Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Candela is the SI Unit of luminous intensity - a measure of wavelength weighted power emitted by a source light. Light is measured in a number of ways even though light is not a physical quantity. However, light has various physical properties like speed, wavelength etc. that can be measured in terms of various units such as candela, lux and lumen. The candela is said to have replaced the standard candle or lamp as a unit of luminous intensity in calculations and derivations involving artificial light.
| Table of Contents |
Key words: Candela, Unit of measurement, Unit of Light, Luminous intensity, SI Unit
Definition of Candela
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
In the field of physics, the Candela, denoted by the symbol ‘cd/m2’, can be defined as the unit of luminous intensity i.e. a measure of the wavelength weighted power emitted by a source of light. According to the International System of Units, popularly known as SI, the candela is a base unit that can be defined by taking the fixed value in numerical terms of the luminous efficacy of the monochromatic radiation having a frequency of 540 x 1012 Hertz.
One candela is mathematically expressed as: 1 cd = (Kcd/ 683) Kgm2s-3sr-1
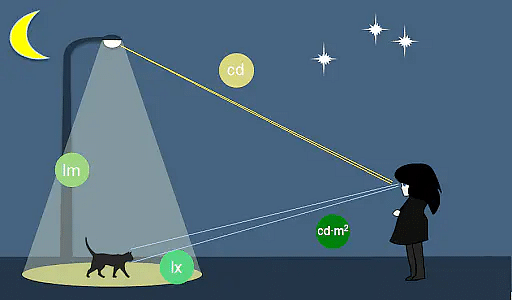
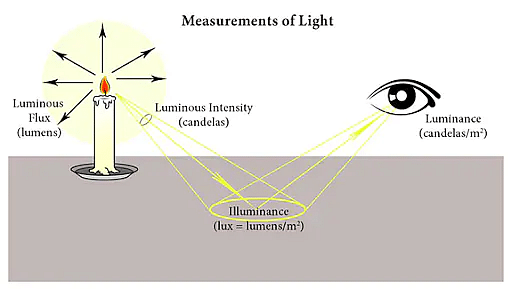
The unit is dependent on luminous intensity and radiant intensity for a given wavelength of light. Luminance is measured in lux, which is defined as one candela per square meter.
Learn More About:
| Important Concepts Related to this Topic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Unit of Light | System of Units | SI Units |
Origin of Candela
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Candela originates from the latin word that translates to “candle” that refers to an ancient light source. In olden times, Candlepower was used to define luminous intensity depending on the candle.
The candela was first defined by French Physicist and inventor, Jules Violle. In 2018, the 26th general conference introduced candela as the official unit of measurement of luminous intensity.
Other Measures of Light
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The two other main measures of light are: Lumen and Lux.
- Lumen is the SI unit of luminous flux, which refers to the rate at which the visible light is emitted from a source. The lumen, in relation to the candela, is defined as:
1lm= 1cd . sr
Where, lm = lumen
Cd = candela
Sr = steradian
- Lux is the SI unit of illuminance and luminous emittance. Lux is related to lumen in a way that one lux is equivalent to lumen per square meter and is given by:
1 lx= 1 lm/m2 = 1 cd.sr/m2
Things to Remember
- Candela is the SI unit of luminous intensity.
- Candela is denoted by ‘cd/m²’.
- It is the luminous power per unit solid angle emitted by a point light source in a specified direction.
- Luminous intensity is comparable to radiant intensity.
- Candela has originated from a Latin word which means “candle”.
- It is mathematically expressed as 1 cd = (Kcd/ 683) Kgm2s-3sr-1.
Do Check Out:
| Important Concepts Related to this Topic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Measurements of Length | Unit of Sound | Precision of a measurement |
| The International System of Units | Unit of Resistance | Uncertainty in Measurement |
| Unit Conversion | Unit of Force | Unit of Time |
Previous Year's Questions
|
Sample Questions
Ques: What is the origin of Candela? (3 marks)
Ans: Candela was first defined by French Physicist and inventor, Jules Violle. Candela originates from the latin word that translates to “candle” that refers to an ancient light source. In 2018, the 26th general conference introduced candela as the official unit of measurement of luminous intensity.
Ques: Define Candela. (2 marks)
Ans: Candela is the SI unit of luminous intensity. It is the luminous power per unit solid angle emitted by a point light source in a specified direction. It is represented as cd/m2.
Ques What is the basic unit of light? (2 marks)
Ans: The behavior of light can be seen in the behavior of waves and photons, the basic unit of light. A wavelength, which varies inversely with frequency, manifests itself as color, whilst wave amplitude is seen as luminous intensity or brightness; it is measured by the standard unit of a candela.
Ques: How accurate is the measurement of Candela? (3 marks)
Ans: Candela is a SI unit that mostly depends on human perception, hence its accuracy is not that high. The measurement laboratory is trying to reduce this uncertainty in luminous intensity management. It is estimated that the accuracy of a candela is less than 0.1%. However, it is important to improve this percentage as a SI unit should have high accuracy due to its many industrial applications.
Ques: How to increase the accuracy of Candela? (3 marks)
Ans: The national measurement laboratory, NIST is finding ways to improve the accuracy of candela. It has listed a number of ways such as developing a pulsed laser that can be tuned to particular wavelengths of light, which will further allow the creation of photometers that mimic the human vision mechanism.
Read More:






Comments