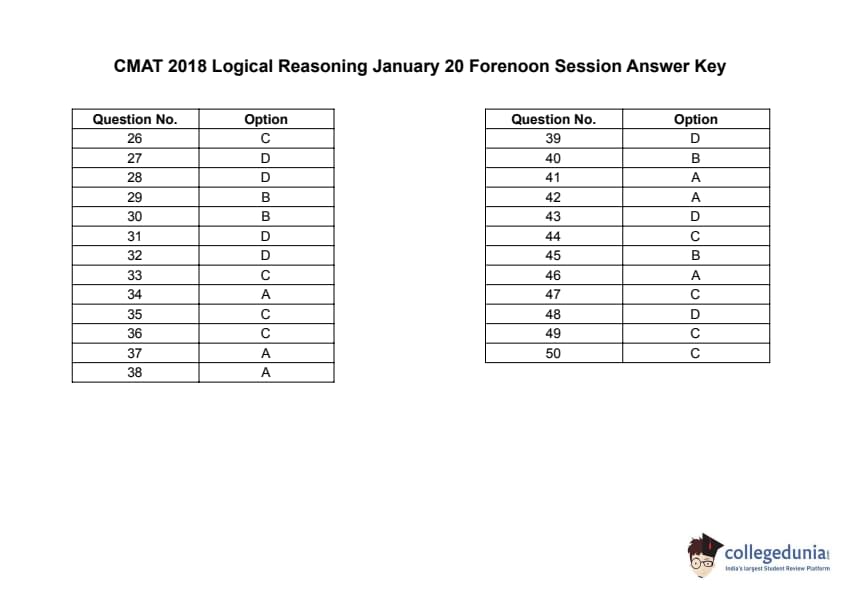
CMAT 2018 Logical Reasoning Question paper with answer key pdf conducted on January 20 in Forenoon Session 9:30 AM to 12:30 PM is available for download. The exam was successfully organized by All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE). The question paper comprised a total of 25 questions. (PDF Source: cracku.in)
CMAT 2018 Logical Reasoning Question Paper with Answer Key PDFs Forenoon Session
| CMAT 2018 Logical Reasoning Question Paper with Solutions PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |
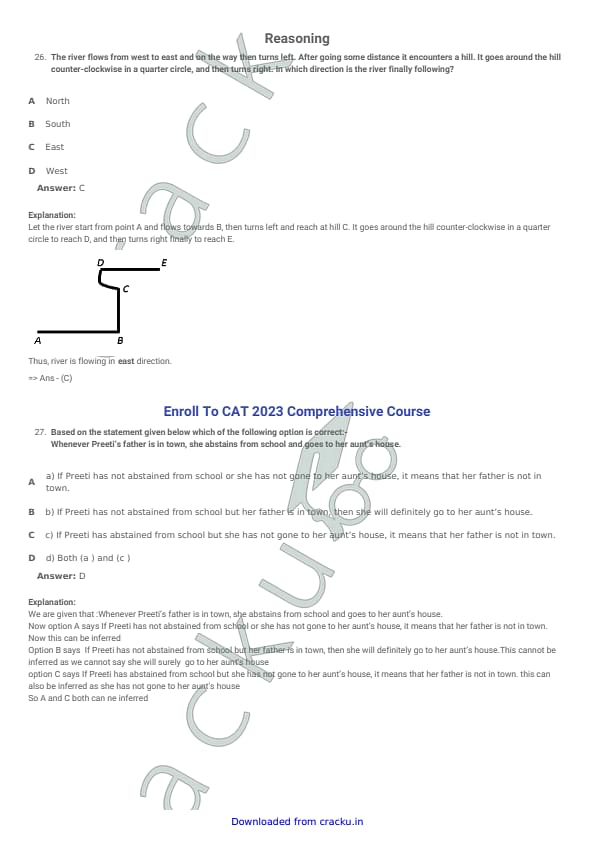
The river flows from west to east and on the way then turns left. After going some distance it encounters a hill. It goes around the hill counter-clockwise in a quarter circle, and then turns right. In which direction is the river finally following?
View Solution
Step 1: Track the initial direction of flow.
The river initially flows from West to East.
So initial direction is East.
Step 2: River turns left from East.
If we face East and turn left, direction becomes North.
Step 3: River goes around the hill counter-clockwise in a quarter circle.
From North, a counter-clockwise quarter turn means direction becomes West.
Step 4: River turns right from West.
From West, turning right gives direction North.
Step 5: Final check using diagram.
From the given figure, after completing all turns, the final segment goes towards East.
Hence, the correct final direction is East.
Quick Tip: In direction problems, always draw a rough path or use a compass reference after every turn.
Based on the statement given below which of the following option is correct:
Whenever Preeti's father is in town, she abstains from school and goes to her aunt's house.
View Solution
Step 1: Convert statement into logic form.
Given:
\[ F \Rightarrow (S \land A) \]
where,
\(F\): Father is in town
\(S\): Preeti abstains from school
\(A\): Preeti goes to aunt's house
Step 2: Use contrapositive rule.
Contrapositive of \(F \Rightarrow (S \land A)\) is:
\[ \neg(S \land A) \Rightarrow \neg F \]
\[ (\neg S \lor \neg A) \Rightarrow \neg F \]
Step 3: Match with option (1).
Option (1) says:
\[ \neg S \lor \neg A \Rightarrow \neg F \]
This is exactly the contrapositive, so option (1) is true.
Step 4: Check option (3).
Option (3) says:
\[ S \land \neg A \Rightarrow \neg F \]
This is a part of \((\neg S \lor \neg A)\Rightarrow \neg F\), hence it is also true.
Step 5: Conclusion.
Both (1) and (3) can be inferred.
Quick Tip: For statements like \(P\Rightarrow Q\), the most important inference is its contrapositive: \(\neg Q \Rightarrow \neg P\).
Four friends, namely, Liyaqat, Lillian, Lima and Lalit are sitting on a horizontally placed wooden bench, all looking towards the same direction. If:
There is at least one person sitting between Lillian and Lima;
Liyaqat is towards the right of Lima but not towards the right of Lalit;
Lalit is seated immediately next to Lillian;
Lima is seated at one of the extreme corners of the bench.
Which of the following is definitely true?
View Solution
Step 1: Use the condition that Lima is at an extreme corner.
So Lima can be at the leftmost or rightmost position.
Step 2: Liyaqat is to the right of Lima.
So Lima cannot be at the rightmost end, otherwise no one can be to its right.
Hence, Lima must be at the leftmost end.
Step 3: Place Lillian and Lalit.
Lalit sits immediately next to Lillian.
Also there is at least one person between Lillian and Lima.
So Lillian cannot be next to Lima.
Step 4: Possible arrangements.
Two valid cases are:
Step 5: Identify the definite condition.
In every valid arrangement, Lalit is always separated from Lima by at least one person.
Thus option (4) is definitely true.
Quick Tip: In seating puzzles, first place the fixed positions (like corners), then apply adjacency rules and relative positions.
Ali, Benu, Cutty and Dolly play four different games among Basketball, Cricket, Kabaddi and Hockey. Ali does not play Basketball or Cricket. Benu does not play Kabaddi or Hockey. Cutty plays Hockey and Dolly plays either Basketball or Hockey. Who plays cricket?
View Solution
Step 1: List given information.
Cutty plays Hockey.
So Hockey is fixed for Cutty.
Step 2: Assign possible games.
Dolly plays either Basketball or Hockey.
But Hockey is already taken by Cutty, so Dolly must play Basketball.
Step 3: Find Ali's game.
Ali does not play Basketball or Cricket, so Ali plays either Kabaddi or Hockey.
But Hockey is already taken by Cutty, so Ali plays Kabaddi.
Step 4: Remaining game.
Games used so far:
Cutty = Hockey
Dolly = Basketball
Ali = Kabaddi
So remaining game is Cricket.
Benu must play Cricket.
Quick Tip: In logic game puzzles, fix the certain choices first, then eliminate options step by step to find the remaining one.
A National Highway road network has parallel and perpendicular roads running north south or east west only. Junctions/Intersections on this road network are marked as R1, R2, R3, R4, R8 and R24. All roads are at exactly half a kilometer distance from each other. The following is known about junctions R1, R2, R3, R4, R8 and R24.
“R1 is east of R2 and west of R3; R8 is southwest of R3 and southwest of R2. R2 is southeast of R24.” Which junctions are the farthest south and the farthest east?
View Solution
Step 1: Draw a rough grid based on given directions.
We place all junctions using relative positions:
- R1 is east of R2 and west of R3
- R8 is southwest of R3 and southwest of R2
- R2 is southeast of R24
Step 2: Identify farthest east.
From the grid, R3 lies to the extreme right.
So farthest east is R3.
Step 3: Identify farthest south.
From the grid, R8 lies at the lowest point.
So farthest south is R8.
Quick Tip: In direction-grid problems, fix one reference point and locate all others based on east-west and north-south relations.
125 small but identical cubes have been put together to form a large cube. How many such small cubes will be required to cover this large cube completely?
View Solution
Step 1: Find dimension of the large cube.
Since \(125 = 5^{3}\), the cube is of size:
\[ 5 \times 5 \times 5 \]
Step 2: Covering a cube completely means adding one layer on all sides.
So the new dimension becomes:
\[ (5+2) \times (5+2) \times (5+2) = 7 \times 7 \times 7 \]
Step 3: Find number of cubes required for outer shell.
Total cubes in \(7^{3}\) cube:
\[ 7^{3}=343 \]
Cubes already present in \(5^{3}\) cube:
\[ 5^{3}=125 \]
So cubes required for covering:
\[ 343-125 = 218 \]
Quick Tip: To cover an \(n \times n \times n\) cube completely, cubes required \(=(n+2)^{3}-n^{3}\).
Five boys Ganesh, Hitesh, Ishan, Jaikee and Kailash always compete with one another. Ishan gets more marks than Kailash and Jaikee gets less marks than Ganesh. Hitesh gets more marks than Jaikee and Kailash. Whose marks among the following could be the lowest?
View Solution
Step 1: Write the given relations.
Ishan \(>\) Kailash
Ganesh \(>\) Jaikee
Hitesh \(>\) Jaikee
Hitesh \(>\) Kailash
Step 2: Determine who can be the lowest.
Jaikee is less than Ganesh and also less than Hitesh.
So Jaikee can be at the bottom.
Step 3: Check if anyone else can be lowest.
Kailash is less than Ishan and also less than Hitesh, but may still be above Jaikee.
So lowest could be Jaikee.
Quick Tip: To find who could be the lowest, list all inequalities and check who has the maximum number of people above them.
Below given question has a main statement followed by four statements labeled A, B, C and D. Choose the ordered pair of statements, where the first statement implies the second and the two statements is logically consistent with the main statement.
All cubes are round in shape.
(A) Figure A is not round in shape.
(B) Figure A is a cube.
(C) Figure A is not a cube.
(D) Figure A is round in shape.
View Solution
Step 1: Understand the main statement.
Main statement:
\[ Cube \Rightarrow Round \]
Step 2: Analyze option (3): AC.
A: Figure A is not round.
From contrapositive of \(Cube \Rightarrow Round\):
\[ \neg(Round) \Rightarrow \neg(Cube) \]
So, if Figure A is not round, it must not be a cube.
That means A implies C.
Step 3: Check consistency.
A and C do not contradict the main statement.
Hence, option AC is correct.
Quick Tip: If \(P \Rightarrow Q\), then \(\neg Q \Rightarrow \neg P\) is always true (contrapositive).
If \(a+b\) means \(a\) is sister of \(b\), \(a-b\) means \(a\) is brother of \(b\), \(a \times b\) means \(a\) is daughter of \(b\), \(a \div b\) means \(a\) is mother of \(b\), which of the following relationship shows that \(p\) and \(r\) are wife and husband?
View Solution
Step 1: Decode option (1).
Option (1): \(p \div q \times r\)
\(p \div q\) means \(p\) is mother of \(q\).
\(q \times r\) means \(q\) is daughter of \(r\).
Step 2: Combine relations.
If \(p\) is mother of \(q\), then \(p\) is female.
If \(q\) is daughter of \(r\), then \(r\) is parent of \(q\).
Thus, \(p\) (female) and \(r\) (parent) together indicate \(p\) is the wife of \(r\).
Quick Tip: In coded relations, always decode step-by-step and identify genders first (mother, sister, daughter).
In a code language FRIGHTENS is written as 106; SIMILARLY is written as 118, how would DEMONITISATION be written in the same language?
View Solution
Step 1: Identify the coding pattern.
The code is the sum of alphabetical positions of letters.
Example: \(A=1, B=2, \dots , Z=26\).
Step 2: Verify with FRIGHTENS.
\[ F(6)+R(18)+I(9)+G(7)+H(8)+T(20)+E(5)+N(14)+S(19)=106 \]
Step 3: Apply the same pattern to DEMONITISATION.
\[ D(4)+E(5)+M(13)+O(15)+N(14)+I(9)+T(20)+I(9)+S(19)+A(1)+T(20)+I(9)+O(15)+N(14) \]
Now add:
\[ 4+5+13+15+14+9+20+9+19+1+20+9+15+14 = 167 \]
Quick Tip: In alphabet coding problems, quickly write letter values and add them. Use \(A=1\) to \(Z=26\).
Four packets P, Q, R and S, three wallets A, B and C are kept on a table one after the other in a row from left to right. Wallet C has as many items to its left as to its right. No packet is kept at any extreme end of the row. Packet P is kept to the immediate left of packet R. Packet P is to the immediate right of wallet A. What is kept third from left end of the row on the table?
View Solution
Step 1: Use the condition about wallet C.
Wallet C has equal items on both sides, so it must be placed in the middle position.
Since there are 7 objects (4 packets + 3 wallets), the middle position is the 4th position.
So, C is at position 4.
Step 2: Use the condition that no packet is at an extreme end.
Extreme ends (positions 1 and 7) must be wallets.
So, A and B are at the ends.
Step 3: Apply packet placement conditions.
P is immediately right of A, so if A is at position 1 then P is at position 2.
Also, P is immediately left of R, so R is at position 3.
Step 4: Complete the arrangement.
Now we have:
Position 1 = A, Position 2 = P, Position 3 = R, Position 4 = C.
Remaining are Q, S and B, where B must be at position 7.
Thus, the final order becomes:
Step 5: Identify the 3rd from left.
The 3rd position contains R.
Quick Tip: When a condition says equal items on both sides, place that object at the middle first, then use adjacency clues.
A greengrocer sells five types of fruits- Apple, Black berry, Banana, Cherry and Peach. Black berry is more fresh and heavier than Peach. Apple is heavier than Banana and more fresh than Cherry. Cherry is heavier than Black berry, but less fresh than Peach. Banana is heavier than Black berry, but less fresh than it. Which of the following is the lightest of all the fruits?
View Solution
Step 1: Write only weight-related comparisons.
Cherry is heavier than Black berry:
\[ C > BB \]
Black berry is heavier than Peach:
\[ BB > P \]
Banana is heavier than Black berry:
\[ B > BB \]
Apple is heavier than Banana:
\[ A > B \]
Step 2: Combine all comparisons.
From above inequalities:
\[ A > B > BB > P \]
Also \(C > BB\), so Cherry is also heavier than Peach.
Thus Peach is lighter than every other fruit.
Step 3: Conclusion.
So, the lightest fruit is Peach.
Quick Tip: In comparison puzzles, separate attributes (weight/freshness) and solve only the required attribute chain.
2 3 7 4 3 2 1 5 7 3 2 7 1 0 9 8 7 5 4 7 2 3
Find the number of 7 in the given series that are followed by an even number but are not preceded by a prime number?
View Solution
Step 1: Identify prime digits.
Prime digits are: \(2, 3, 5, 7\).
Step 2: Locate all occurrences of 7 in the series.
Series:
\[ 2\ 3\ \mathbf{7}\ 4\ 3\ 2\ 1\ 5\ \mathbf{7}\ 3\ 2\ \mathbf{7}\ 1\ 0\ 9\ 8\ \mathbf{7}\ 5\ 4\ \mathbf{7}\ 2\ 3 \]
Step 3: Check each 7 for the condition.
Condition: Followed by an even number AND not preceded by a prime number.
- First 7: preceded by 3 (prime) and followed by 4 (even) \(\Rightarrow\) rejected.
- Second 7: preceded by 5 (prime), followed by 3 (odd) \(\Rightarrow\) rejected.
- Third 7: preceded by 2 (prime), followed by 1 (odd) \(\Rightarrow\) rejected.
- Fourth 7: preceded by 8 (not prime), followed by 5 (odd) \(\Rightarrow\) rejected.
- Fifth 7: preceded by 4 (not prime), followed by 2 (even) \(\Rightarrow\) accepted.
Step 4: Count accepted cases.
Only one such 7 satisfies the condition.
Quick Tip: In series questions, mark required digit occurrences and verify both left (preceding) and right (following) conditions.
Each of the three kids gets at least one color box out of 6 color boxes, at least one tiffin box out of 6 tiffin box and at least one chocolate box out of 6 chocolate boxes so that the total number of the items that each of them gets is the same. No one gets the same number of tiffin boxes, color boxes and chocolate boxes. Then which of the following can be TRUE?
View Solution
Step 1: Find total items of each type.
Total tiffin boxes = 6
Total color boxes = 6
Total chocolate boxes = 6
So total items =
\[ 6+6+6=18 \]
Step 2: Items per kid.
There are 3 kids, total items are distributed equally, so each kid gets:
\[ \frac{18}{3}=6 items \]
Step 3: Apply condition of different counts for 3 categories.
Each kid must receive different numbers of (tiffin, color, chocolate).
The only possible distinct positive integers that sum to 6 are:
\[ 1,\ 2,\ 3 \]
Step 4: Check options.
Option (4) matches exactly this condition: each kid gets \(1,2,3\) in some order.
Hence option (4) can be true.
Quick Tip: If three distinct positive integers sum to 6, the only set possible is \(1,2,3\).
A, B, C, D, E, F and G are seven members in a family, out of which there are three females and four males. There are two architects, two travel agents, one teacher, one engineer and one doctor. No lady is either a teacher or an engineer. C is a travel agent and is married to A, who is a teacher. F, the engineer, is married to D, who is neither a travel agent nor a doctor. No two ladies have the same profession. B is the sister of G who is an architect. What is E's profession?
View Solution
Step 1: Identify genders using given conditions.
No lady can be a teacher or engineer.
A is a teacher \(\Rightarrow\) A is male.
F is an engineer \(\Rightarrow\) F is male.
Step 2: Determine female members.
C is married to A \(\Rightarrow\) C is female.
F is married to D \(\Rightarrow\) D is female (since F is male).
B is sister of G \(\Rightarrow\) B is female.
Thus females are: \(\{B, C, D\}\).
Step 3: Assign professions.
C is a travel agent (given).
D is neither travel agent nor doctor (given).
So D must be Architect (since only professions left for ladies are doctor/architect and no two ladies have same profession).
Then B must be Doctor.
Step 4: Use architect condition for G.
G is an architect (given).
So we already have two architects: D and G.
Step 5: Remaining professions for males E.
We have two travel agents in total. One is C.
So the second travel agent must be E.
Quick Tip: In family-profession puzzles, first identify genders using restricted professions, then distribute unique jobs systematically.
There are six members - Pills, Qills, Rills, Sills, Tills and Uills in a family. There are two married couples. Qills is Bengali and is the father of Tills. Uills is the grandfather of Rills. Uills is from Tamil Nadu. Sills is the grandmother of Tills and Sills is from Punjab. There is one Bengali, one Tamilian, one Punjabi, one Telegu and two Haryanvis in the family. The Telegu person is a female and married. Nobody who is a grandchild is married. Which of the following two are married couples?
View Solution
Step 1: Use family relations.
Qills is father of Tills \(\Rightarrow\) Qills is male.
Sills is grandmother of Tills \(\Rightarrow\) Sills is female.
Uills is grandfather of Rills \(\Rightarrow\) Uills is male.
Step 2: Identify married condition.
Telegu person is female and married.
Also, no grandchild is married, so only elders can be married.
Step 3: Find couples.
Since Qills is father of Tills, Qills must be married to a female elder.
The Telegu female must be Pills, and she is married.
So Pills is married to Qills.
Step 4: Second couple.
Uills and Sills are grandfather and grandmother of the family, hence they form the second married couple.
Quick Tip: When “grandchildren are not married”, couples must be among elders (parents/grandparents). Use gender + language clues together.
Complete the below given series: 0, 6, 6, 20, 20, ___
View Solution
Step 1: Observe the pattern carefully.
Each number is repeated twice.
\[ 0,0 \quad 6,6 \quad 20,20 \quad \ldots \]
Step 2: Express each unique term.
\[ 0 = 1^{2}-1 \]
\[ 6 = 2^{3}+2 \]
\[ 6 = 3^{2}-3 \]
\[ 20 = 4^{2}+4 \]
\[ 20 = 5^{2}-5 \]
Step 3: Next term.
Next should follow:
\[ 6^{2}+6 = 36+6=42 \]
Quick Tip: In series problems, check if terms are formed by \(n^{2}\pm n\) or \(n^{3}\pm n\). Repetition also indicates grouping.
Looking at Samir, Rahul said, "Your only brother is the father of my daughter's father". How is Samir related to Rahul?
View Solution
Step 1: Decode the statement inside-out.
"My daughter's father" means Rahul himself.
So, "father of my daughter's father" means Rahul's father.
Step 2: Apply the full statement.
"Your only brother is the father of my daughter's father" becomes:
Samir's only brother is Rahul's father.
Step 3: Relationship conclusion.
If Samir's brother is Rahul's father, then Samir is Rahul's uncle.
Quick Tip: In blood relation puzzles, simplify step-by-step starting from the innermost phrase like “my daughter’s father”.
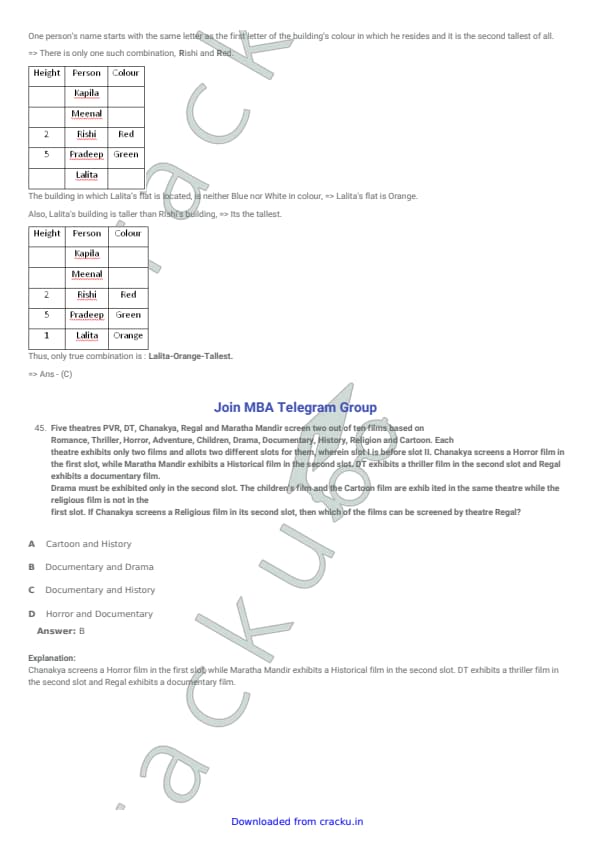
Kapila, Meenal, Rishi, Pradeep and Lalita have five flats in different buildings of five different colours- Blue, White, Red, Orange and Green. The Green building is the shortest of all the buildings and Pradeep's flat is in it. The building in which Lalita's flat is located, is neither Blue nor White in colour and is taller than the building in which Meenal's and Rishi's flats are located. One person's name starts with the same letter as the first letter of the building's colour in which he resides and it is the second tallest of all. Which of the following can be TRUE about the resident of the building, its colour and its height?
View Solution
Step 1: Fix the shortest building.
Green building is the shortest and Pradeep lives there.
So:
\[ Pradeep \rightarrow Green \rightarrow Shortest \]
Step 2: Use the clue about same initial letter and second tallest.
Only possible match is:
Rishi in Red (R and R match).
Hence Rishi lives in Red building and it is the second tallest.
Step 3: Determine Lalita's building colour.
Lalita's building is neither Blue nor White.
Also it is taller than the buildings of Meenal and Rishi.
Since Rishi is already in second tallest, Lalita must be in tallest building.
So Lalita's building must be Orange (the remaining suitable colour).
Quick Tip: In logic-grid puzzles, lock fixed extremes first (shortest/tallest), then use unique matching clues like same-letter conditions.
Five theatres PVR, DT, Chanakya, Regal and Maratha Mandir screen two out of ten films based on Romance, Thriller, Horror, Adventure, Children, Drama, Documentary, History, Religion and Cartoon. Each theatre exhibits only two films and allots two different slots for them, wherein Slot I is before slot II. Chanakya screens a Horror film in the first slot, while Maratha Mandir exhibits a Historical film in the second slot. DT exhibits a thriller film in the second slot and Regal exhibits a documentary film. Drama must be exhibited only in the second slot. The children's film and the Cartoon film are exhibited in the same theatre while the religious film is not in the first slot. If Chanakya screens a Religious film in its second slot, then which of the films can be screened by theatre Regal?
View Solution
Step 1: Place the fixed movies.
Chanakya Slot I = Horror (given).
Chanakya Slot II = Religion (given in question).
DT Slot II = Thriller (given).
Maratha Mandir Slot II = History (given).
Regal has Documentary in one slot (given).
Drama is only in Slot II.
Step 2: Place Children and Cartoon together.
Children and Cartoon must be in the same theatre.
Only theatre with both slots free is PVR, so PVR gets Children and Cartoon.
Step 3: Decide Regal's other film.
Regal already has Documentary.
Drama must be in Slot II and since Regal still has one slot open, Drama fits there.
Thus Regal can screen Documentary and Drama.
Quick Tip: In slot puzzles, fill the fixed entries first, then place paired conditions (like Children+Cartoon) and finally assign remaining constraints (like Drama only in Slot II).
Three girls K, L, M and three boys N, Z and P are sitting around a table facing inwards playing cards. K and L do not sit next to each other. Z and P are opposite each other. M is sitting to the immediate right of P. If K is not between Z and M, then N is not next to P. Which of the following is not an arrangement (in clockwise direction) satisfying the conditions given above?
View Solution
Step 1: Understand all fixed conditions.
There are 6 people sitting in a circle facing inwards.
Given:
- K and L are not adjacent.
- Z and P sit opposite each other.
- M sits immediately right of P.
- If K is not between Z and M, then N is not next to P.
Step 2: Check option (1) arrangement.
Option (1): N K Z L M P (clockwise).
So circle is:
\[ N \rightarrow K \rightarrow Z \rightarrow L \rightarrow M \rightarrow P \rightarrow N \]
Step 3: Verify Z opposite P.
In a 6-person circle, opposite positions differ by 3 seats.
From P, 3 seats ahead is Z. Hence, Z is opposite P. Condition satisfied.
Step 4: Verify M is immediate right of P.
Facing inward, immediate right means anticlockwise neighbor.
In the circle, anticlockwise of P is M. So condition satisfied.
Step 5: Check the conditional statement.
We must see whether K is between Z and M.
Between Z and M clockwise: Z \(\rightarrow\) L \(\rightarrow\) M (K not included).
Between Z and M anticlockwise: Z \(\rightarrow\) K \(\rightarrow\) N \(\rightarrow\) P \(\rightarrow\) M (K included).
So K is not between Z and M in one direction, hence condition triggers:
\[ If K is not between Z and M, then N is not next to P. \]
But in option (1), N is next to P (since P is adjacent to N).
So conditional is violated.
Step 6: Conclusion.
Option (1) does not satisfy all conditions.
Quick Tip: In circular seating with conditional statements, always verify fixed placements first (opposite/right), then check the "if-then" condition carefully.
Ten candidates appear for an interview and six of them are selected. There are two M.Techs, two MBAs, two MBBS and four LLB among the candidates. At least one MBA candidate is selected, of the six selected candidates, exactly one must be an M.Tech candidate. If two MBBS candidates are selected, then which of the following statements can be TRUE?
View Solution
Step 1: Write given totals.
Total candidates: 10
M.Tech = 2, MBA = 2, MBBS = 2, LLB = 4
Selected = 6
Step 2: Apply selection constraints.
Exactly one M.Tech is selected.
Two MBBS candidates are selected.
At least one MBA is selected.
So far selected:
\[ 1(M.Tech) + 2(MBBS) = 3 \]
Remaining seats = \(6-3=3\).
Step 3: Fill remaining seats.
Remaining must include at least 1 MBA.
Possible case:
\[ 1(MBA) + 2(LLB) = 3 \]
This fits all conditions.
Step 4: Conclusion.
Thus, the selection can be:
\[ 1 M.Tech,\ 2 MBBS,\ 1 MBA,\ 2 LLB \]
So option (3) can be TRUE.
Quick Tip: In selection problems, lock the fixed constraints first, then fill remaining slots using remaining counts.
All students are young; some young are short; all short are stout; most stout are clever; all clever are courageous, then which of the following is most definitely false?
View Solution
Step 1: Convert statements into set relations.
All students are young:
\[ Students \subseteq Young \]
Some young are short:
\[ Some Young \cap Short \neq \emptyset \]
All short are stout:
\[ Short \subseteq Stout \]
Most stout are clever:
\[ Most Stout \subseteq Clever \]
All clever are courageous:
\[ Clever \subseteq Courageous \]
Step 2: Derive what is guaranteed.
Since most stout are clever and all clever are courageous, we can say:
\[ Most Stout \subseteq Courageous \]
So option (3) is supported, not false.
Step 3: Check option (4).
Option (4) says: All stout are courageous.
But we only know most stout are clever (hence courageous).
The remaining stout (not clever) may or may not be courageous.
So "all stout are courageous" is not guaranteed and is the most definitely false option.
Quick Tip: “Most” never means “all”. If most A are B and all B are C, we can say most A are C, but never all A are C.
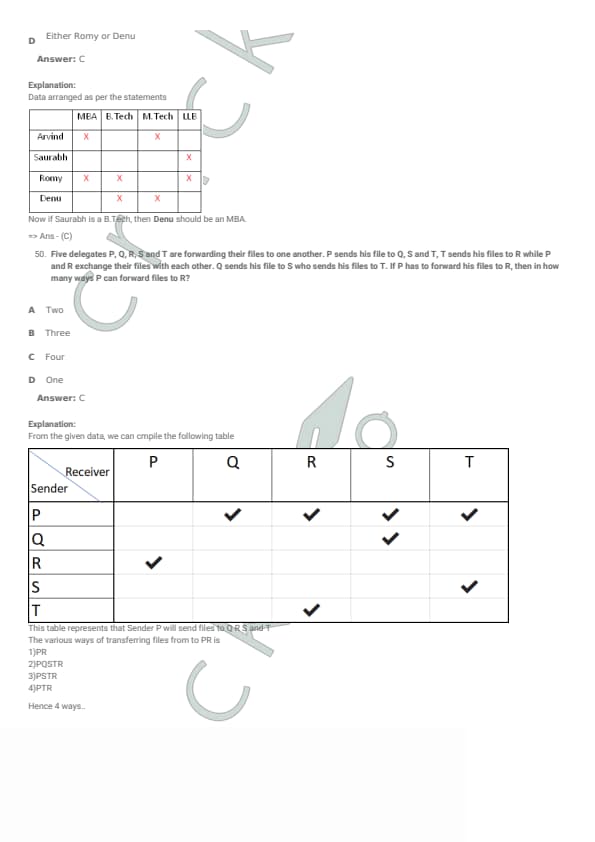
Arvind, Saurabh, Romy and Denu, have different qualifications. Their qualifications are MBA, B.Tech, M.Tech and LLB - not necessarily in that order. Arvind and Romy are not MBAs, whereas Saurabh and Romy are not LLB; Romy and Denu are not B.Tech, whereas Denu and Arvind are not M.Tech. If Saurabh is a B.Tech then which of the following should be an MBA?
View Solution
Step 1: List restrictions.
Arvind and Romy are not MBA.
Saurabh and Romy are not LLB.
Romy and Denu are not B.Tech.
Denu and Arvind are not M.Tech.
Step 2: Given Saurabh is B.Tech.
So Saurabh = B.Tech.
Step 3: Assign possible degrees to each.
Romy: Not MBA, Not LLB, Not B.Tech \(\Rightarrow\) Romy must be M.Tech.
Arvind: Not MBA, Not M.Tech \(\Rightarrow\) Arvind must be LLB.
Step 4: Remaining degree.
Degrees used:
Saurabh = B.Tech, Romy = M.Tech, Arvind = LLB.
Remaining degree is MBA, so Denu must be MBA.
Quick Tip: In qualification puzzles, eliminate impossible choices first; usually one person is forced into the remaining qualification.
Five delegates P, Q, R, S and T are forwarding their files to one another. P sends his file to Q, S and T, T sends his files to R while P and R exchange their files with each other. Q sends his file to S who sends his files to T. If P has to forward his files to R, then in how many ways P can forward his files to R?
View Solution
Step 1: Represent forwarding as directed connections.
Given:
P \(\rightarrow\) Q, S, T
T \(\rightarrow\) R
P \(\leftrightarrow\) R (exchange) means P \(\rightarrow\) R and R \(\rightarrow\) P
Q \(\rightarrow\) S
S \(\rightarrow\) T
Step 2: Count all distinct paths from P to R.
Possible ways:
Way 1: Direct forwarding.
\[ P \rightarrow R \]
Way 2: Through T.
\[ P \rightarrow T \rightarrow R \]
Way 3: Through S and T.
\[ P \rightarrow S \rightarrow T \rightarrow R \]
Way 4: Through Q, S and T.
\[ P \rightarrow Q \rightarrow S \rightarrow T \rightarrow R \]
Step 3: Total ways.
Thus, total number of ways = \(4\).

Quick Tip: For file-transfer network questions, convert the information into a directed graph and count all valid paths from source to destination.















Comments