Arpita Srivastava Content Writer
Content Writer
Hand Anatomy is a branch of biology that deals with bones and muscles found in the human body. Bones and muscles work in a synchronized manner to produce desired hand movements.
- The hand is a multi-fingered organ that is located at the end of the forearm.
- Various parts of the hands include fingers, thumb and wrist.
- Hand anatomy gives a detailed description of each part of the hand.
- Fingers are the richest source of neural structure.
- Muscles, bones and nerves together contribute to initiating a varied range of motion.
- The neurovascular structures found inside the hand control the touching or holding capacity of the hand.
- Hand anatomy helps us understand about the types of muscles and bones of the hand.
Read More: Bones
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Hand Anatomy, Hand, Bones, Nerves, Organ, Forearm, Muscles, Human Body, Minerals, Cells, Wrist, Nervous System
Bones
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bone is a rigid organ that provides structure to the human body. It provides protection to various organs of the body and produces required red and white blood cells. Bone is a type of connective tissue that stores minerals in the body.
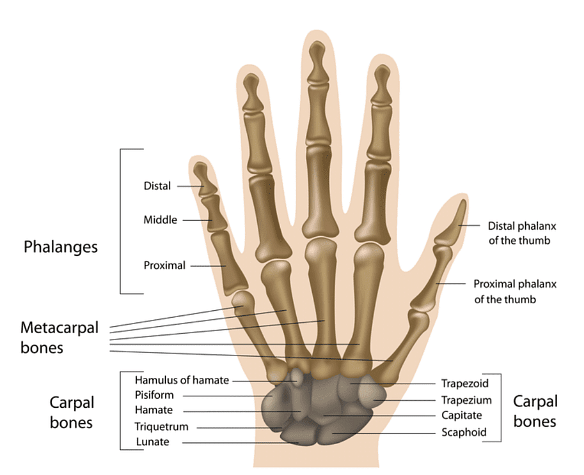
- A human hand consists of a total of 27 bones.
- Each bone is divided into three different types, namely carpals, metacarpals and phalanges.
- Out of 27 bones, 8 are carpal bones, 5 are metacarpal bones, and 14 are phalanges.
- Each of them represents a part of the hand and together leads to any kind of hand movement.
Bones and Types of Bones
Read More: Types of Joints - Classification of Joints
Types of Bones
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The various types of bones found in human body are as follows:
Carpal Bones
Carpal are eight bones found in the wrist. The eight bones are arranged in two almost horizontal rows, with each row containing four bones. The lower row acts as a connector between bones of the forearm, i.e., radius, ulna and the metacarpal bones.
- Carpal bones help soft tissues in the hand for various movements and also provide a great amount of flexibility in doing work.
- It is divided into two rows, namely the proximal row and the distal row.
- Proximal is the upper carpal row consisting of Hamate, Trapezoid, Trapezium and Capitate.
- These are directly connected to the metacarpal bones by a synovial fluid.
- The proximal row helps in the smooth movement of the bones.
- Distal is the lower carpal row consisting of Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetral and Pisiform.
- These are in direct touch with forearm bones, i.e., radius and ulna, which are again joined by synovial fluid.

Carpal Bones
Read More: Gonads: Definition, Function & Examples
Metacarpal Bones
Metacarpals form the middle part of the hand, i.e., the palm. It consists of a base, shaft and head. The base of each metacarpal is connected with the proximal or upper carpal row, while the head is connected to phalanges or fingers. There are five metacarpals:
- Metacarpal 1, attached to the trapezium
- Metacarpal 2, attached to trapezoid, trapezium and capitate
- Metacarpal 3, attached to capitate
- Metacarpal 4 and 5 are attached to the hamate

Metacarpal Bones
Phalanges
Phalanges are the bones that constitute the finger. A total of 14 phalanges are present in each hand. Phalanges are further divided into three distinct types, namely proximal, middle and distal phalanx. The thumb consists only of proximal and distal phalanx, whereas the rest of the fingers consists of all three phalanxes.

Phalanges
Read More: Difference between Cardiac Muscle and Skeletal Muscle
Muscles
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
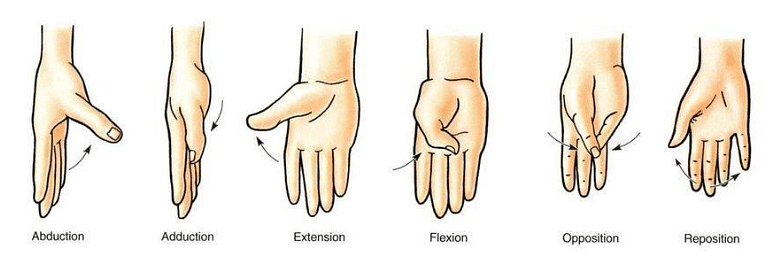
A muscle is a form of tissue that consists of a special type of proteins called actin and myosin, which help in the body's movement. It coordinates with the bones to cause various hand movements like abduction, adduction, flexion, opposition, repositioning and extension.
- The Human Body is made of around 600 muscles.
- It helps in running, jumping and doing other delicate tasks.
- Muscle tissue is divided into three categories, namely skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
- These tissues are activated by either the central nervous system or by endocrine activation.
Read More: Leg Muscles: Definition & Parts
Types of Muscles
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The various types of muscles found in human body are as follows:
Thenar Muscles
Human body consists of four types of thenar muscles. The four types of muscles are adductor pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis. Thenar muscles are responsible for forming the fleshy part of the thumb called the thenar eminence. These muscles are found on the white side of the palm.

Thenar Muscles
Hypothenar Muscles
Hypothenar Muscles are present at the base of the little finger. They are identified as a fleshy area at the little finger’s base on the palmar side. This fleshy part is known as hypothenar eminence, which consists of muscles, abductor digiti-minimi, palmaris brevis, flexor digiti-minimi and opponens digiti-minimi. These muscles are responsible for the movements of the little finger.

Hypothenar Muscles
Lumbrical muscles
Lumbrical muscles are four small muscles of the hand located between the metacarpal bones. They are numbered as Lumbrical 1, 2, 3, and 4. These are located in the palmer side of the hand between the thenar and hypothenar eminence.
- Lumbrical 1 originates from the radial side and the palmar portion of the index finger.
- Lumbrical 2 originates from the radial side and palmar surface of the middle finger.
- Lumbrical 3 originates from the ulnar side of the middle finger tendon and the radial side of the ring finger tendon.
- Lumbrical 4 originates from the ulnar side of the ring finger tendon and the radial side of the middle finger tendon.

Lumbrical muscles
Palmar Interossei Muscles
The palmar interossei muscles are present in the palmar side of the hand. There are four types of palmar interossei muscles, named numerically from 1 to 4. The four muscles are attached to the 1st , 2nd , 4th and 5th fingers. The 3rd finger has no palmar interossei muscle attached to it. Sometimes, even the thumb has no palmar interossei muscles attached.

Palmar interossei
Dorsal Interossei Muscle
Dorsal Interossei Muscles, as suggested, are present in the dorsal side of the hand. Palmar and Dorsal interossei muscles together fill the gap between metacarpal bones. There are four types of dorsal interossei muscles, each attaching to its corresponding palmar interossei muscle.

Dorsal Interossei Muscle
Read More: Muscular Tissue Types Anatomy and Physiology
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Hand Anatomy is the study of the synchronized movement of bones and muscles.
- A human hand consists of five digits, namely four fingers and one thumb.
- The tissue found in the hand provides shape and stability.
- Bone is divided into three categories, namely carpals, metacarpals and phalanges.
- Muscles are responsible for various hand movements, such as flexion, opposition, repositioning and extension.
- The diagram for bone anatomy and muscle anatomy of the hand is different.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the total number of bones in hand? (2 Marks)
Ans. The hand is a grasping organ found at the end of the forelimb that provides great mobility and flexibility in human fingers. The human digit is made up of a medial thumb containing two phalanges and four fingers, each containing three phalanges. A human hand consists of a total of 27 bones. Out of 27 bones, 8 are carpal bones, 5 are metacarpal bones, and 14 are phalanges.
Ques. Why does it feel fleshy below the thumb and the little finger? (2 Marks)
Ans. The fleshy sensation is observed at the base of the thumb due to thenar eminence. These muscles are found on the white side of the palm. Whereas below the little finger, the fleshy sensation is due to the presence of hypothenar eminence. These muscles are responsible for the movements of the little finger.
Ques. Explain the structure of bones in the wrist? (5 Marks)
Ans. Carpal bones are eight bones that form the structure of the wrist. The eight bones are arranged in two almost horizontal rows, with each row containing four bones. The lower row acts as a connector between bones of the forearm, i.e., radius, ulna and the metacarpal bones.
- Carpal bones help soft tissues in the hand for various movements and also provide a great amount of flexibility in doing work.
- It is divided into two rows, namely the proximal row and the distal row.
- The upper row or proximal consists of 4 bones named Hamate, Trapezium, Trapezoid and Capitate.
- The lower row or distal consists of 4 bones named Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrul and Pisiform.
- Both rows together from the wrist; the proximal is connected to the metacarpals, and the distal is connected to the radial and ulna of the forearm.
Ques. Which muscle forms the palm region of the hand? (1 Marks)
Ans. The five lumbrical muscles form the palm region of the hand. It is present on the palmar side of the hand between the thenar and hypothenar muscles.
Ques. What are the various hand movements studied in hand anatomy? (1 Marks)
Ans. Some of the common hand movements are adduction, abduction, flexion, opposition, reposition and extension.
Ques. Which liquid connects the carpals and metacarpals? (1 Marks)
Ans. The joint between carpals, metacarpals and carpals and radial, the ulna is joined by synovial fluid. This is the reason both the joints are considered synovial joints.
Ques. How different is the thumb from the fingers structurally? (3 Marks)
Ans.The difference between thumb and fingers are as follows:
| Thumb | Finger |
|---|---|
| The thumb is only made of proximal and distal. | All the fingers are made of three bones, proximal, middle and distal |
| It has only joint. | It has two types of joints. |
| The position of thumb is out to the side of the hand. | The position of fingers are in side of the hand. |
Ques. Name the constituents of thenar muscles? (2 Marks)
Ans. Human body is made of four types of thenar muscles. Thenar muscles are responsible for forming the fleshy part of the thumb called the thenar eminence. These muscles are found on the white side of the palm. The four thenar muscles are as follows:
- Adductor pollicis
- abductor pollicis brevis
- flexor pollicis brevis
- opponens pollicis
Ques. What is the difference between bone and muscle? (3 marks)
Ans. The difference between bone and muscles are as follows:
| Bone | Muscles |
|---|---|
| Bones are responsible for helping us stand straight and still. | Muscles are attached to bones which help in various body movements. |
| These are found from the top of the skull to the bottom of the toe. | These are attached with tendons and spread across bones. |
| A human body is made up of 206 bones. | A human body is made up of 600 muscles. |
Ques. What are the functions of human skeletal system? (3 marks)
Ans.
The various functions of the human skeletal system are as follows:- It provides structural support to the body by balancing human weight.
- The main function of the column includes providing protection to the brain.
- The skeletal system helps in the body's movement with the help of muscles and ligaments.
- It provides support to the fibula.
Ques. Explain the working of four finger found in the human hand? (4 marks)
Ans. The working of four finger found in the human hand are as follows:
- Index finger: It is also known as the forefinger. The index finger is found between the thumb and the middle finger. It is the most sensitive digit of the hand.
- Middle Finger: It is also known as the longer finger. The middle finger is found between the index finger and the ring finger. It is used for finger snapping together with the thumb.
- Ring Finger: It is also known as the leech finger. Individuals generally use this finger to wear their wedding ring.
- Little Finger: It is also known as the baby finger or pinky finger. The little finger is located close to the ring finger and works independently.
Check-Out:




Comments