Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
Adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which there is no heat transfer in or out of the system. It is such a sudden process that there is no time for a significant heat transfer to take place. Naturally occurring adiabatic processes are irreversible in nature. Adiabatic Process is a key concept of thermodynamics that supports the theory that explains the first law of thermodynamics.
Adiabatic Process is an ideal process with no heat transfer in which the change in internal energy is equal to the work done. In an adiabatic process, no heat is gained or lost by the system. The first law of thermodynamics (Q = 0) demonstrated that all change in internal energy is in the form of work done.
Key Terms:- Heat Transfer, Adiabatic processes, exchange of heat, ideal gas equation, a mole of gas, pressure.
What is Adiabatic Process?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which there is no exchange of heat from the system to its surroundings neither during expansion nor during contraction.
- A rapid expansion or contraction of gas is nearly adiabatic in nature.
- The adiabatic processes are either reversible or irreversible.
- Any process that occurs within a container that is a good thermal insulator is called an adiabatic process.
For example, gas compression in an engine cylinder is expected to happen so fast that a minimum amount of system energy can be produced and sent out in the form of heat. The process is regarded as an adiabatic process even though the cylinders are not insulated and have a conductive nature.
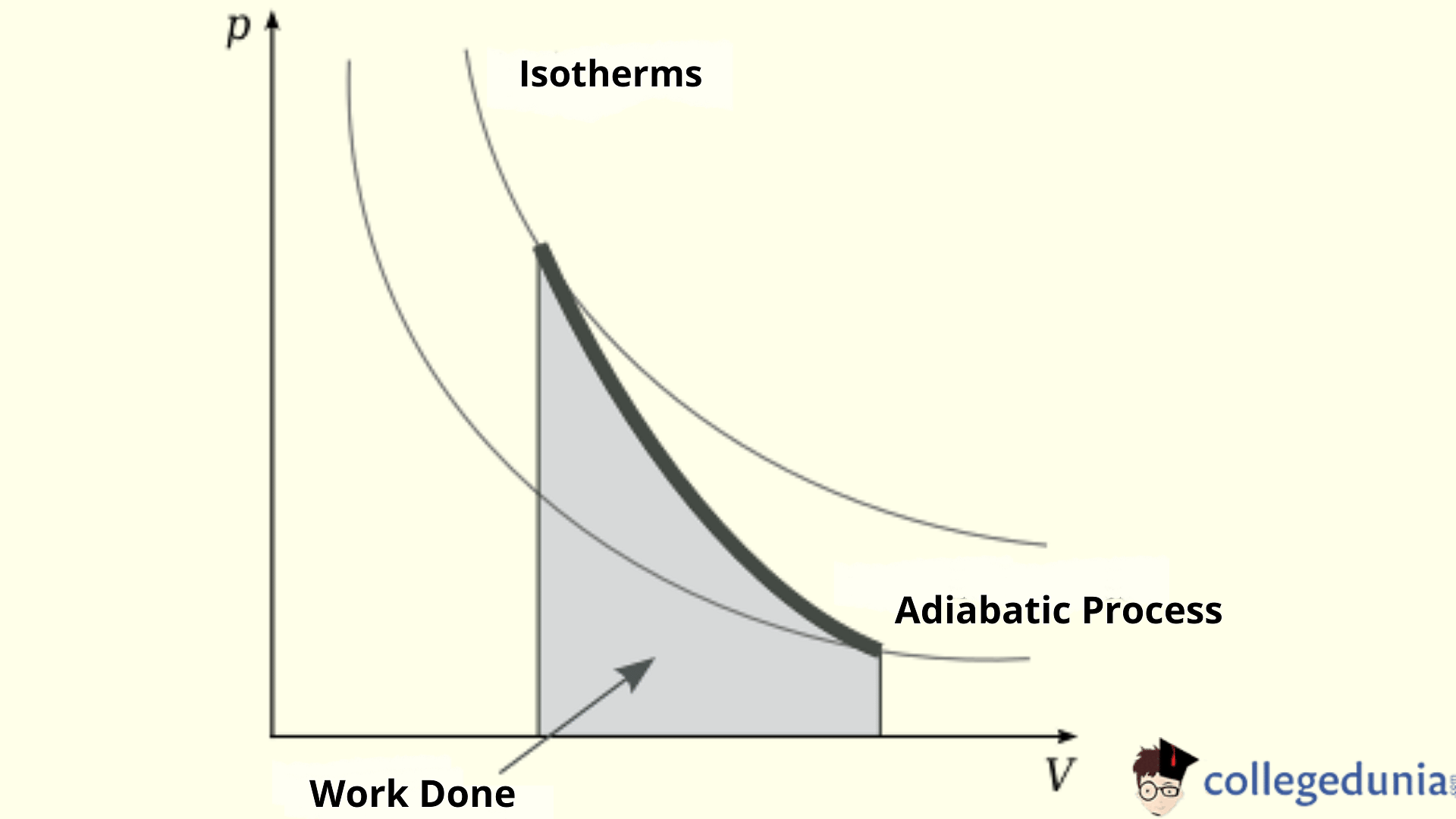
Conditions for Adiabatic Process
For an adiabatic process to take place, the following conditions must be met:
- The system should be perfectly insulated from its surroundings.
- The process should be carried out quickly to leave sufficient time for the heat transfer to take place.
| Concepts Related to Adiabatic Process | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reversible and Irreversible Processes | Zeroth law of Thermodynamics | Second law of thermodynamics |
| Carnot engine | Efficiency Formula | Heat engines |
Adiabatic Process Equation
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The adiabatic process equation is given as:
PVϒ = Constant
- Where P is the pressure of the system
- V is the volume of the system
- ϒ is the adiabatic index, ϒ = CP/CV
- Cp is the heat capacity at constant pressure
- Cv is the heat capacity at a constant volume
Adiabatic relation between P and T
The ideal gas equation for 1 mol is given by PV=RT
∴ V = RT/P
Putting this value in the adiabatic process equation PV1-ϒ =constant
P(RT/P)ϒ=constant
∴ P(1-ϒ )*Tϒ= Constant (As T = nRT/P)
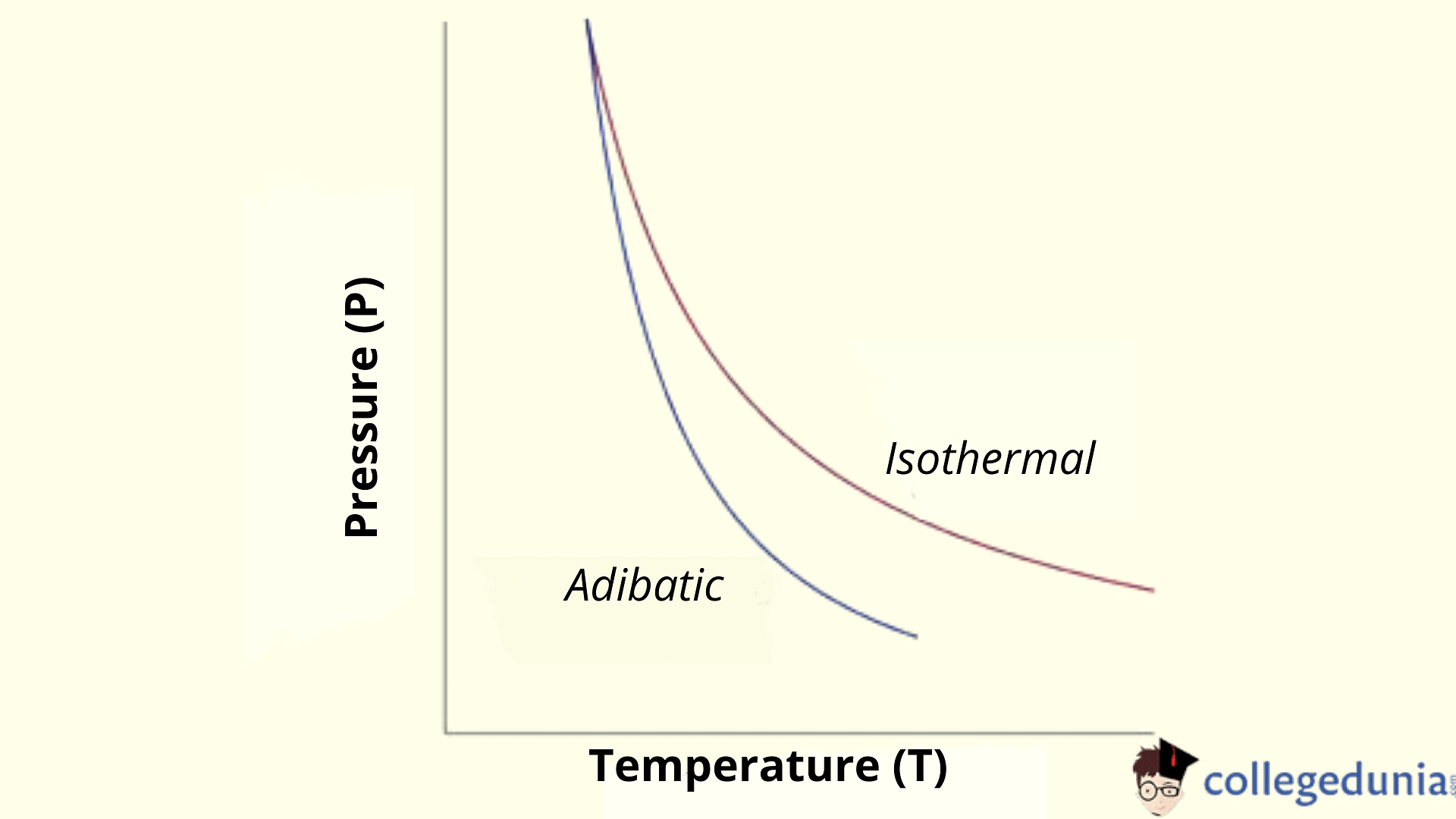
Adiabatic Relation between P and T
Adiabatic relation between V and T
For one mole of gas, the ideal gas equation is given by: PV = RT
∴ P = RT/V
Putting this value in the adiabatic process equation PV = constant.
(RT/V)*Vϒ = Constant
TV (1-ϒ) = Constant
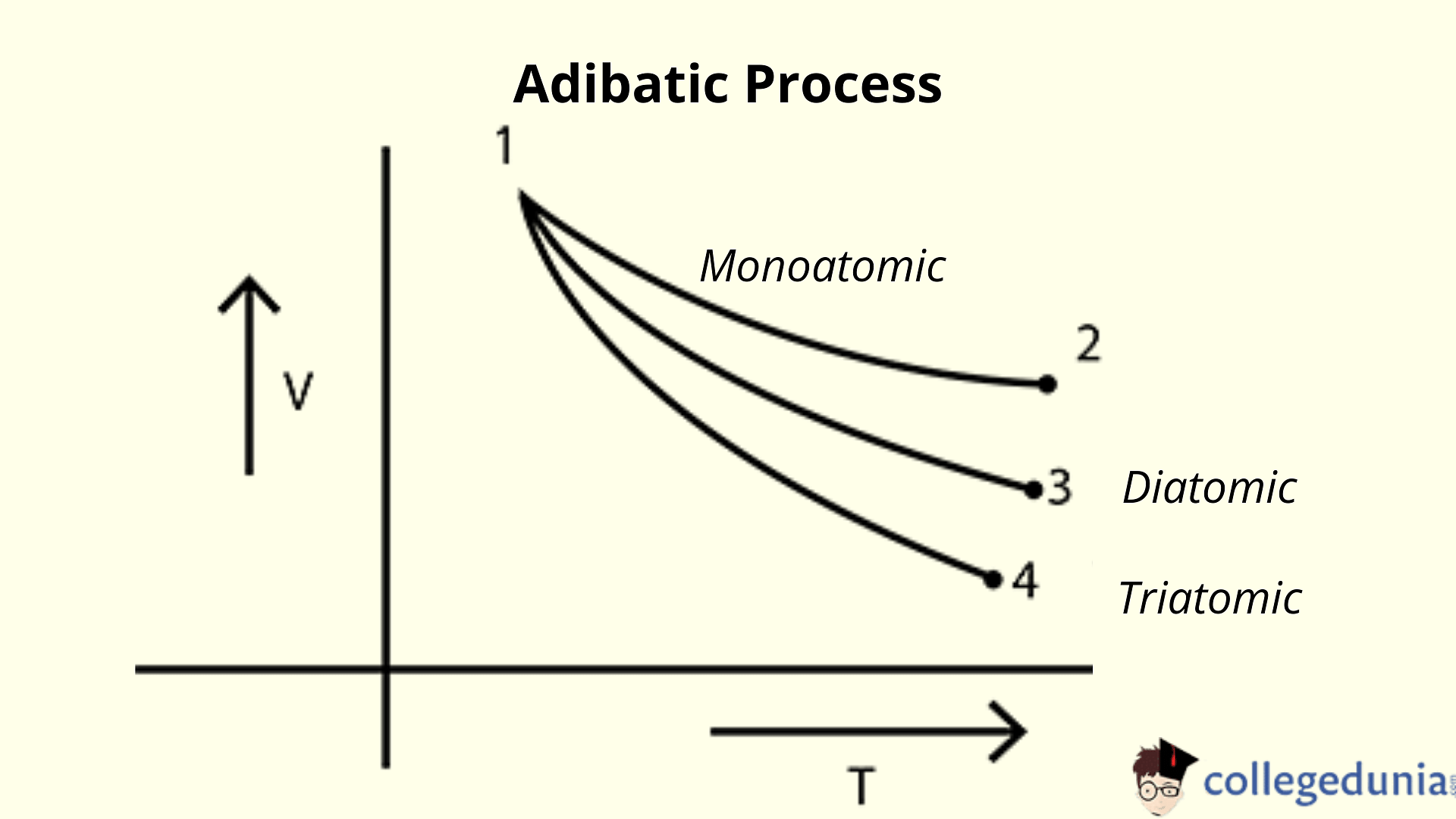
V-T graph for adiabatic process
Adiabatic Compression
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Adiabatic compression is a process during which no heat is gained or lost from the air and therefore the internal energy of the air is increased.
- In this process, pressure increases more quickly than the decrease in volume due to an increase in temperature.
- During this process, energy is transferred only by work.
Adiabatic Expansion
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Adiabatic expansion is an adiabatic process in which an external work acts upon a system by utilizing the internal energy of gas which in turn results in lowering the temperature.
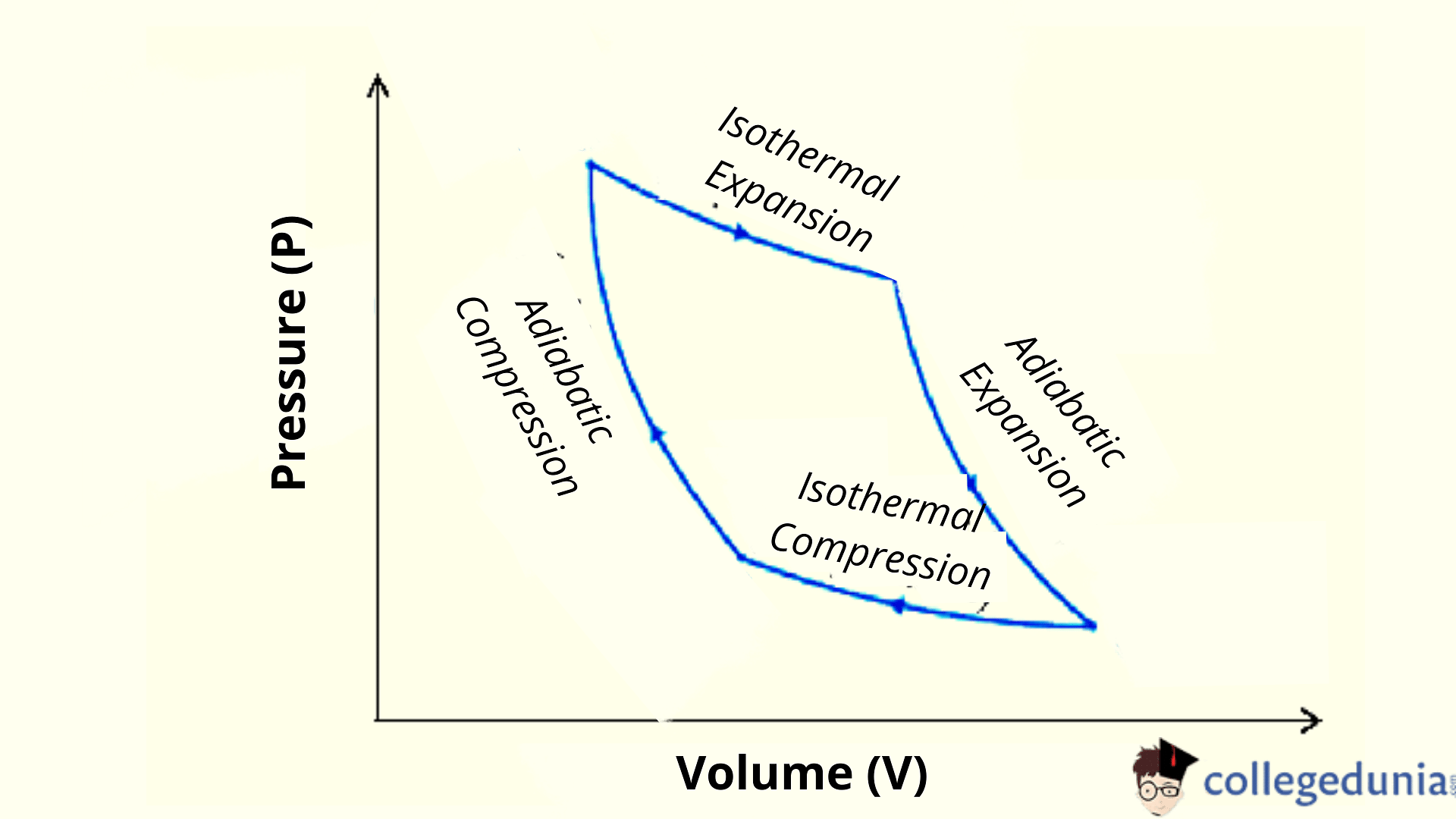
Adiabatic Expansion and Compression
Real-time Examples of Adiabatic Processes
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some of the examples of the adiabatic process are as follows –
- The turbines are great examples of adiabatic systems as they utilize heat as a source to supply work so any heat lost to the environment would scale back their efficiency.
- Hot tea lept in a thermos.
- As we speak, the air is compressed and expanded as a result of the passage of the acoustic waves.
- Also, explosions, rapid compressions, expansions, mixing 2 chemicals in a flask, a lightning strike, etc can also be called approximated adiabatic processes.
Reversible Adiabatic Process
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The reversible adiabatic process is an Isentropic thermodynamic process that is adiabatic in nature and in which the work transfer of the system is frictionless.
- There is no transfer of matter or heat. The process is reversible.
- This process is also called the isentropic process because the change in entropy is 0.
- It is an idealized case used for comparison with real-time processes.
Work Done in Adiabatic process
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Consider a mole of gas contained in a cylinder with insulating walls, provided with a frictionless and insulating piston. When the piston moves up through a small distance dX, let the pressure of gas be P, then the work done will be given as:
dW = PAdX = PdV
- Where A is the cross-sectional area of the piston
- dV = AdX(increase within the volume)
As the gas expands adiabatically, there will be a change in P, V, and T from its initial stage (P1, Vi, T1) to (P2, Vf, T2)
Total work done will be:
W = vf∫vi PdV
According to the adiabatic equation;
PVϒ= Constant (C)
Hence, by substituting this value, we get
W = vf∫vi C (V-ϒ)dV
= nR/1 -ϒ (T1 - T2)
Read More: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Thermodynamics
Difference between Isothermal and Adiabatic Process
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The differences between Isothermal and adiabatic processes are as follows –
| Isothermal Process | Adiabatic Process |
|---|---|
| Isothermal Process is a thermodynamic process that occurs at a constant temperature. | Adiabatic Process is a thermodynamic process that occurs without any heat transfer between the system and the surrounding. |
| It contains the transfer of heat | It doesn’t contain any transfer of heat |
| The temperature remains constant in an isothermal process. | The temperature can be varied in an adiabatic process. |
| The transformation is slow in such processes. | The transformation is fast in such a process |
| Example – A refrigerator | Example – Pendulum oscillating in a vertical plane |
Things to Remember
- Adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which there is no change of heat from the system to its surroundings.
- The adiabatic process can occur if the container has thermally insulated walls or the process happens in a concise time.
- Isothermal processes are often considered the opposite extreme of the adiabatic process
- A system that expands under the adiabatic process does positive work, so internal energy decreases.
- A system that contracts under an adiabatic process does negative work, so internal energy increases.
- The adiabatic process can be either reversible or irreversible in nature.
- The adiabatic equation is PVϒ = Constant
- The total heat of the system remains constant during the adiabatic process.
Sample Questions
Ques. The work done in an adiabatic change in a gas depend only on? (1 mark)
a) Change in pressure
b) Change in volume
c) Change in temperature
d) None of above
Ans. C) Change in temperature
Ques. In the adiabatic expansion: (1 mark)
a) ΔU=0
b) ΔU=Positive
c) ΔU=negativr
d) ΔW=0
Ans. B) ΔU=positive
Ques. An adiabatic process occurs at constant: (1 mark)
a) Temp
b) Pressure
c) Heat
d) Temp and pressure
Ans. C) Heat
Ques. A monoatomic gas is compressed to 1/8 of its original volume adiabatically, what will be the change in pressure? (y=5/3) (2 mark)
Ans. P2/P1=(v1/v2)ϒ
P2 = 85/3P1 =32P1
Ques. A cycle tire bursts suddenly, this indicates which process? (1 mark)
a) Isothermal
b) Isobaric
c) Isochoric
d) Adiabatic
Ans. D) Adiabatic process
Ques. If a cylinder that contains gas at high pressure explodes, the gas undergoes? (1 mark)
a) Reversible adiabatic changes and fall of temperature
b) Reversible adiabatic change and rise of temperature
c) Irreversible adiabatic change and rise of temperature
d) Irreversible adiabatic change and fall of temperature
Ans. Irreversible adiabatic change and fall of temperature
Ques. A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3 moles of hydrogen at degree Centigrade and pressure. The walls of the cylinder are formed from a heat insulator, and therefore the piston is insulated thereon by having a pile of sand. The pressure of the gas increases by what factor if the gas is compressed to half of its original volume? (5 mark)
Ans. As the process is totally insulated from surroundings, it is an adiabatic process. Initial pressure inside the cylinder: P1
Final pressure inside the cylinder: P2
The initial volume inside the cylinder: V1
The final volume inside the cylinder: V2
ϒ=1.4
For an adiabatic process, we have
P1V1ϒ=P2V2ϒ
Now, the final volume is compressed to half of the initial volume
So, V2=V1/2
P1V1ϒ=P2(V1/2)ϒ
P2/P1=21.4=2.639
Ques. If 2 moles of gas is expanded adiabatically, the interior energy of the gas decreases by 2 joules. What will be the work done? (2 mark)
Ans. dQ = 0 = -2 + dW
dw=2J
Ques. 22.3 J of energy is expended on a system in changing the state of a gas adiabatically from an initial equilibrium state A to the final equilibrium state B. If the gas is taken from state A to B via a process during which heat absorbed by the system is 9.35 cal, what proportion is the net work done by the system within the latter case? (Take 1 cal = 4.19 J) (3 mark)
Ans. Within the first case, the method is adiabatic in nature so ΔQ=0,
ΔW= -22.3 J (As the work is done on the system)
ΔQ = ΔU + ΔW
0 = ΔU - 22.3
ΔU = 22.3 J
For the second case, ΔU is the same,
but the Q =9.35*4.2=39.3 J
ΔW = ΔQ - ΔU
= 39.3 - 22.3
ΔW =17 J
Ques. The pressure in the tyre of a car is 4 times the atmospheric pressure at 300K. If this tyre suddenly bursts, its new temperature will be? (3 mark)
Ans. For adiabatic process:
P(1-ϒ)* Tϒ= Constant
T2/T1=(P1/P2)1-ϒ/ϒ
T2/300=(4/1)1-1.4/1.4
T2=300(4)-0.4/1.4
Ques. The pressure and density of a diatomic gas (y=7/5),change adiabticaly from (p,d) to (p1,d1). If d1/d = 32,then p1/p is? (2 mark)
Ans. v=m/d
So, p1/p = (v/v1)ϒ
=(d1/d)ϒ
= 327/5
=128
Check out:




Comments