymes of Krebs cycle etc and outer membrane forms the continuous limiting boundary of the organelle. Inner membrane forms a number of infoldings called the cristae which increases the surface area. Oxysomes are present on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Mitochondria are semiautonomous organelles, i.e., have their own DNA and ribosomes.

A Mitochondrion in Section
Functions of mitochondria:
- Mitochondria are essential for aerobic respiration.
- Mitochondria provide intermediates for synthesis of important biomolecules such as chlorophyll, cytochrome, steroids etc.
- Mitochondria regulate the calcium ion concentration in the cell.
- Mitochondrial matrix contains enzymes for the synthesis of fatty acids.
- Synthesis of many amino acids takes place here
Chloroplast: They are green coloured plastids which are disc shaped. The space limited by the inner membrane of chloroplast is called stroma. Stroma has organised flattened membranous sacs called the thylakoids. Thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana. Matrix of a chloroplast contains DNA, RNA, ribosomes and enzymes. Chloroplast is also a semi autonomous organelle.

RD Structure of a Chloroplast
Functions of chloroplast:
- Photosynthesis is performed by chloroplast.
- Chloroplast stores starch grains.
- Maintains balance of CO2 concentration in the air.
- Keeps oxygen balance constant in the atmosphere by liberating O2 into the atmosphere, used during respiration and combustion.
Also Check:




Comments