Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Cytoplasm makes about 70% of the cell's content. It's made up of water and structural filaments. The cytoplasm, nucleus, and nucleoplasm together make up protoplasm. Protoplasm is made up of all the organelles floating in the cytoplasm, as well as the nucleus. Cytoplasm protects the genetic material of a cell by acting as a buffer while protoplasm is responsible for giving an organism a form. In this article, we will have a look at the difference between cytoplasm and protoplasm.
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms:- Cell Organelles, Cytoplasm, Nucleus, mitochondria, protoplasm.
What is Cytoplasm?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The viscous liquid that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane is known as cytoplasm. The bulk of it is made up of water, minerals, and Proteins. The cytoplasm in the cells of the eukaryotes comprises all of the material within and outside of the nucleus. All of the organelles present in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria, are located in the cytoplasm.

The cytosol is the portion of the cytoplasm outside of the organelles. Despite its appearance of being devoid of structure or order, the cytoplasm is actually extremely organized. The Cytoskeleton is a network of protein scaffolding that provides structure to the cytoplasm and the cell.
Also Read:
Functions of Cytoplasm
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
- Mitochondria are essential for cellular respiration.
- The cytoplasm is where glycolysis and cell division take place.
- The cytoplasm is in charge of maintaining the cell's components together and protecting them from harm.
- The cytoplasm is responsible for the cell's shape.
- Various substances are found in the cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasm supports processes such as cellular respiration for breathing and protein synthesis.
- It aids cell division during mitosis and meiosis.
- It aids in the movement of objects throughout the cell through a process known as cytoplasmic streaming.
- The cytoplasm contains several salts that allow it to conduct electricity.
- It protects the cell's genetic material by acting as a buffer.
Also Read: Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
What is Protoplasm?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The live component of the cell, protoplasm, is made up of several cellular organelles. Within the cell wall, it is a jelly-like, colorless, transparent, and viscous living material. The word protoplasm was coined in 1835, and it is recognized as the main component since it is involved in all life activities. Cells were once thought to be protoplasm-containers. The idea, on the other hand, was unable to explain the origins of structures generated within the cell, particularly the nucleus.

Functions of Protoplasm
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
- Protoplasm gives the organism form since it is a transparent, viscid, and fluid material.
- Protoplasm reacts to stimuli and aids in the elimination of excretory waste.
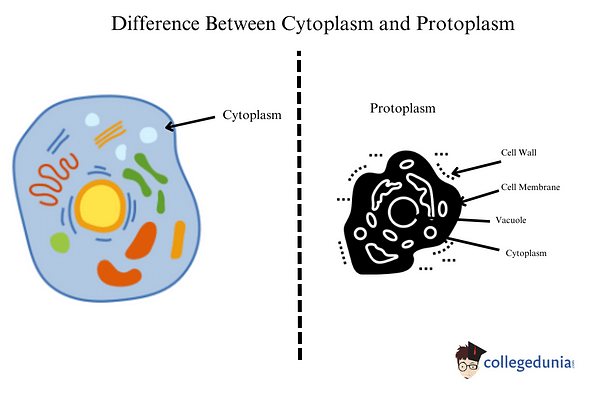
Difference between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are various differences between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm. Some of them are:
| Parameters on which the difference is made | Cytoplasm | Protoplasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The cytoplasm is made up of all of the biological components of the cell that are encased by the plasma cell membrane, except the nucleoplasm. | The biological component of an animal cell is encircled by a plasma cell membrane, which is known as protoplasm. |
| Nucleus | The nucleus is not included. | The nucleus is included. |
| Constituents | The cytoplasm is made up of inclusions, cytosol, and organelles, among other things. | Protoplasm is made up of Amino Acids, water, ions, monosaccharides, and other micro molecules, as well as proteins, polysaccharides, Lipids, and nucleic acids, which are macromolecules. |
| Correlation | The cytoplasm is one of the parts of the protoplasm. | The protoplasm includes cytoplasm. |
| Forms | It has been discovered to exist in the forms of sol-gel, glass, and occasionally unusual shapes. | It has been discovered to exist in two forms: a jelly-like gel form and a liquefied sol-shaped form. |
| Structure | With the exception of the nucleoplasm, its structure consists of mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and so on. | Cytoplasm and nucleoplasm combine to form the structure of protoplasm. |
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
- Cytoplasm and protoplasm, both words are distinct yet are frequently used interchangeably, despite the fact that they have separate meanings.
- Mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum make up the cytoplasm.
- Protoplasm, on the other hand, is made up of a nucleus and cytoplasm.
- Nucleoplasm is not included in the cytoplasm, although it is a component of protoplasm.
- In the cytoplasm, it must exist in the form of sol-gel, glass, or other unusual forms.
- The protoplasm, on the other hand, is formed like a jelly-like gel or a liquefied sol.
Also Read:
| Related Topics To The fundamental unit of life | ||
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Engineering | Denitrification | Inclusion Bodies |
| Discovery of Cells | Endomembrane system | Gene Regulation |
| Packaging of DNA | DNA Polymerases | Euchromatin and Heterochromatin |
Previous Year Questions
- A bivalent consists of… (NEET 1989)
- A cell organelle containing hydrolytic enzymes is... (NEET 2016)
- Water soluble pigments found in plant cell vacuoles are... (NEET 2016)
- Which of the following are not membrane - bound?... (NEET 2015)
- Which one of the following is not an inclusion body found in prokaryotes?... (NEET 2015)
- Flagella of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in... (NEET 2004)
- A major site for synthesis of lipids is... (NEET 2013)
- According to fluid mosaic model, plasma membrane is composed of...(NEET 1988)
- Acetabularia used in Hammerling's nucleocytoplasmic experiments is...(NEET 1988)
- Active and passive transports across cell membrane differ in...(NEET 1993)
- All types of plastids possess essentially the same structure because they...(NEET 1992)
- An outer covering membrane is absent over...(NEET 1992)
- Balbiani rings are the sites of...(NEET 1993)
- Besides giving out secretory vesicles, the Golgi apparatus is also concerned with the formation of...(NEET 1994)
- Biological organisation starts with... (NEET 2007)
- Cell recognition and adhesion occur due to biochemicals of cell membranes named...(NEET 1993)
- Cell wall shows...(NEET 1991)
- Cellular organelles with membranes are...(NEET 2015)
- Cellular totipotency is demonstrated by...(NEET 2003)
- Chlorophyll in chloroplast is located in...(NEET 2005)
Sample Questions
Ques. What would happen to the cell which does not have cytoplasm? (2 marks)
Ans. A cell would lose its form if it doesn’t have cytoplasm, which implies it would be deflated and flat. Without the help of Cytoplasm, organelles would sink to the bottom of a cell's solution.
Ques. What are the parts of a cytoplasm? (2 marks)
Ans. There are two primary sections or components of the cytoplasm: Endoplasm and Ectoplasm. The endoplasm, which contains organelles, is found in the cytoplasm's core region. Ectoplasm is a gel-like material found on the cytoplasm's outer surface.
Ques. How is the cytoplasm of one cell connected with the others? (2 marks)
Ans. A nonliving cell wall surrounds a Plant Cell. In plants, plasmodesmata form cell-to-cell connections. The cell wall comprises cytoplasmic bridges, that aid in connecting the neighboring cells, which are known as plasmodesmata. A plasmodesmata is a small cytoplasmic channel bordered by a plasma membrane and typically including a desmotubule endoplasmic reticulum tubule.
Ques. Is cytoplasm present in both plant and animal cells? (1 mark)
Ans. A nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and cell membrane are all present in both animal and plant cells. Additional components found in plant cells include a vacuole, chloroplast, and cell wall.
Ques. What is Cyclosis? (5 marks)
Ans. Cyclosis, also known as cytoplasmic streaming, is the movement of chemicals within a cell. Cyclosis can be seen in a variety of cells, including amoeba, plant cells, fungi, and protozoa.
Temperature, light, hormones, and chemicals are all factors that influence streaming movement. The activity of microfilm is cyclosis. Within the cytoplasm, motor proteins can move organelles and molecules. The goal of cyclosis is to allow materials, such as oxygen and nutrients, to reach all sections of a cell. Large plant and animal cells exhibit cyclosis. Cytoplasmic streaming happens along the actin in one direction. Chloroplasts can move about in cytoplasmic streaming to improve light absorption for photosynthesis.
Do Check Out:





Comments