Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
Adipose tissue is a connective tissue that is mainly composed of fat cells called ‘adipocytes’. It is a source of numerous hormones, including leptin, estrogen, and resistin. Adipocytes, often known as fat cells, make up the majority of adipose tissue. These are lipid storage droplets that contain triacylglycerol and range in size according to the quantity of fat that is being stored. The main functions of adipose tissue are energy storage, energy release, and insulation. Adipose tissue connects with various organs throughout the human body via hormone signals and contains nerve cells and blood arteries.
Read More: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation in Animals
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Adipose Tissue, Connective Tissues, Adipocytes, Fats, Lipids, Insulation, Cells, Brown Adipose Tissue, Fat Cells
What are Tissues?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Tissues are collections of cells with a common structure and function that work cooperatively to carry out the desired purpose. Animals have four different types of tissues, which are as follows:
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Epithelial Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
There are two distinct subtypes of connective tissues namely Loose Connective Tissue and Thick Connective Tissue. The following divisions can be made between these subclasses:
Loose Connective Tissue
- Areolar Connective Tissue
- Adipose Connective Tissue
- Reticular Connective Tissue
Thick Connective Tissue
- Dense Regular Connective Tissue
- Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
- Elastic Connective Tissue
Read More:
| Relevant Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Difference between Lipids and Fats | Difference between Cell and Tissue | Fatty Liver |
| Animal Tissues | Squamous | Difference between Saturated and Unsaturated Fats |
What is Adipose Tissue?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Adipose is a specific type of fat or lipid cell, that makes up the connective tissue. 20 to 25 percent of the total body weight of a healthy person is made up of fat tissue.
- Adipocytes, which are fat cells, make up the majority of adipose tissue, a unique and distinct type of connective tissue.
- The primary purpose of adipose tissue is to store energy as fat.
- In addition to fat cells, adipose tissue also contains a variety of nerve cells and blood vessels.
- It stores and releases energy to power the body as well as vital hormones required for survival.
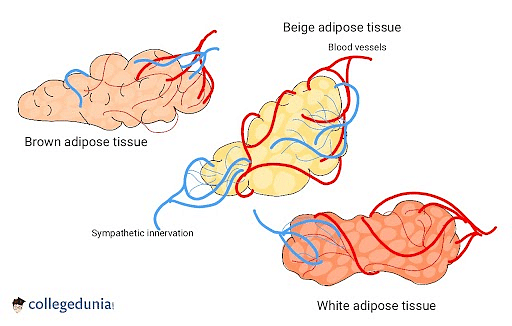
- White adipocytes, brown adipocytes, and beige adipocytes are the different types of adipocytes.

Adipose Tissue
Read More: Structural Organisation In Animals
Types of Adipose Tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Adipose tissue can be classified into two types:
- Brown Adipose tissue
- White Adipose tissue
Brown adipose tissue is made up of brown fat cells and white adipose tissue is mostly made of white and beige fat cells.
White Adipose Tissue
- The most prevalent form of fat in an adult human is white adipose tissue.
- It can be found in the central chamber of the bones (marrow fat), under the skin (subcutaneous fat), surrounding the internal organs (visceral fat), and around the internal organs.
- Its primary function is to serve as a source of energy.
- It also acts as a buffer for essential organs, protects the body from severe temperatures, and secretes hormones and biological substances.
Brown Adipose Tissue
- Most brown adipose tissue is seen in the fetus and in young children.
- The mediastinum, upper clavicles, and vertebral bodies are where it is most frequently found in the upper back.
- The primary function of brown adipose tissue is non-shivering thermogenesis, which is crucial for preventing hypothermia in infants.
Types of Adipose Tissue
Read More: Structural Organization in Animals Important Questions
Functions of Adipose Tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Besides serving as a source of fat storage, adipose tissue also carries out a number of other functions such as
- It is an organ that regulates metabolism and aids in maintaining homeostasis.
- Isolation from the heat.
- The creation of several bioactive substances.
- Serves as an endocrine gland and is in charge of hormone production.
- Serves as a cushion for the organs.
Structure of Adipose Tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Adipose tissue is the organ in our bodies that stores fat. There are two ways that this fat is dispersed throughout the body:
- Subcutaneous fat, or parietal fat, is the term for the substance that is present beneath the skin.
- Visceral fat is found covering internal organs including the kidneys and eyes.
Extracellular matrix and cells make up the fat tissue. The majority of the cellular matrix, which only makes up a minor portion, is made up of these cells, which are also its structural components.
- Adipocytes are the predominant type of cells present.
- Along with these, other cell types include fibroblasts, preadipocytes, capillary endothelial cells, macrophages, and stem cells.
- Non-adipocyte cells are the name given to these cells in most cases.
- A stromal vascular fraction is created by the fusion of non-adipocytes.
- Adipocytes support and safeguard adipose tissue as their primary job.
- The extracellular matrix is produced with assistance from adipocytes and stromal cells.
- The matrix is made up of reticular fibers that are linked together to form a fine network that aids in holding and positioning the cells.
- There are numerous blood arteries and unmyelinated nerve fibers in adipose tissue.
Check More:
| Related Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tissue Culture | Epithelial Tissue | Muscular Tissue |
| Plant Tissue Vs Animal Tissue | Test for Fats | Difference between Fats and Oils |
Adipocytes
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Adipocytes are the atomic units of adipose tissue. Adipose cells or fat cells are other names for them. The distribution of two different forms of adipose tissue determines how the adipocytes are separated into two groups.
- White Adipocytes: The major cells that make up white adipose tissue are called white adipocytes. Spherical, oval, or polyhedral shapes are all possible. The nucleus of the cell is pushed to the outer side of the cell by a single lipid droplet. Fewer mitochondria can be seen in the cytoplasm, which surrounds the lipid droplet.
- Brown Adipocytes: These are the main cells found in brown adipose tissue. They are incredibly tiny and are made up of many lipid droplets. These droplets encircle the nucleus that is located in the middle. The droplets' dark color is caused by the numerous mitochondria that are scattered throughout them. The cytoplasm also contains the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, and a few ribosomes.
- Beige Adipocytes: It is found scattered throughout the white fat tissue as beige adipocytes. Visceral fat contains a minor amount of it as well.

Adipocytes
Read More: Structural Organization of Animals MCQs
Things to Remember
- Adipose Tissue is a connective tissue that consists of fat or lipid cells covering the entire body.
- The primary purpose of adipose tissue is to store energy as fat.
- The atomic units of adipose tissue are called adipocytes.
- The two major types of adipose tissue are White Adipose Tissues and Brown Adipose Tissues.
- Brown adipose tissue is made up of brown fat cells and white adipose tissue is mostly made of white and beige fat cells.
- Adipose tissues have multiple nerve cells and blood vessels in addition to fat cells.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is Adipose Tissue? (3 Marks)
Ans. Adipose Tissue, also referred to as body fat, is a connective tissue that covers the entire body. It can be located in the spaces between the internal organs (visceral fat), beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat), and even inside the cavities of the bones (bone marrow adipose tissue). Adipose tissues help in energy storage along with providing insulation to the body.
Ques. What use does adipose tissue serve? (3 Marks)
Ans. The numerous function performed by adipose tissue are as follows:
- Storing and releasing energy
- Protection against heat and cold.
- Protect fragile organs with padding.
- Controlling satiety and hunger.
- Preserving an energy balance.
- Controlling cholesterol and glucose.
- Keeping insulin sensitivity intact.
- Producing heat by thermogenesis.
- Strengthening immunity
- Converting sexual hormones.
Ques. What is the difference between white adipose tissue and brown adipose tissue? (5 Marks)
Ans. The difference between white adipose tissue and brown adipose tissue is as follows:
| White Adipose Tissue | Brown Adipose Tissue |
|---|---|
| White Adipose Tissues are located in subcutaneous, intraabdominal, epicardial, and gonadal regions. | Brown Adipose Tissues are located in interscapular, perirenal, cervical, paravertebral and supraclavicular regions. |
| They are spherical in shape. | They are elliptical and smaller in shape. |
| They have a single lipid droplet, a flattened nucleus, a few mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. | They have multiple lipid droplets, an oval-shaped nucleus, and numerous mitochondria. |
| They help to store fat. | They help to produce heat. |
Ques. What components make up adipose tissue? (1 Mark)
Ans. The three layers of collagen fibers that make up adipous tissue are covered by a loose assemblage of specialized cells called adipocytes.
Ques. What use does perirenal fat serve? (3 Marks)
Ans. The structure located between the renal fascia and renal capsule is known as the adipose capsule of the kidney, perinephric fat, or perirenal fat. Blood is supplied to it by the abdominal aorta. White adipose tissue makes up its structure. It carries out a variety of physiological tasks, including fat storage and adipokine production that promotes inflammation.
Ques. What functions do adipose tissues perform? (3 Marks)
Ans. Adipose tissue is essential for good health since it not only serves as a place for fat cells to be stored but also houses a significant number of blood vessels and nerve cells that aid in the storage and release of energy for the body. Adipose tissue also surrounds organs, acting as a barrier to guard against physical injury. This tissue has a fat composition of 82–88%, a protein content of 2-2.6%, and a water content of 10–14%.
Ques. What is the relationship between adipose tissue and other organs? (3 Marks)
Ans. Adipose tissue interacts with your central nervous system as well as other organs throughout your body by secreting some hormones and reacting to others. Through signals of hunger and satiety (feeling full), it controls energy demand and supply. As a response to insulin, it transforms extra blood sugar into lipids and stores them for later use. The body part where the fat is stored in your body is influenced by sex hormones.
Additionally, adipose tissue possesses active immune cells of its own that react to particular stimuli by removing dead fat cells or by triggering an inflammatory reaction. Defects in these processes lead to metabolic disorders.
Ques. Is having adipose tissue healthy? (3 Marks)
Ans. The health of adipose tissue is essential. Its regulating systems, however, can become ineffective if there is too much or too little of anything. Healthy levels range from 10% to 35%, depending on age and sex. When a person is obese, their body has to enlarge the existing fat cells since there isn't enough tissue left to store lipids.
Chronic inflammation and a number of subsequent metabolic diseases are linked to enlarged fat cells. Ironically, because the body doesn't have enough tissue to store lipids already, a lack of overall fat tissue can have the same effects.
Ques. How are diseases of adipose tissue treated? (3 Marks)
Ans. Most adipose tissue problems are caused by malnutrition, which can refer to either undernutrition or overnutrition, in addition to genetic factors. Supplemental nutrition, often known as "refeeding," is used to address undernutrition. Diet and exercise are used to cure overeating first. Medication or surgery may be options for class III obesity, which is more severe obesity.
Although obesity is linked to a number of metabolic illnesses, not everyone who is overweight has these problems. Some consequences, such as insulin resistance, might need to be treated directly.
Ques. What does adipose tissue look like? (2 Marks)
Ans. Adipose tissues are found in humans as subcutaneous fat, visceral fat, and intramuscular fat. Subcutaneous fat is the type of fat found beneath the skin (i.e. fat interspersed in skeletal muscle). They can also be found in breast tissue and yellow bone marrow.
Check-Out:





Comments